AP® Human Geography Unit 7 Review and Practice Test
AP Human Geography Unit 7 explores how industries develop, why economies grow unevenly, and how globalization shapes production and labor patterns. These ideas can feel abstract without clear explanations, but UWorld helps you break them down so your AP Human Geography Unit 7 review becomes more focused, intuitive, and exam-ready.
Boost Exam Confidence and Score High with
Our AP Human Geography Unit 7 Review
Unit 7 becomes much clearer when you can see how industry, development, and global trade interact with one another. UWorld helps you connect these patterns through visual lessons, structured guides, and explanation-driven practice, so your understanding of industrial and economic development becomes solid and exam-ready.
Video Walkthroughs That Turn Complex Ideas Into Simple Steps
These short, visual videos help you understand development models, industrial location factors, global supply chains, and the causes of unequal economic growth. You see how industry shifts across regions, why labor and capital move, and how development indices compare countries. Each video prepares you for AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQ questions by simplifying ideas that students often struggle with.
Interactive Study Guides That Explain Development Patterns Clearly
The study guide organizes economic development content into structured notes with visuals, diagrams, comparison charts, and checkpoints. You learn development theories, industrial location factors, global trade routes, economic sectors, and how to interpret HDI, GII, and other indices. This structure prepares you for AP Human Geography Unit 7 FRQ prompts that require clear reasoning.
Raise Your Exam Performance with Realistic AP Human Geography Unit 7 Practice Test Questions
Question
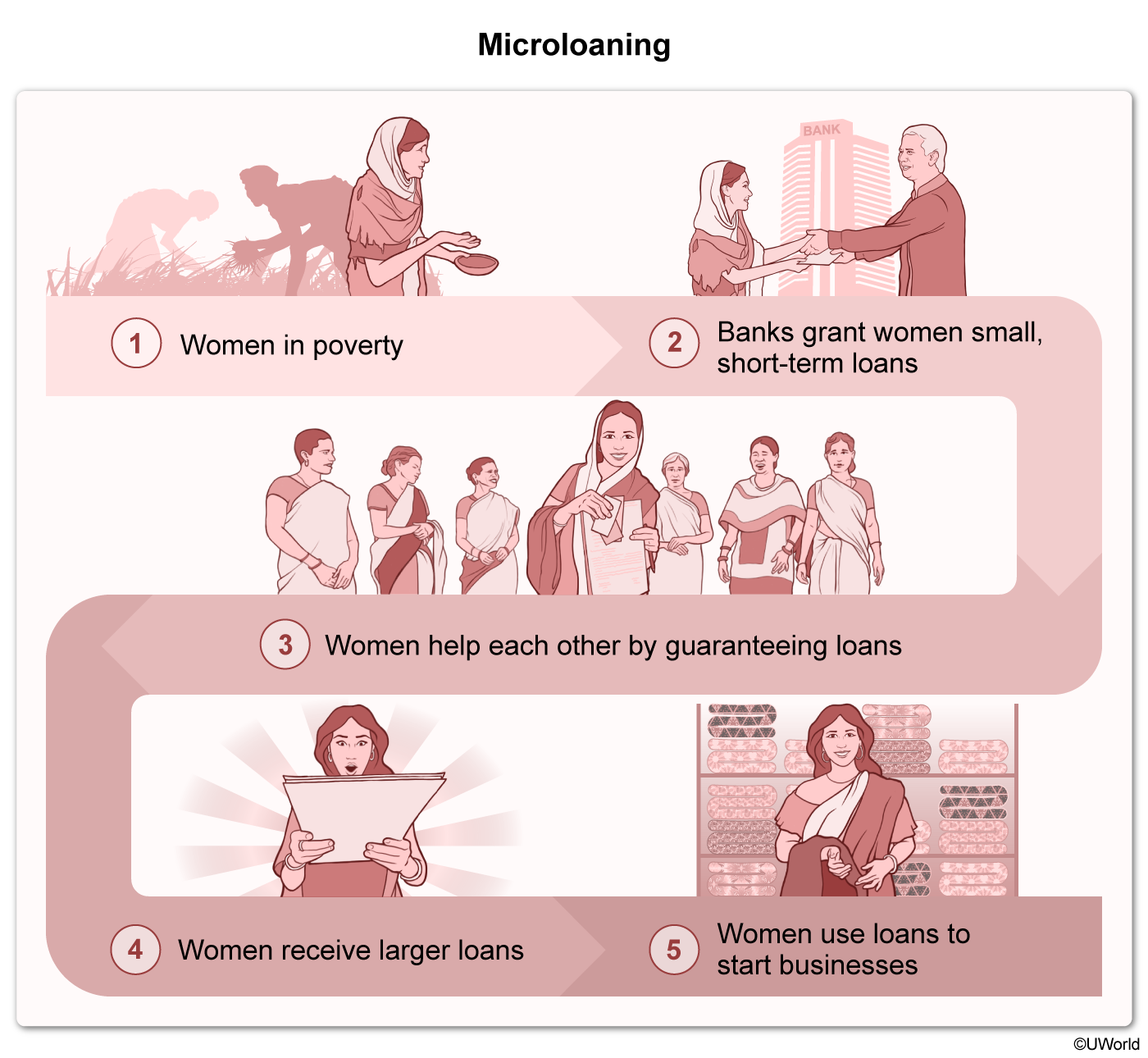
Which of the following is a likely outcome of microfinancing?
| A. Increasing a country's Gross Domestic Product through loans to corporations | |
| B. Raising the price of food and other basic necessities in the periphery | |
| C. Diverting money from government defense projects to social welfare programs | |
| D. Increasing the involvement of women in the family decision-making process | |
| E. Slowing economic growth in less developed countries |
Explanation
Microfinancing is the act of giving by providing microloans (small loans) to individuals and small businesses, particularly in developing countries. Most of these loans, ranging from $200 to $2,000, are granted to women to improve their economic status in a community. In 2015, 100 million women received roughly $80 billion in microloans.
As a result of their improved economic status, women who receive microloans are increasingly involved in family decisions. For example, they are more likely to make financial choices independent of others in the home.
(Choice A) Microfinancing is directed toward individuals or small businesses, not corporations.
(Choice B) Microfinancing loans are small; therefore, the prices of food and basic necessities in the periphery are unlikely to rise.
(Choice C) Since microfinancing is directed at individuals and small businesses rather than governments, the money cannot be diverted from the military to social programs.
(Choice E) Since microfinancing improves the economic status of individuals and small businesses in less developed countries, it is more likely that economic growth in developing countries would rise, not decline.
Things to remember:
Microfinancing provides small loans to both small businesses and individuals, particularly women in developing countries. As a result, these women experience improved economic status and greater involvement in family decisions.
Passage:
Question
The photograph above reflects which of the following?
| A. Religious differences among Indonesians | |
| B. The importance of foreign diplomacy | |
| C. The significance of high crude death rates | |
| D. The influence of rapid deindustrialization | |
| E. The impact of low human development |
Explanation
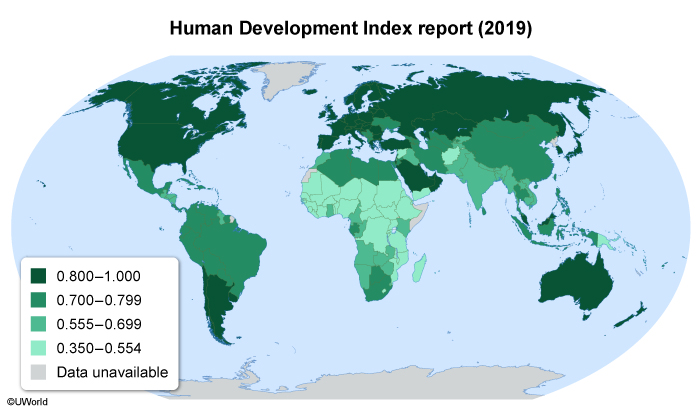
Indonesia's Bantar Gebang landfill contains several villages and as many as 20,000 people. The on-site population consists of families whose children attend underfunded village schools. To supplement their parents' income, most children leave school by age ten to scavenge for recyclables full time, earning the equivalent of $2–$10 per day. This cycle of poverty is largely responsible for the area's low human development.
A country's Human Development Index (HDI) is based on its citizens' life expectancy, educational attainment, and the gross national income per capita. Currently at 0.718, Indonesia's HDI is considered high, but they rank 107th out of 189 countries.
Indonesia's overall HDI ranking has been negatively impacted by the low human development found in Bantar Gebang, where children rarely escape poverty. In response, international observers have pressured Indonesia to help address this concern and raise the area's HDI.
(Choices A and B) The photograph doesn't show religious differences among Indonesians or indicate the importance of foreign diplomacy.
(Choice C) Indonesia has a crude death rate of 6.57 per 1,000 people, which is considered low.
(Choice D) Classified as a newly industrialized country, Indonesia has not undergone deindustrialization.
Things to remember:
A country's Human Development Index (HDI) is based on its citizens' life expectancy, educational attainment, and gross national income per capita. The circumstances of people living and working near Indonesia's Bantar Gebang landfill indicate low human development, which negatively impacts the country's HDI.
Question
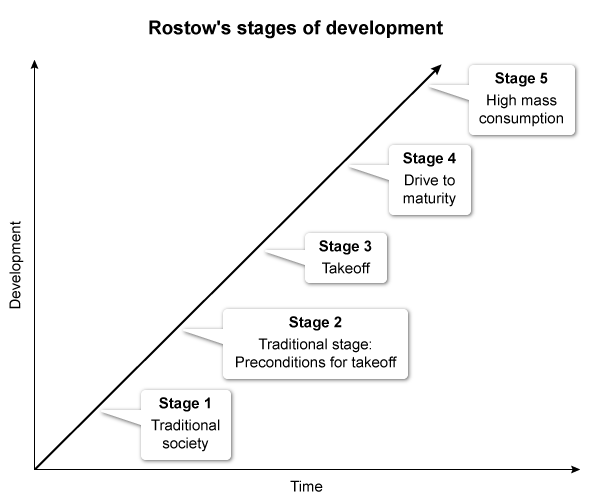
Which of the following concepts is most relevant to Rostow's modernization model?
| A. Colonialism | |
| B. Devolution | |
| C. Cultural divergence | |
| D. Economic development | |
| E. Possibilism |
Explanation
The decolonization of developing countries increased after WWII, and researchers began studying the economic development of the newly independent countries. The economist W.W. Rostow developed a theory that outlines the necessary stages of economic development a country must go through to modernize to be considered a developed nation:
- In Stage 1, a traditional society becomes a developing country.
- In Stage 2, educated individuals or wealthy groups introduce new technology and infrastructure.
- In Stage 3, a limited amount of production occurs in a few industries.
- In Stage 4, technologies spread to other industries and workers become specialized laborers.
- In Stage 5, the country transitions from heavy industry to producing consumer goods.
(Choice A) Rostow's model was created during the postcolonial era and therefore isn't relevant to colonialism.
(Choices B and E) Devolution and possibilism aren't associated with any stage in Rostow's model.
(Choice C) Cultural divergence, the process by which cultural barriers cause increasing difference within cultures over time, doesn't apply to Rostow's model.
Things to remember:
The economist W.W. Rostow developed a theory suggesting that countries pass through five stages of economic development as they modernize and become developed nations.

Carry Your Unit 7 Prep Wherever You Go
Turn short moments into powerful review sessions. Watch a video on development theories, answer AP Human Geo Unit 7 practice test questions during a break, or revisit explanations on the bus. The UWorld app helps you stay consistent and confident throughout your Unit 7 preparation.
Stand Out
with a Top Score in AP Human Geography
Complete your comprehensive AP Human Geo Unit 7 review to boost your performance and make yourself a standout candidate for competitive colleges, majors, and scholarships by earning a top score.
Get our all-in-one AP HUG review course today!
- Focused AP HUG Videos
- Print & Digital Study Guide
- 300+ Exam-style Practice Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Adjustable Study Planner
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards & Digital Notebook
Hear From Our AP Students

UWorld’s service is pretty good and helps provide a lot of explanations on subjects I haven’t been confident on before.

The questions here are the most realistic to the AP tests I've seen so far! I appreciate the ability to customize tests as well.

The best part is that all options are well-explained, telling clearly why they are not the right option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main topics covered in AP Human Geography Unit 7: Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes?
AP Human Geography Unit 7 focuses on why economic development varies across regions, how industries grow, and how globalization changes production and labor. To succeed, you need to understand models that explain economic change, as well as the spatial factors that influence where industries relocate. This unit enhances your ability to interpret data, analyze maps, and apply theories to real-world contexts. Using a structured resource like UWorld helps you make sense of these patterns in a way that feels logical rather than overwhelming.
Key topics in Unit 7 include:
- The Industrial Revolution
- Economic sectors and patterns
- How economic development affects the roles of women
- Trade and the world economy
Once you understand how these topics connect, Unit 7 AP Human Geography becomes much easier. You begin to understand why core and periphery relationships emerge, how industrial shifts impact labor, and why countries progress through development stages at varying rates. This prepares you well for AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQ questions, FRQs, and progress checks.
How should I prepare for an AP Human Geography Unit 7 exam?
Preparing for Unit 7 AP Human Geography requires understanding development theories and being able to apply them to real examples. You need to understand how industries evolve, why some countries industrialize more rapidly, and how economic inequality develops. Instead of trying to memorize every term, focus on understanding the logic behind industrial location and development stages. Using explanation-driven practice from UWorld helps because it shows you how to interpret economic data and identify spatial patterns accurately.
A strong Unit 7 study routine includes:
- Reviewing development indicators and what each one measures
- Studying models like Rostow, Wallerstein, and Weber
- Analyzing maps that show industrial growth or development levels
- Comparing economic sectors across core, semi-periphery, and periphery regions
- Practicing AP Human Geo Unit 7 practice test questions
- Using FRQ prompts to practice development-based explanations
This approach builds confidence because you learn how to recognize economic relationships instead of memorizing concepts out of context. Once you can tie development theories to real situations, you are ready for classroom tests, progress checks, and the AP exam.
Are any free resources available for AP Human Geography Unit 7?
Yes, several free resources can help you study AP Human Geography Unit 7, and the strongest starting point is UWorld’s free 7-day trial. It provides clear video lessons, interactive study guides, and realistic AP Human Geo Unit 7 practice test questions that explain development models, industrial shifts, and economic data step by step.
Beyond UWorld, you can find free global development datasets, short video explainers on industrialization, and map-based resources that show economic growth patterns. Teachers often share worksheets on Rostow’s model, Wallerstein’s theory, and industrial location factors. AP Classroom offers topic questions and progress checks aligned with the exam that help you see how Unit 7 is tested.
However, most free resources lack detailed explanations, which makes it harder to understand why countries develop differently or why industries relocate. That is why many students pair free materials with UWorld’s deeper reasoning support. This combination strengthens your understanding of Unit 7 and helps you prepare efficiently for both MCQs and FRQs.
What types of questions are on the AP HUG Unit 7 test?
The AP Human Geography Unit 7 test includes multiple choice questions, data interpretation, development model application, and FRQs that focus on economic growth, globalization, and industrial shifts. Instead of memorizing definitions, you need to recognize patterns in development indicators, understand spatial relationships, and explain why economic processes differ across regions. Many AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQ questions require analyzing graphs, maps, and charts. UWorld helps you prepare because explanations show how to read economic data and identify the logic behind each pattern.
You can expect to see:
- MCQs involving HDI, GII, GNI, and economic sector distribution
- Data-based questions comparing development levels across countries
- Model application tasks using Rostow or Wallerstein concepts
- Items on industrial location, Weber’s theory, and cost minimization
- Questions about globalization, outsourcing, and free trade zones
- FRQs requiring explanations of development processes or economic change
Understanding how these question types work helps you approach the unit confidently. You begin to recognize economic patterns, interpret data more quickly, and apply theories accurately. This prepares you well for classroom quizzes and the AP Human Geo Unit 7 exam.
How can I improve my score on the Free-Response Questions (FRQs) for Unit 7?
Improving your Unit 7 FRQ performance requires a clear understanding of development models, the ability to compare countries, and strong economic reasoning. FRQs often ask you to explain why development varies, how globalization affects production, or how industries relocate. Many students lose points because they describe terms without connecting them to real examples. Using explanation-driven practice, such as UWorld, strengthens your reasoning by showing you how to justify each point clearly for AP Human Geography Unit 7 FRQ tasks.
An effective FRQ strategy includes:
- Defining economic concepts before applying them
- Using real examples from the core, semi-periphery, and periphery regions
- Referencing development indicators to support your reasoning
- Explaining how industrial location factors influence economic growth
- Organizing responses in separate, clear points
- Practicing with FRQ prompts to build clarity and speed
With this method, FRQs become easier to handle. You learn how to explain economic relationships, compare development patterns, and apply theories correctly. This builds strong confidence for classroom FRQs and the AP exam.
What is the "Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes" unit's weight on the AP Human Geography exam?
Unit 7, which accounts for 12-17% of the exam score, directly connects to patterns in agriculture, migration, political geography, and cities, making it a central part of the course. Economic development plays a major role on the AP Human Geography exam because it explains why countries grow at different rates, how global systems shape economies, and how industries move across space.
Several AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQ items require analyzing development indicators, comparing countries, or understanding how globalization influences production. FRQs often ask students to apply development models, explain why certain regions industrialize faster, or evaluate the effects of outsourcing and trade networks. The exam rewards students who understand the logic behind economic disparities rather than memorizing terms.
Using a resource like UWorld helps you break these concepts down with clear explanations that link theories to real-world examples. Understanding economic development enables you to interpret data graphs, read global maps, and explain why economic change occurs. This makes Unit 7 one of the most important foundations for success across the entire AP Human Geography exam.
What should be in your AP Human Geography Unit 7 study guide?
A strong AP Human Geography Unit 7 study guide should help you understand how industry, development, and globalization shape each other. This unit contains several models and indicators, and without a clear guide, it is easy to feel lost. You want a resource that clearly explains each concept, provides real-world examples, and effectively utilizes visuals to connect ideas. UWorld supports this because its structured notes and explanations walk you through development patterns step by step, making your AP Human Geography Unit 7 study guide review more effective.
A high-quality Unit 7 study guide should include:
- Development indicators such as HDI, GNI, GII, and economic sectors
- Explanations of development models like Rostow and Wallerstein
- Industrial location concepts, including Weber’s Least Cost Theory
- Real examples of outsourcing, deindustrialization, and global supply chains
- Questions that reinforce understanding instead of memorization
When your guide presents information clearly and visually, Unit 7 becomes easier to grasp. You begin to recognize why some countries industrialize rapidly while others lag, and you develop the ability to connect development theory to real-world regions. This helps you answer AP Human Geo Unit 7 review questions with confidence.
Can I find practice tests specifically for AP HUG Unit 7?
Yes, there are practice tests specifically focused on Unit 7, which help you understand how the exam assesses industrial and economic development concepts. These practice tests challenge you to interpret data, apply development models, and analyze global economic relationships. They also prepare you for the style and difficulty level of AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQ questions. UWorld offers realistic practice tests with detailed explanations that strengthen your reasoning and help you identify patterns across economic development scenarios.
A strong Unit 7 practice test should include:
- MCQs that compare development indicators across countries
- Questions using Rostow or Wallerstein models
- Scenarios involving industrial location and Weber’s theory
- Items on outsourcing, deindustrialization, and free trade zones
- Data interpretation tasks using charts or maps
- Explanations that show how the economic process works
Working through these questions helps you predict what the exam expects. You learn to quickly interpret graphs, apply theories correctly, and understand how development varies across different regions. This leads to stronger performance on AP Human Geo Unit 7 practice test assessments.
How can I prepare for the AP Human Geography Unit 7 progress check in AP Classroom?
Preparing for the AP Human Geography Unit 7 progress check requires a clear understanding of economic development models, global production patterns, and the indicators that measure development. The progress check MCQs focus heavily on data interpretation and theoretical application, so start by reviewing key concepts such as HDI, GII, GNI, development sectors, and major models like Rostow’s and Wallerstein’s. Then spend time analyzing maps and charts that show industrial growth, economic disparities, or trade networks.
After reviewing the concepts, practice with AP-style questions to strengthen your reasoning. UWorld offers a check for understanding experience that mirrors the logic and structure of AP Classroom, enabling you to work through real-world development scenarios. The explanations not only show why an answer is correct but also why the distractors fail, which is essential for building accuracy. Reviewing your mistakes is key because it helps you identify weak areas before taking the progress check. When you combine concept review with consistent practice, the Unit 7 progress check MCQs for AP Human Geography become much easier to handle, boosting both clarity and confidence for the exam.
How do I stay organized while studying AP Human Geography Unit 7?
Unit 7 encompasses a range of complex components, including development indicators, global trade networks, industrial location factors, and world systems. Without structure, these concepts can blend. Staying organized helps you not only understand each idea but also see how they connect. A clear study structure, combined with reasoning-based practice from UWorld, enables you to build a predictable and effective review system, making your AP Human Geography Unit 7 review less stressful.
A strong organization method includes:
- Separating topics into themes like development models, indicators, and industrial location
- Using charts to compare Rostow’s stages and Wallerstein’s world system framework
- Taking notes on examples of outsourcing, deindustrialization, and trade zones
- Reviewing AP Human Geo Unit 7 MCQ items in small, consistent batches
- Revisiting economic indicators regularly to reinforce understanding
Once you create this structure, Unit 7 content becomes easier to navigate. You start recognizing patterns more quickly, making it easier to interpret data and apply models accurately. This organization helps you build confidence for the AP exam, classroom tests, and FRQs.
What are the most common mistakes students make in AP Human Geography Unit 7?
Many students struggle with Unit 7 because the concepts involve data analysis, theoretical application, and understanding how development varies across real places. Mistakes often occur when trying to memorize all the vocabulary instead of understanding how the ideas work together. Using guided explanations from a resource like UWorld helps you avoid these errors by strengthening your reasoning and building clearer links between concepts.
The most common mistakes include:
- Confusing development indicators or misreading economic data
- Mixing up Rostow’s model stages or applying them incorrectly
- Misinterpreting Wallerstein’s core and periphery relationships
- Treating GII and GNI as interchangeable instead of distinct measures
- Applying Weber’s Least Cost Theory without considering transport or labor costs
- Forgetting how globalization changes production and supply chains
- Providing weak, vague examples in FRQs instead of concrete cases
Recognizing these mistakes early helps you avoid them on exams. When you focus on understanding processes rather than memorizing terms, industrial and economic development patterns become easier to explain and apply. This leads to stronger performance on AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQs, FRQs, and progress checks.
Can I study AP Human Geography Unit 7 offline if I need to?
Yes, you can study Unit 7 offline, which is especially useful for reviewing economic development concepts without needing constant internet access. Offline study works well for this unit because many ideas can be reinforced through diagrams, notes, and practice with economic indicators.
UWorld allows you to download question sets so you can work through AP Human Geo Unit 7 practice test problems, revisit explanations, or check development models even when you’re offline. Pairing downloaded questions with printed charts or maps helps you practice interpreting HDI, GII, GNI, and sector data.
Offline study also gives you the freedom to review industrial location factors, globalization impacts, or trade networks during commutes or short breaks. Once you reconnect, the UWorld mobile app syncs your progress, keeping your performance data up to date. This flexibility helps you stay consistent, avoid gaps in studying, and build confidence for the AP Human Geography Unit 7 exam. By combining offline practice with your regular study sessions, you strengthen your understanding of development patterns and walk into your test feeling prepared.