AP® Human Geography Unit 5 Review and Practice Test
Prepare for AP® Human Geography Unit 5 with clear videos, study guides, and AP Human Geo Unit 5 practice test questions that break down agriculture and rural land-use patterns so you can strengthen your understanding and build confidence for the exam.
Explore AP Human Geography Unit 5 with Targeted,
Concept-Driven Review
Understand how agriculture shapes economies, landscapes, and communities with an AP® Human Geo Unit 5 review built for clarity and real exam alignment. These resources guide you through food production systems and rural land-use patterns so you can approach Unit 5 questions with confidence.
Engaging Video Lessons
Explore AP Human Geography Unit 5 with video lessons that break down agriculture, food production systems, and rural land-use patterns in a clear, visual way. Each AP Human Geo Unit 5 lesson connects real-world farming examples to exam topics. These videos make complex geographic processes easier to follow and retain.
Interactive Study Guides
Work through AP Human Geography Unit 5 topics with interactive study guides that simplify agricultural systems, land-use models, and farming practices. Each AP Human Geo Unit 5 study guide uses clear visuals, summaries, and definitions to help you understand how agriculture shapes rural landscapes.
Test Your Knowledge with AP Human Geography Unit 5 Practice Sets
Question
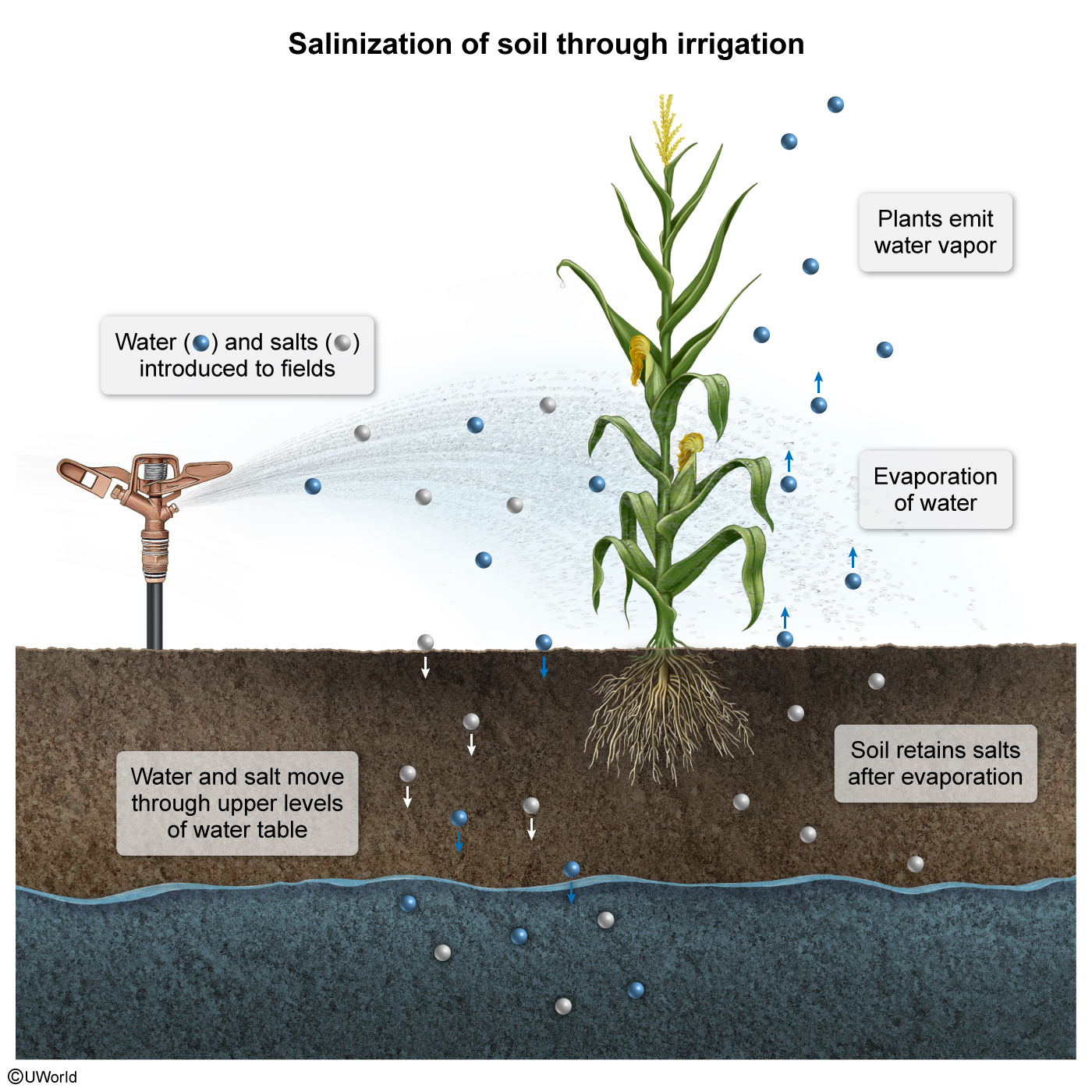
Which of the following best describes an effect of irrigation?
| A. Land cover change | |
| B. Acid precipitation | |
| C. Monoculture | |
| D. Soil salinization | |
| E. No-tillage cultivation |
Explanation
Irrigation systems contribute to the growth of crops by drawing water from environmental sources, such as rivers and reservoirs. In those waters are sediments composed of various minerals, including salt. When fields are irrigated and the water evaporates, the salt is left behind in the soil. Therefore, one effect that irrigation has on the environment is increased soil salinization.
Soil salinization decreases fertility because the high salt content reduces plants' ability to absorb water from the ground. To prevent this, farmers must carefully monitor the irrigation of their fields and periodically test the soil for salinity (salt content).
(Choice A) Irrigation tends to extend or preserve agricultural areas. Therefore, it is unlikely to contribute to land cover change, in which agricultural lands are lost to the growth of urban areas.
(Choice B) Acid precipitation is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide mixing with atmospheric moisture, not water from irrigation.
(Choices C and E) The irrigation of crops has little influence on whether farmers practice monoculture or no-tillage cultivation.
Things to remember:
One adverse effect of irrigation on the environment is increased soil salinization, which reduces the ability of plants to absorb water.
Question
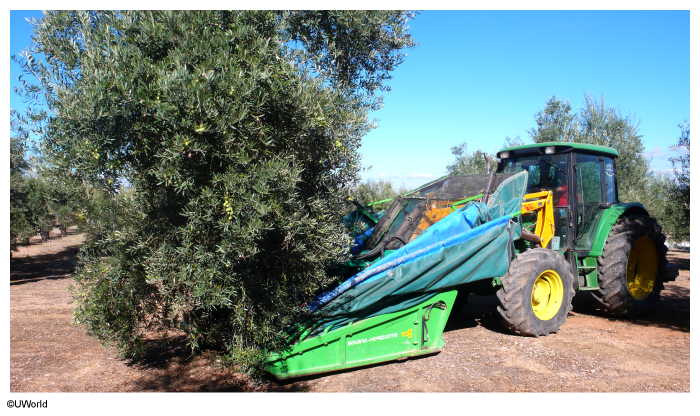
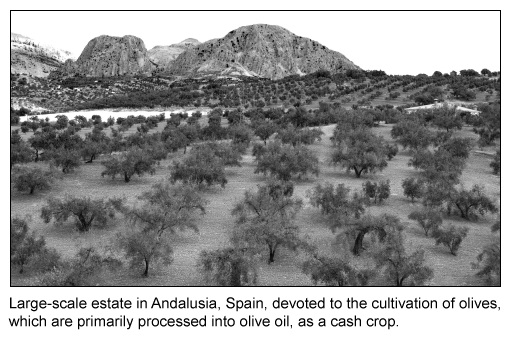
Which factor is most responsible for the large-scale cultivation of Spanish olives shown in the picture above?
| A. A decrease in Spain's dependence on olive oil exports | |
| B. An improvement in harvesting technologies | |
| C. An increase in the salinity of Spanish soils | |
| D. The United States' increased tariffs on Spanish olive oil | |
| E. The reterritorialization of Spanish olives |
Explanation
Mechanization has permitted the expansion of both businesses and economies. In the olive industry, improvements in harvesting technologies increase efficiency and eliminate the cost of harvesting by hand, which is the highest cost in olive production worldwide.
By mechanizing their harvests, Spain's olive growers can expand by buying more land on which to grow olives. This process increases olive producers' economies of scale, a factor that permits the large-scale cultivation of olives worldwide.
(Choice A) Spain exports nearly 50% of the world's olive oil, which has increased the country's dependence on its olive production.
(Choice C) Soil salinization is known to hinder the growth of plants, including olives, so increasing soil salinity would typically prevent the emergence of large-scale olive plantations.
(Choice D) US import tariffs on Spanish olive oil likely restrict the large-scale cultivation of Spanish olives.
(Choice E) Olive production has been a part of this region's culture for thousands of years, so reterritorialization doesn't apply to Spanish olives.
Things to remember:
In the olive industry, mechanical harvesters increase efficiency and eliminate the cost of hand harvesting. This allows Spain's olive growers to expand by buying more land, which increases olive producers' economies of scale.
Question
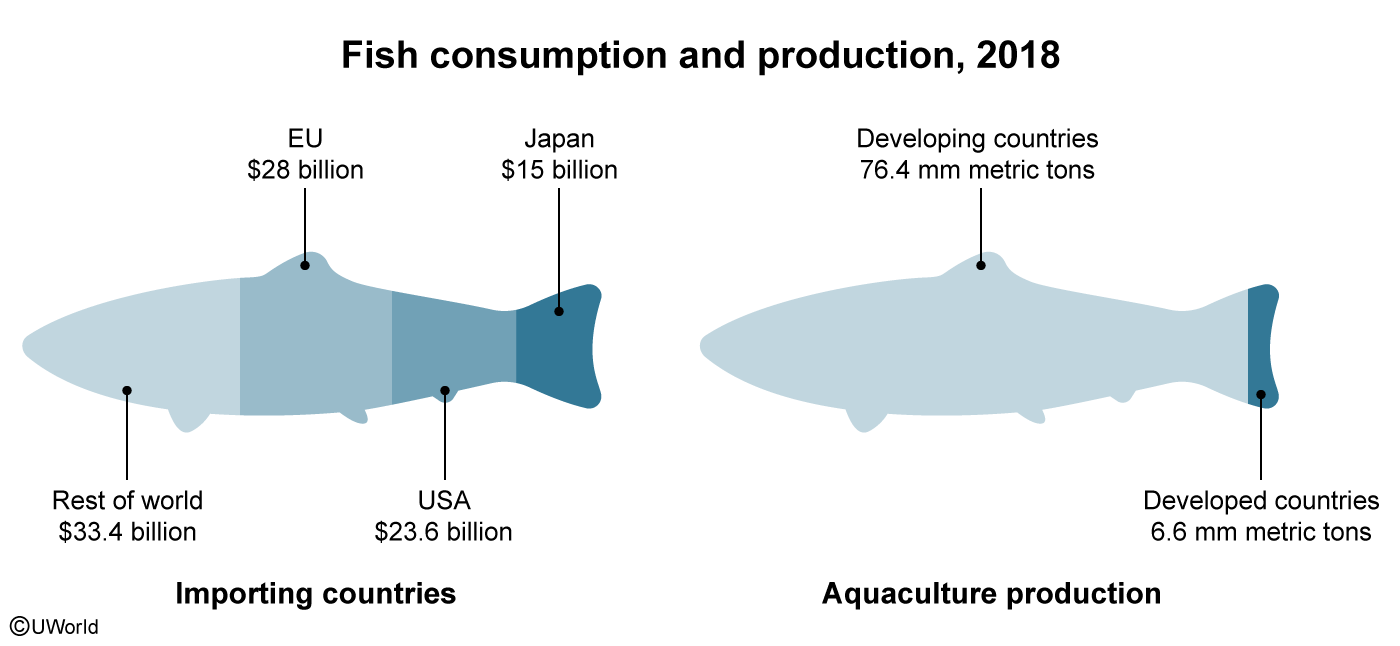
Which of the following statements best describes the effects of aquaculture on developing nations?
| A. Since aquaculture accounts for a small percentage of total food production, the economies of developing countries will likely not change | |
| B. Through the fair trade of cultured fish in international markets, the economies of developing nations will likely improve | |
| C. Owing to the large differences in food distribution systems, the economies of developing nations will likely decline | |
| D. Because of aquaculture's positive effects on the oxygen cycle, the economies of developing nations will likely improve | |
| E. Because of the global trend away from primary economic activities, the economies of developing nations will likely decline |
Explanation
In 2019, the nearly $285 billion aquaculture industry accounted for over 50% of the fish consumed worldwide. Developed nations such as Japan, the US, and European states import the majority of farmed and captured fish harvests—most of which come from aquaculture in the developing world.
To boost their economies, developing nations—which are responsible for 90% of worldwide aquacultural production—pursue fair trade deals to ensure the best prices for their fish farmers. Considering the industry's value and the percentage produced by developing nations, the fair trade of cultured (farm-raised) fish in international markets will likely improve developing nations' economies.
(Choice A) Developing countries account for over 90% of cultured fish consumed worldwide, which helps improve their economies.
(Choice C) Farmers in developing nations sell their fish harvests wholesale and aren't a part of the distribution process.
(Choice D) Aquaculture generally has negative, not positive, effects on the oxygen cycle. These include increased biochemical oxygen demand and undesirable levels of dissolved oxygen in marine ecosystems.
(Choice E) Because primary economic activities are the base source of food for global populations, there isn't a global trend to turn away from activities like aquaculture.
Things to remember:
Accounting for roughly 90% of all aquacultural production, developing nations' economies will likely improve through the fair trade of cultured (farm-raised) fish that they export in international markets.

Study Anywhere, Anytime
Study on your schedule with instant access to AP Human Geography Unit 5 review tools wherever you are. Whether you’re commuting, between classes, or taking a quick break, you can review agriculture concepts, explore rural land-use patterns, or complete practice test questions right from the UWorld app.
Stand Out
with a Top Score in AP Human Geography
Boost your performance and make yourself a standout candidate for competitive colleges, majors, and scholarships by earning a top score.
Get our all-in-one AP HUG review course today!
- Focused AP HUG Videos
- Print & Digital Study Guide
- 300+ Exam-style Practice Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Adjustable Study Planner
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards & Digital Notebook
Hear From Our AP Students

UWorld’s service is pretty good and helps provide a lot of explanations on subjects I haven’t been confident on before.

The questions here are the most realistic to the AP tests I've seen so far! I appreciate the ability to customize tests as well.

The best part is that all options are well-explained, telling clearly why they are not the right option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main topics covered in AP Human Geography Unit 5: Agriculture and Rural Land-Use Patterns and Processes?
AP Human Geography Unit 5 explores how agriculture develops, spreads, and operates across different landscapes. These concepts appear frequently in AP Human Geo Unit 5 practice test questions and help explain how farming shapes rural and global systems.
Key Unit 5 Topics:
- How physical geography influences farming practices: Terrain, climate, and soil determine what farmers grow and how they grow it.
- The origins and spread of agriculture: Examines early agricultural hearths and how farming innovations diffused worldwide.
- The Green Revolution: High-yield seeds and modern technology that dramatically increased food production.
- How farming practices affect the environment and society: Analyzes sustainability, pollution, land use, labor systems, and economic impacts.
These ideas form the foundation of your AP Human Geography Unit 5 review and appear often in AP HUG Unit 5 FRQs and MCQs.
How should I prepare for an AP Human Geography Unit 5 exam?
A strong study plan for Unit 5 focuses on understanding agricultural systems, land-use patterns, and the geographic forces behind them. Using a balanced structure like Read, Watch, and Practice helps you prepare efficiently.
- Read: Use UWorld’s AP Human Geo Unit 5 study guides to review key models, farming types, and the environmental effects of agriculture.
- Watch: Engaging Unit 5 video lessons help you visualize land-use patterns, the Green Revolution, and the historical development of agriculture.
- Practice: Work through AP Human Geography Unit 5 practice test questions to strengthen your ability to interpret maps, graphs, and real-world examples.
This approach prepares you to handle both MCQs and FRQs with confidence.
Are any free resources available for AP Human Geography Unit 5?
Yes. You can begin your AP Human Geography Unit 5 review with several high-quality free resources that introduce the essential agricultural concepts covered in this unit.
UWorld’s 7-Day Free Trial gives you access to Unit 5 video lessons, interactive study guides, and AP Human Geo Unit 5 practice test questions, allowing you to experience how the platform simplifies agriculture and rural land-use patterns.
College Board AP Classroom provides AP Daily videos, Unit 5 progress checks, and official course materials, while Khan Academy offers free lessons that reinforce agricultural patterns and rural land-use concepts. These resources help you build a strong foundation before choosing a full study program.
What types of questions are on the AP Human Geography Unit 5 test?
The AP Human Geography Unit 5 test features questions that measure your understanding of agricultural processes, spatial patterns, and environmental impacts.
You’ll encounter:
- Multiple-choice questions (MCQs): Interpret maps, land-use models, charts, agricultural regions, and case studies related to farming and food production.
- Free-Response Questions (FRQs): Require written analysis using agricultural concepts, environmental impacts, and real-world rural land-use examples.
Practicing AP Human Geo Unit 5 practice test questions helps you recognize how Unit 5 concepts appear on the exam.
How can I improve my score on the Free-Response Questions (FRQs) for Unit 5?
Scoring well on Unit 5 FRQs requires clear explanations and accurate application of agricultural concepts. Strong responses break down geographic relationships and connect farming practices to broader consequences.
To improve your performance:
- Use diagrams such as the Von Thünen Model when relevant.
- Describe how physical geography guides farming decisions.
- Incorporate examples from the Green Revolution or agricultural diffusion.
- Explain economic and environmental impacts using precise geographic terms.
Review UWorld’s step-by-step explanations in AP Human Geo Unit 5 practice items to see effective reasoning in action. Consistent practice builds the clarity and organization needed for high-scoring FRQs.
What is the "Agriculture and Rural Land-Use Patterns and Processes" unit's weight on the AP Human Geography exam?
Unit 5 carries notable importance on the AP Human Geography exam because agriculture plays a central role in connecting economic systems, environmental challenges, and global development trends. Understanding these relationships helps you interpret how farming shapes both local and global landscapes.
On the multiple-choice section, Unit 5 typically represents about 12–17% of the exam, and Free-Response Questions (FRQs) often include agricultural examples even when prompts blend content from multiple units. This makes agricultural concepts relevant across different question types.
Topics such as farming types, land-use models, food production systems, and sustainability appear frequently throughout the exam. A strong AP Human Geography Unit 5 review can significantly strengthen your overall performance and boost your confidence on test day.
Where can I find a good study guide for AP Human Geography Unit 5?
You’ll find one of the most effective AP Human Geography Unit 5 study guides in UWorld’s AP Human Geography Course. The guide breaks down agricultural origins, farming systems, the Green Revolution, and rural land-use patterns in a way that is easy for students to understand and apply.
UWorld’s Unit 5 study guide features visual summaries of major agricultural concepts, clear definitions of AP Human Geo Unit 5 vocabulary, and simplified explanations of land-use models and environmental impacts. These elements help you grasp complex ideas quickly and accurately.
In addition to concise summaries, the study guide includes integrated practice questions that reinforce each topic and support faster recall. It’s designed to help you understand and remember the most important Unit 5 concepts so you feel confident going into the exam.
Can I find practice tests specifically for AP HUG Unit 5?
Yes. UWorld offers AP HUG Unit 5 practice test questions that closely match real exam style and difficulty. These questions cover agricultural origins, food production systems, and rural land-use processes with detailed explanations to reinforce understanding.
Other sources include:
- College Board AP Classroom: Unit 5 progress checks
- Khan Academy: Limited agriculture-related practice
For the most realistic preparation, UWorld remains the strongest option for Unit 5 MCQs and FRQs.
How does AP Human Geography Unit 5 connect to real-world agricultural issues?
AP Human Geography Unit 5 builds a bridge between classroom concepts and real-world agricultural challenges. By understanding farming systems, land-use patterns, and food production methods, students can better interpret global issues shaping communities today.
Many of the environmental and economic concerns discussed in the unit, such as soil degradation, sustainability, and shifts in food demand, mirror the problems countries face as populations grow and resources become strained. These connections help you see how agricultural decisions directly affect societies and landscapes.
Reviewing AP Human Geo Unit 5 study guides and practice test questions makes it easier to visualize how local farming practices contribute to broader environmental outcomes. This perspective strengthens your ability to analyze current events through a geographical lens, a valuable skill for both the exam and real-life understanding.
Why is it important to understand agricultural models in AP Human Geography Unit 5?
Agricultural models are essential tools in AP Human Geography Unit 5 because they help explain how farmers choose land, resources, and production methods. Models such as Von Thünen’s and the Boserup Theory show how economic forces, population pressures, and land value shape farming decisions.
These models also help you identify patterns such as where certain crops are grown, why some areas specialize in livestock, or how market access affects food production. Understanding these relationships strengthens your confidence when interpreting maps, diagrams, and spatial patterns on the exam.
When you use UWorld’s AP Human Geo Unit 5 practice test questions, you see how these models appear in real exam-style scenarios. This exposure builds your ability to apply each model accurately, which is a key skill for both multiple-choice questions and FRQs on the AP exam.