AP® Psychology Unit 2 Review and Practice Test
AP® Psychology Unit 2 covers cognition, memory, and thinking. This AP Psych Unit 2 review helps you understand key cognitive processes with clear explanations and practice so you can prepare for your Unit 2 AP Psychology test with confidence.
Your Essential AP Psychology Unit 2 Study Review for Cognition
Build confidence for your Unit 2 AP Psychology practice test with step-by-step lessons that simplify memory, decision-making, and cognitive processes. UWorld helps you learn smarter and prepare for every type of question you’ll see.
Engaging Video Lessons
UWorld’s video lessons make AP Psychology Unit 2 easier to understand by breaking down cognition with simple explanations and real examples. You’ll see how memory, attention, and problem-solving actually work in the brain. These AP Psych Unit 2 videos help you connect concepts quickly so you feel confident for your Unit 2 AP Psychology test.
Interactive Study Guides
UWorld’s AP Psychology Unit 2 study guide breaks down cognition into simple explanations you can review quickly. You’ll learn key ideas like memory processes, problem-solving, and how we think and reason. With visuals, examples, and clear summaries, these AP Psych Unit 2 notes help you understand tough concepts and feel prepared for your practice tests and progress checks.
Prepare for Your AP Psych Unit 2 Test with Real Practice Questions
Question
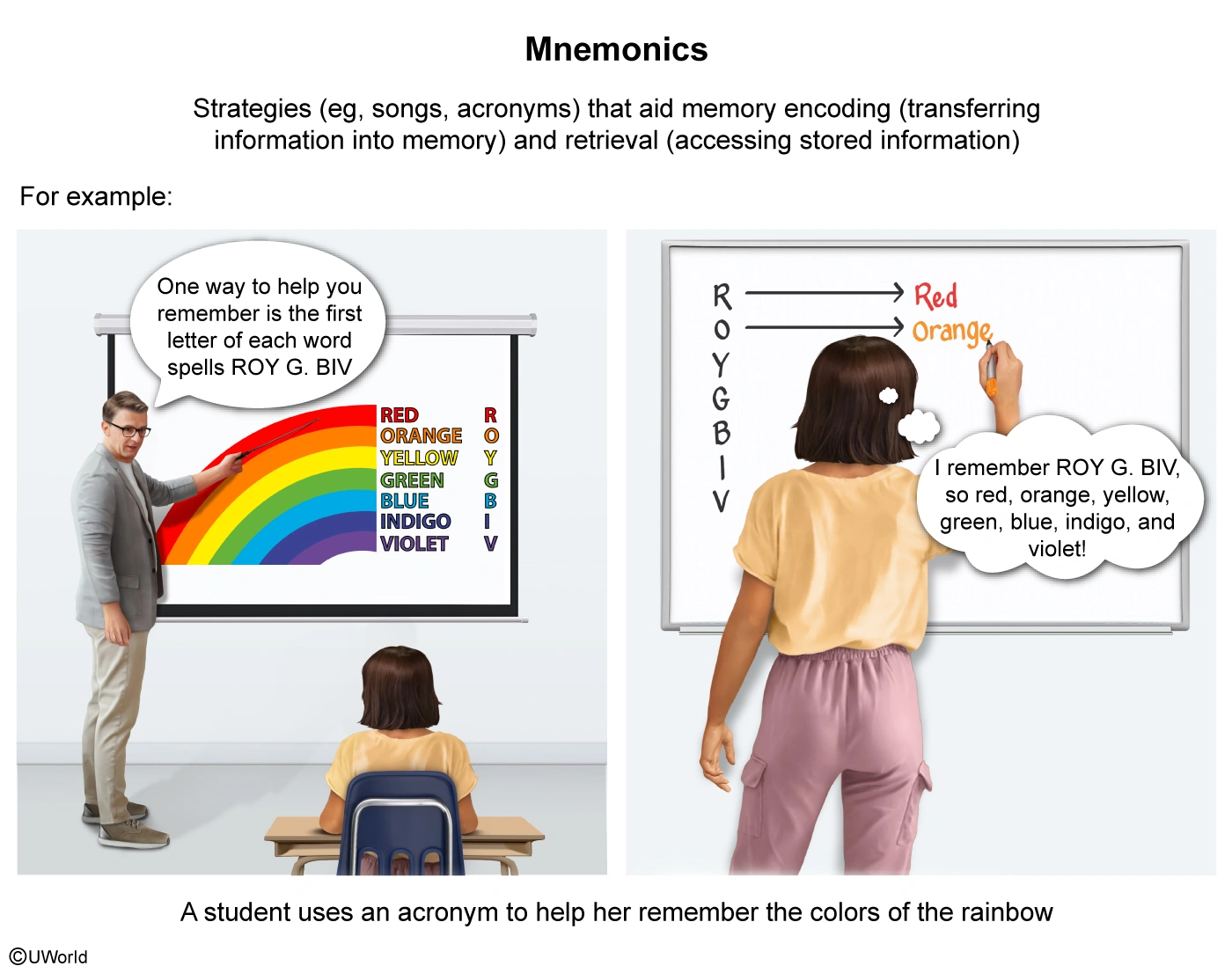
Xue wants to memorize the colors of the rainbow. She uses the acronym ROY G. BIV to help her remember that the colors are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This illustrates
| A. maintenance rehearsal | |
| B. the spacing effect | |
| C. implicit memory | |
| D. a mnemonic |
Explanation
Memory involves encoding, the transfer of information into memory, storage (retaining the information), and retrieval (accessing the information).
Mnemonics are strategies (eg, songs, acronyms) that aid memory encoding and retrieval. For example, reciting the ABCs in tune with a song helps people learn the alphabet.
Therefore, Xue using an acronym to help her remember the colors of the rainbow illustrates a mnemonic.
(Choice A) Maintenance rehearsal, mentally repeating something over and over, can prolong the duration of short-term memory.
(Choice B) The spacing effect refers to how repeated rehearsal of information over time (ie, distributed practice) leads to better recall than all at once (ie, massed practice).
(Choice C) Implicit memory (also called nondeclarative memory) is memory for things that cannot be consciously recalled, such as skills, tasks, emotions, and reflexes.
Things to remember:
Memory involves encoding (transferring information into memory), storage (retaining the information), and retrieval (accessing the information). Mnemonics are strategies (eg, songs, acronyms) that aid memory encoding and retrieval.
Question
Malik has a difficult time remembering passwords, so he decides to change his email password to the date he was married. Now he can easily recall his password. Malik's memory strategy is an example of the
| A. self-reference effect | |
| B. availability heuristic | |
| C. representativeness heuristic | |
| D. serial position effect |
Explanation
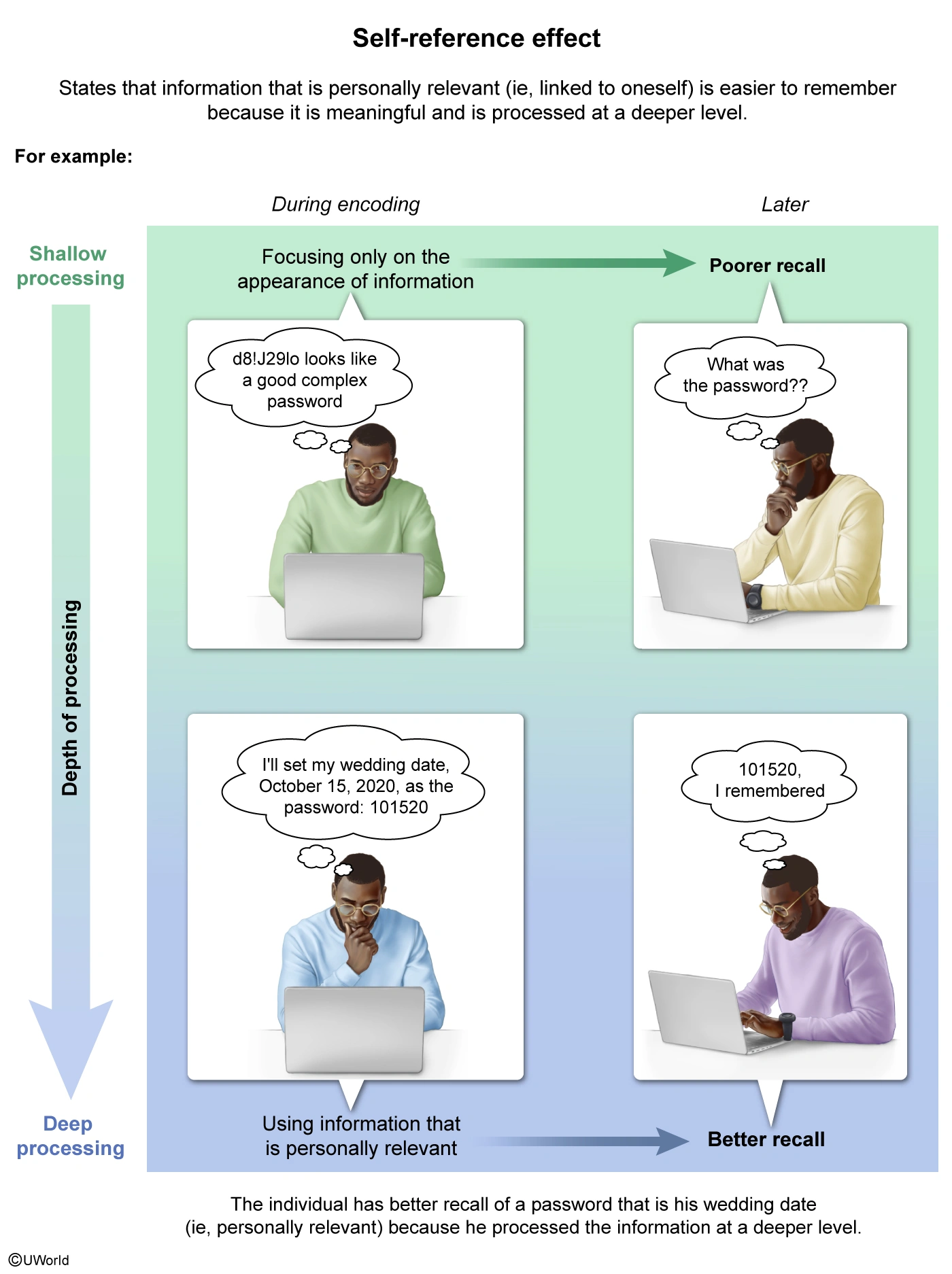
The self-reference effect states that information that is personally relevant (ie, linked to oneself) is easier to remember because personally relevant information is meaningful and so is processed at a deeper level.
For example, Malik, who has difficulty remembering passwords, more easily remembers his email password after changing it to the date of his wedding because this makes the information personally relevant, which leads to easier retrieval.
Therefore, Malik's memory strategy (ie, choosing a password that is personally relevant) is an example of the self-reference effect.
(Choice B) The availability heuristic is the tendency to believe that if something is easily recalled from memory, it must be common or likely (eg, easily recalling news of a plane crash and incorrectly assuming that plane crashes are common).
(Choice C) The representativeness heuristic is the tendency to compare things (eg, people) to mental prototypes when making judgments (eg, a mental prototype of a nurse as female leads to the inaccurate assumption that a male nurse is a doctor).
(Choice D) The serial position effect explains how the relative ease (or difficulty) of remembering an item from a list is related to the item's position on the list; items at the beginning or end of a list are easier to recall.
Things to remember:
The self-reference effect states that information that is personally relevant (ie, linked to oneself) is easier to remember because personally relevant information is meaningful and so is processed at a deeper level.
Question
Tamera just moved to a new house and memorized her new address. Now, she can recite her new address but struggles to recall her old address. Tamera's difficulty is most likely due to a memory error known as
| A. anterograde amnesia | |
| B. proactive interference | |
| C. retrograde amnesia | |
| D. retroactive interference |
Explanation
Many factors impact how easily memories are retrieved. Encoding is the first step in memory and is necessary for memory storage and retrieval; in other words, information must be encoded to be remembered.
A common memory error that occurs when previously learned information interferes with the ability to recall new information is called proactive interference (Choice B). For example, an individual cannot remember their new phone number (ie, recent information) and repeatedly confuses it with their old phone number (ie, older information).
Conversely, retroactive interference occurs when recently encoded information prevents the recall of older information. For example, an individual cannot remember their old phone number (ie, older information) and repeatedly confuses it with their new phone number (ie, recent information).
Therefore, Tamera's difficulty (struggling to recall her old address once she memorized her new address) is most likely due to a memory error known as retroactive interference.
(Choice A) Anterograde amnesia is a medical disorder in which a person cannot form new memories following a physiological trauma (eg, head injury, stroke). For example, while the patient is paying attention, information such as a new name can be temporarily learned but not permanently stored and recalled later.
(Choice C) Retrograde amnesia is a medical disorder in which a person cannot access old memories acquired prior to a physiological trauma (eg, head injury, stroke). For example, the patient cannot remember what they were doing before the trauma.
Things to remember:
Retroactive interference occurs when recently encoded information prevents the recall of older information. For example, an individual's new address interferes with her ability to recall her old address.

Study Anywhere, Anytime
Study for AP Psychology Unit 2 whenever you have a spare moment. You can answer a few cognition practice questions on the bus, watch a quick video lesson between classes, or review your notes while hanging out at the coffee shop. With the UWorld app, your entire AP Psych Unit 2 review is always ready when you are.
Stand Out
with a Top Score in AP Psychology
Earn a top score and stand out for colleges, majors, and scholarships. With UWorld’s AP Psychology online course, you’ll be ready from your first unit review to your final exam.
Get our all-in-one course today!
- Focused AP Psychology Videos
- Print & Digital Study Guide
- 350+ Exam-style Practice Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Adjustable Study Planner
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards
- Digital Notebook
Hear From Our AP Students

UWorld’s service is pretty good and helps provide a lot of explanations on subjects I haven’t been confident on before.

The questions here are the most realistic to the AP tests I've seen so far! I appreciate the ability to customize tests as well.

The best part is that all options are well-explained, telling clearly why they are not the right option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main topics covered in AP Psychology Unit 2: Cognition?
AP Psychology Unit 2 focuses on cognition, which includes the mental processes we use to think, solve problems, remember information, and understand the world. This unit helps you see how the mind works behind the scenes and why people make certain decisions, forget things, or approach problems differently.
The main topics covered in AP Psychology Unit 2 include:
- Perception: How we interpret information from our senses.
- Biases and errors in thinking: How mental shortcuts can lead to mistakes.
- Creative thinking and problem solving: How we generate ideas and find solutions.
- Memory processes: How information is encoded, stored, and retrieved.
- Forgetting and memory errors: Why we lose information or remember things incorrectly.
- Intelligence and achievement: How cognitive abilities are defined and measured.
Studying these cognition topics with UWorld helps you understand each idea clearly and apply them confidently on Unit 2 MCQs, progress checks, and FRQs.
How should I prepare for an AP Psychology Unit 2 exam?
A helpful way to prepare for the AP Psychology Unit 2 exam is to follow a simple Read, Watch, and Practice routine with UWorld. Start by reading the Unit 2 study guide to learn the main ideas behind cognition, such as perception, memory systems, and problem-solving. This gives you a solid understanding before you take on more complex Unit 2 tasks.
After reading, continue by watching UWorld’s AP Psychology Unit 2 video lessons. These videos help you understand cognitive biases, creative thinking, and how memory errors happen. Seeing the information explained visually makes the concepts easier to remember during the Unit 2 AP Psychology test.
Finally, practice with UWorld’s AP Psych Unit 2 questions. These questions match the style and difficulty of the actual exam, and each one includes a detailed explanation. Practicing consistently helps you get comfortable with cognition concepts and perform better on test day.
Are any free resources available for AP Psychology Unit 2?
Yes, there are good free resources that can help you prepare for AP Psychology Unit 2. UWorld offers a free trial with a selection of AP Psych Unit 2 practice questions, sample explanations, and short lesson previews. These resources help you understand key cognition topics such as perception, memory, and thinking processes.
You can also review free Unit 2 materials from the College Board®. Their website includes sample FRQs, progress check-style items, and the official AP Psychology Course and Exam Description. These tools show how cognitive topics appear on the actual exam, including intelligence, memory errors, and reasoning tasks.
Khan Academy provides free AP Psych videos on cognition and memory. When you combine these videos with UWorld’s detailed explanations and realistic practice questions, you build a stronger understanding of Unit 2 content and perform better on your AP Psychology exam.
What types of questions are on the AP Psychology Unit 2 test?
The AP Psychology Unit 2 test includes multiple-choice questions, free-response questions, and evidence- and article-based question formats. UWorld helps you prepare by giving you practice questions that cover perception, memory, cognitive biases, and problem-solving. These questions match the style and difficulty of real AP Psych Unit 2 exams.
You will see traditional multiple-choice questions along with two newer formats. The Article Analysis Question asks you to read a short passage and apply cognition concepts to it. The Evidence-Based Question requires you to analyze data or research related to memory, intelligence, or thinking. UWorld gives step-by-step guidance for approaching each question type.
FRQs often ask you to define cognition terms or apply concepts like forgetting, memory errors, or problem-solving strategies. Practicing with UWorld helps you write clear and accurate responses that follow AP scoring expectations.
How can I improve my score on the Free-Response Questions (FRQs) for Unit 2?
To improve your FRQ score for AP Psychology Unit 2, start by reviewing the main cognition concepts using UWorld’s study guide. Understanding perception, memory processes, intelligence, and common thinking errors helps you write stronger explanations on your FRQs. A clear understanding of these topics increases your confidence when applying them to scenarios.
Next, practice explaining cognition terms in your own words. FRQs often require you to apply concepts like forgetting, cognitive biases, or problem-solving strategies. UWorld shows you how to break down each question so you can write responses that are organized and accurate.
Finally, work through UWorld’s AP Psych Unit 2 FRQ-style questions. These guided practice items help you understand how to structure your answers and avoid common mistakes. With consistent practice, your FRQ writing becomes more precise and aligned with scoring guidelines.
What is the "Cognition" unit's weight on the AP Psychology exam?
The Cognition unit, also known as AP Psychology Unit 2, usually makes up 15%–25% of the AP Psychology exam. UWorld helps you understand all key topics in this section so you are ready for both MCQs and FRQs. Since cognition covers skills like perception, memory, and problem solving, it shows up often on the test.
Many Unit 2 questions focus on memory processes, forgetting, intelligence, and cognitive biases. UWorld’s practice questions help you review these skills and apply them to realistic scenarios that mirror actual exam questions.
Because the Cognition unit appears frequently on the AP Psychology test, using UWorld’s study guides, videos, and practice questions helps you build a strong foundation and improve your overall exam performance.
Where can I find a good study guide for AP Psychology Unit 2?
UWorld offers one of the best study guides for AP Psychology Unit 2. The guide makes cognition easy to understand by breaking it down into simple, organized parts. This makes it easier to understand perception, memory systems, problem-solving, and intelligence. Each topic is broken into clear sections that help you learn faster.
The UWorld study guide includes visuals, charts, and examples that show how cognitive processes work in real situations. These explanations also match the style of Unit 2 progress checks, quizzes, and MCQs. This helps you understand what the AP Psychology exam expects.
If you want a study guide that feels easy to follow and is designed for students, UWorld is the best place to start. It prepares you for both practice tests and real AP Psychology Unit 2 exam questions.
Can I find practice tests specifically for AP Psych Unit 2?
You can find AP Psych Unit 2 practice tests that focus on cognition, and UWorld is one of the best places to get them. Their question bank includes realistic Unit 2 AP Psychology practice test questions that match the difficulty and style of the AP exam. This helps you get comfortable with real cognition scenarios.
UWorld’s practice tests cover memory, perception, problem solving, thinking, and intelligence. Each question includes a detailed explanation, which helps you understand why the answer is correct and how to avoid mistakes on the real exam.
Practicing with UWorld builds confidence for Unit 2 MCQs, FRQs, and progress checks. With enough repetition, you will feel ready for any cognition question the AP Psychology exam includes.
How does memory improve with effective study strategies in AP Psychology Unit 2?
Memory plays a major role in AP Psychology Unit 2, since much of cognition involves how we encode, store, and retrieve information. Your performance on this unit improves when you understand how memory works and which strategies help you learn more efficiently. Techniques like spaced practice, retrieval practice, and elaboration help strengthen the connections in your brain.
Some helpful strategies include:
- Reviewing information over several days to strengthen long-term memory
- Testing yourself regularly to make recall more automatic
- Connecting new ideas to things you already understand
- Teaching the material to someone else to deepen understanding
- Breaking content into smaller chunks to improve focus and memory retention
Using UWorld with these study strategies helps you retain Unit 2 concepts like perception, problem solving, and memory processes more effectively. Their explanations reinforce what you learn so you remember it for tests and progress checks.
Why is understanding cognitive biases important in AP Psychology Unit 2?
Cognitive biases are a major part of AP Psychology Unit 2 because they explain why people think the way they do, even when their thinking is not fully logical. Understanding these mental shortcuts helps you see how individuals make decisions, judge situations, and solve problems. Many AP questions ask you to identify these patterns in real-life examples.
Unit 2 focuses on several key biases, such as:
- Confirmation bias, when people look for information that supports their beliefs
- Availability heuristic, where recent or vivid examples come to mind more easily
- Overconfidence, when someone believes they know more than they actually do
- Representativeness heuristic, when people rely on stereotypes to make judgments
Learning these biases with UWorld helps you apply them accurately on AP Psych Unit 2 MCQs and FRQs. Their examples and explanations make it easier to recognize how these errors show up in real scenarios and test questions.