AP® Human Geography Unit 3 Review and Practice Test
AP® Human Geography Unit 3 explores how culture develops, spreads, and influences space, identity, and human behavior. UWorld’s AP HUG Unit 3 practice tests help you turn these abstract ideas into something you can actually apply, making your AP Human Geography Unit 3 review more focused, confident, and exam ready.
Make AP Human Geography Easier and Boost Your Confidence with Our Comprehensive Review
Unit 3 AP HUG becomes much easier when your review tools work together. Short videos help you visualize cultural patterns, interactive study guides deepen understanding, and structured guidance helps you prepare for the AP Human Geography Unit 3 test questions with confidence. Everything builds toward clearer thinking and stronger recall.
Understand Cultural Patterns with Easy, Guided Videos
These short, visual lessons simplify complex cultural concepts, including diffusion, cultural landscapes, language families, religious distributions, and identity. You see how cultural processes shape spatial patterns and how these patterns reappear on the AP Human Geography Unit 3 MCQs. Each video helps you understand why certain cultural elements spread, persist, or transform.
Companion that Breaks Down Concepts and Builds Real Understanding
The interactive study guide organizes AP Human Geography Unit 3 notes into clear, structured explanations supported by visuals, definitions, comparison charts, and application examples. You learn how to interpret language maps, analyze religion patterns, understand cultural diffusion, and connect concepts across regions. This guide also supports your preparation for AP Hug Unit 3 FRQ tasks by focusing on reasoning, not memorization.
Score Higher with Targeted AP Human Geography Unit 3 Practice Tests
Question
The examination of a culture based solely on that culture's distinctive standards is known as
| A. Cultural convergence | |
| B. Cultural divergence | |
| C. Cultural relativism | |
| D. Cultural diffusion | |
| E. Cultural ecology |
Explanation
Whaling is a controversial practice condemned by many developed nations, especially in the West. However, whaling is a traditional practice that is central to the diets, economies, and cultures of many indigenous peoples.
Cultural relativism looks to understand behaviors within the context of a society's unique cultural norms and is the examination of a culture based solely on its distinctive standards. Cultural relativism has led to exceptions to the international laws that ban whaling, such as granting these peoples limited, noncommercial whaling rights.
(Choices A and B) Cultural convergence and cultural divergence are processes that make cultures more similar or dissimilar, respectively, over time.
(Choice D) Cultural diffusion is the spread of a cultural element from its place of origin to a wider area.
(Choice E) Cultural ecology examines the relationship between humans and their environment and is not based solely on a particular culture's distinctive standards.
Things to remember:
Cultural relativism is the examination of a culture based solely on its distinctive standards.
Question
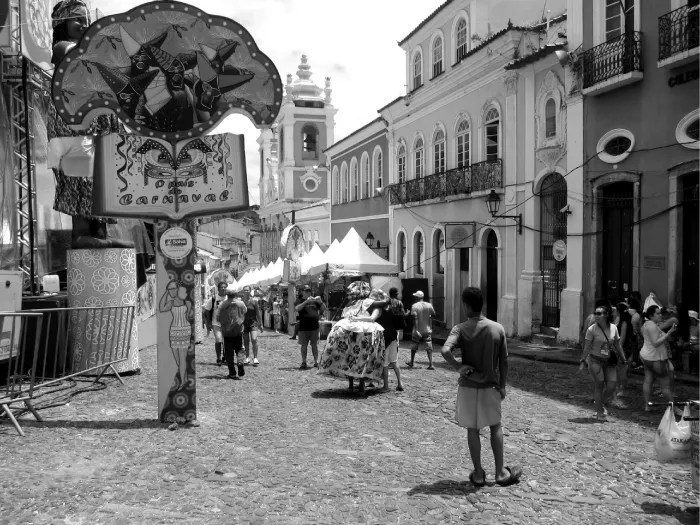
Historically, Carnival has been a Catholic celebration that originated in Europe during the Middle Ages. Today, there are annual celebrations in North America, South America, the Caribbean, Africa, and India. As a result, the spread of Carnival is a good example of which of the following processes?
| A. Colonialism | |
| B. Gentrification | |
| C. Industrialization | |
| D. Suburbanization | |
| E. Independent invention |
Explanation
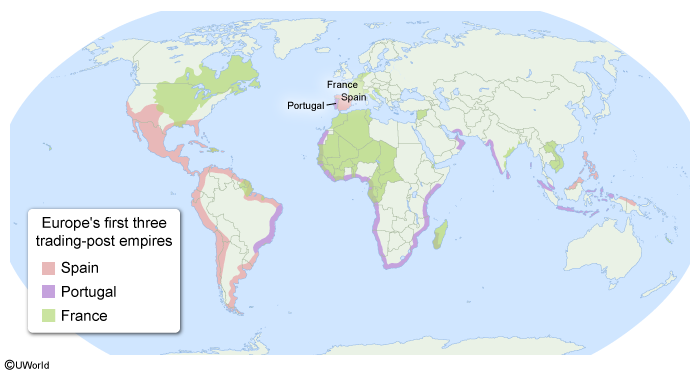
Carnival, a Roman Catholic festival that originated in Europe, has been celebrated in Catholic countries such as Spain, Portugal, and France since the Middle Ages. During the Age of Exploration, European countries colonized territories in North and South America, the Caribbean, Africa, and Asia. As a result of colonialism, aspects of European culture diffused across the world.
Spain, France, and Portugal spread Catholicism and its traditions, including Carnival. In some countries, such as Brazil, Catholic traditions mixed with African celebrations that had spread through the trans-Atlantic slave trade, a central element of colonialism in the Americas.
(Choices B, C, and D) Gentrification, industrialization, and suburbanization are not responsible for spreading cultural traits such as Carnival across the world.
(Choice E) Independent invention is the opposite of diffusion.
Things to remember:
As a result of colonialism, aspects of European culture diffused across the world. Spain, France, and Portugal spread Catholicism and its traditions, including Carnival, which is still celebrated in many of their former colonies.
Question
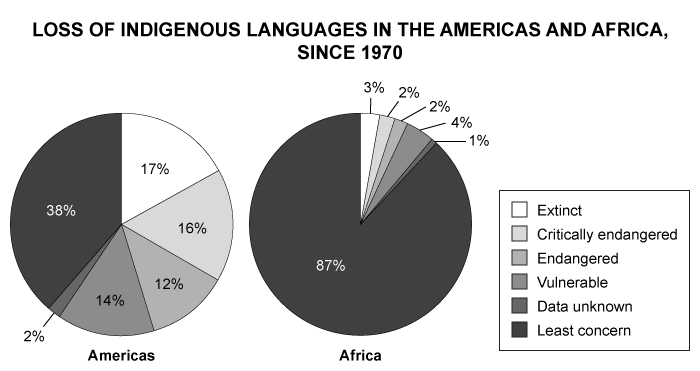
Which of the following is a primary reason for the loss of indigenous languages in the Americas and Africa since 1970?
| A. Communication technologies have accelerated interactions among people | |
| B. Widespread governmental efforts to assimilate indigenous peoples | |
| C. Decolonization accelerated the loss of indigenous languages | |
| D. Globalization has increased distance decay | |
| E. A decrease in the use of English as a worldwide lingua franca |
Explanation
Over the past 50 years, globalization has eroded native cultures. Since the 1970s, television and radio viewership has increased among indigenous peoples in Africa and the Americas, connecting them with the rest of the world. In addition, digital communication technologies, such as cell phones and the internet, have connected isolated indigenous cultures in Africa and the Americas with other cultures worldwide.
Television, radio, and digital communications have accelerated interactions with indigenous peoples and increased the use of English. This has increased cultural convergence, reshaping once-isolated cultures and contributing to the loss of indigenous languages.
(Choice B) In the 19th and early 20th centuries, governmental efforts to assimilate indigenous peoples, such as the creation and upkeep of Indian Boarding Schools, were common in North America.
(Choice C) The decolonization of Africa has helped to temporarily preserve indigenous languages.
(Choice D) Globalization has decreased, not increased, distance decay.
(Choice E) The increase, not decrease, in the use of English as a worldwide lingua franca has caused the loss of indigenous languages in the Americas and Africa since the 1970s.
Things to remember:
Television, radio, and digital communications have accelerated interactions with indigenous peoples, increasing the use of English and contributing to the loss of indigenous languages.

Study AP HUG Unit 3 Anywhere, Anytime
Turn short moments throughout your day into meaningful review. Whether you’re commuting, between classes, or waiting for friends, the UWorld app lets you review videos, work through AP HUG Unit 3 practice test questions, or revisit explanations. Every quick session strengthens your understanding of cultural patterns and prepares you for the test.
Stand Out
with a Top Score in AP Human Geography
Finish your AP HUG Unit 3 review and continue mastering all units with UWorld. Boost your performance and make yourself a standout candidate for competitive colleges, majors, and scholarships by earning a top score.
Get our all-in-one AP HUG review course today!
- Focused AP HUG Videos
- Print & Digital Study Guide
- 300+ Exam-style Practice Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Adjustable Study Planner
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards & Digital Notebook
Hear From Our AP Students

UWorld’s service is pretty good and helps provide a lot of explanations on subjects I haven’t been confident on before.

The questions here are the most realistic to the AP tests I've seen so far! I appreciate the ability to customize tests as well.

The best part is that all options are well-explained, telling clearly why they are not the right option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main topics covered in AP Human Geography Unit 3: Cultural Patterns and Processes?
Unit 3 AP HUG covers the cultural processes that shape human identity, interaction, and spatial organization. Understanding these concepts requires more than memorizing definitions. You need to see how culture spreads, evolves, and influences landscapes. This unit explores language patterns, religion, ethnicity, cultural diffusion, and the forces that create both cultural diversity and cultural change. Using a structured resource like UWorld helps you connect these ideas clearly, making your AP Human Geography Unit 3 review more manageable.
Key topics in Unit 3 include:
- The different ways that cultural practices spread
- Historical forces, such as colonialism and trade, that affect cultural patterns
- Modern forces, such as globalization, that affect cultural patterns
- Why do different religions spread in different ways
Once you see how these themes connect, cultural patterns feel more intuitive. You begin understanding why certain traits spread widely while others remain localized. This helps you analyze AP Human Geography Unit 3 multiple-choice questions and interpret cultural maps with greater confidence. Strong comprehension of the unit also prepares you for FRQs that require clear reasoning about cultural systems and spatial processes.
How should I prepare for an AP Human Geography Unit 3 exam?
Preparing for the AP Human Geography Unit 3 test requires understanding cultural concepts and learning how they apply to real geographic situations. Instead of trying to memorize every vocabulary term, focus on how cultural patterns develop, spread, and influence space. A structured resource like UWorld helps reinforce this understanding by guiding you through explanations that show how cultural traits interact and why certain patterns appear on maps.
A strong Unit 3 study routine includes:
- Reviewing cultural diffusion types and how they shape global patterns
- Studying language and religion distributions using real maps
- Comparing folk and popular culture characteristics
- Practicing AP Human Geography Unit 3 MCQ-style questions
- Using FRQ prompts to practice explaining cultural processes
- Reviewing changes caused by globalization and cultural convergence
When you combine concept review with steady practice, the unit becomes more predictable. You learn to interpret cultural maps, identify diffusion patterns, and explain the impact of cultural traits on landscapes. This deeper understanding helps you perform better on AP HUG Unit 3 practice test questions and classroom assessments. Over time, you build stronger confidence, making the exam feel less like memorization and more like clear reasoning.
Are any free resources available for AP Human Geography Unit 3?
Yes, several free resources can help you begin studying AP Human Geography Unit 3. The most comprehensive starting point is UWorld’s free 7-day trial. The trial provides access to guided videos, interactive study guides, and realistic AP Human Geography Unit 3 practice test questions, enabling you to understand cultural diffusion, language patterns, religion, geography, and identity more clearly.
Beyond UWorld, you can find free cultural maps online, short video explainers about cultural landscapes, and open-source vocabulary lists for AP HUG Unit 3 vocab review. Teachers often share cultural pattern activities or map analyses that help you recognize real-world examples. The College Board’s AP Classroom also provides topic questions and progress check items that align with your textbook, offering additional practice.
However, free resources often lack the depth needed to understand why patterns occur or how cultural processes interact. That is why many students pair these materials with UWorld’s step-by-step reasoning, which helps you learn how to eliminate distractors and recognize the logic behind cultural trends. The combination of supplemental free materials with UWorld’s structured support enables you to build a strong foundation for understanding Unit 3.
What types of questions are on the AP Human Geography Unit 3 test?
The AP Human Geography Unit 3 test includes multiple choice questions, map interpretation tasks, and free response questions that evaluate your understanding of cultural patterns and processes. Instead of testing isolated facts, the exam measures how well you can explain cultural diffusion, analyze spatial patterns, and interpret how culture shapes human behavior. The MCQs pull directly from real-world examples, making it essential to understand how cultural traits interact. UWorld helps with this by showing the logic behind each question, which strengthens your approach to AP Human Geography Unit 3 multiple-choice items.
You can expect to see:
- Questions analyzing cultural diffusion patterns across regions
- Map-based items that test language, religion, or ethnicity distribution
- Comparisons of folk and popular culture characteristics
- Scenarios describing cultural convergence or divergence
- FRQs asking you to explain cultural processes or analyze spatial impacts
- Conceptual items about cultural landscapes and cultural identity
When you are familiar with these formats, the test becomes easier to navigate. You learn what the exam emphasizes and how to apply concepts, rather than memorizing lists. Understanding cultural patterns helps you interpret AP Human Geo Unit 3 test questions more confidently and approach FRQs with stronger reasoning.
How can I improve my score on the Free-Response Questions (FRQs) for Unit 3?
Improving your FRQ performance for Unit 3 requires clear explanations, a strong understanding of cultural processes, and the ability to apply concepts to specific spatial examples. FRQs often ask about diffusion, cultural landscapes, language distribution, or the impact of cultural change. Many students lose points because they describe terms rather than explaining how cultural patterns function. Using structured practice, such as UWorld explanations, helps you learn how to justify your reasoning for AP HUG Unit 3 FRQ prompts.
A strong FRQ strategy includes:
- Defining terms clearly before applying them
- Using evidence from regions, maps, or cultural phenomena
- Explaining how cultural traits diffuse or create patterns
- Organizing responses into clear, separate points
- Avoiding vague descriptions and focusing on specific processes
- Practicing with sample prompts to strengthen clarity
When you build these habits, FRQs become less stressful. You learn to connect cultural concepts to real-world examples and explain how spatial patterns develop. This stronger reasoning helps you perform well on the FRQs.
What is the "Cultural Patterns and Processes" unit's weight on the AP Human Geography exam?
Unit 3 carries meaningful weight on the AP Human Geography exam because cultural patterns and processes form the foundation for understanding many other units. The College Board states that the unit accounts for 12-17% of the multiple-choice score, covering questions on cultural concepts. You can expect several MCQ items related to diffusion types, language families, religious spatial patterns, and cultural landscapes. These topics also show up in writing-based questions, where you may be asked to explain cultural convergence, identify effects of cultural diffusion, or analyze how cultural identity shapes space.
This unit connects to themes such as migration, political geography, and urban patterns; a strong understanding of culture enhances performance across the entire exam. Tools like UWorld help reinforce these connections by explaining how cultural traits interact and why patterns emerge. When you build a solid grasp of diffusion, cultural identity, and spatial variation, you gain the clarity needed to answer map questions, interpret cultural graphs, and write well-supported FRQ responses. All of this makes Unit 3 one of the most crucial building blocks for success in AP Human Geography.
What should be in your AP Human Geography Unit 3 study guide?
A strong AP Human Geography Unit 3 study guide should help you understand cultural patterns clearly rather than overwhelm you with long vocabulary lists. The best guides explain how culture spreads, how identity is formed, and how cultural traits influence space. You want a resource that breaks down processes such as diffusion, cultural convergence, and cultural landscapes, allowing you to apply them to real-world regions. A structured tool like UWorld helps because its explanations connect each idea to the logic behind cultural patterns, making your AP Human Geography Unit 3 review easier to manage.
A high-quality AP Human Geography Unit 3 study guide should include:
- Clear explanations of diffusion types and cultural change
- Maps that show language, religion, and ethnicity distributions
- Examples of cultural convergence and divergence
- Charts comparing folk culture and popular culture
- Spatial analysis prompts that build reasoning for FRQs
- Concept checks to reinforce understanding as you go
When your study guide emphasizes reasoning over memorizing, the unit becomes far more intuitive. You begin to recognize why certain cultural traits spread quickly while others remain localized, and you see how cultural identity influences political boundaries and settlement patterns. This prepares you well for FRQs and MCQs that require spatial thinking rather than definition recall.
Can I find practice tests specifically for AP HUG Unit 3?
Yes, you can find practice tests focused specifically on Unit 3, and using them helps you understand how the exam tests cultural processes. These practice tests train you to interpret maps, identify diffusion patterns, and analyze cultural change across regions. They also help you build confidence for AP Human Geo Unit 3 practice test items that require careful reasoning. UWorld offers realistic practice questions with detailed explanations that walk you through the logic behind cultural patterns.
A good Unit 3 practice test should include:
- MCQs analyzing language, religion, and ethnicity maps
- Items comparing cultural convergence and divergence
- Questions testing diffusion patterns and spatial impacts
- Real-world examples involving cultural conflict or integration
- FRQ-style prompts that require reasoning and explanation
- Explanations that strengthen spatial interpretation skills
As you practice across these formats, you begin to recognize the patterns AP HUG uses repeatedly. You learn to identify which diffusion type matches a scenario, how cultural traits spread differently in folk and popular cultures, and how identity influences spatial organization. This makes the Unit 3 practice test and classroom assessments feel more predictable, boosting both accuracy and confidence.
How can I prepare for the Unit 3 progress check in AP Classroom?
Preparing for the AP Human Geography Unit 3 progress check requires a clear understanding of cultural diffusion, cultural landscapes, language patterns, and the forces that shape cultural identity. Progress check MCQs emphasize map interpretation and conceptual reasoning, so your first step is to review cultural processes and study how they appear spatially. Practice analyzing maps that show religion distributions, language families, or ethnicity clusters. After reviewing core concepts, work through AP style practice questions to build familiarity with the format.
UWorld offers a check for understanding experience similar to AP Classroom, helping you practice the exact style of reasoning expected on the Unit 3 progress check for MCQs on the AP HUG. The explanations demonstrate why the correct answer is effective and why other options are ineffective, which helps to strengthen your interpretation skills.
When reviewing, focus on understanding why a cultural trait spreads in one way and not another, and make sure you can explain how cultural patterns create spatial variation. Once you feel comfortable identifying diffusion types and interpreting cultural maps, the progress check becomes much easier to navigate. Consistent practice builds confidence and prepares you well for both classroom assessments and the final AP exam.
How do I stay organized while studying AP Human Geography Unit 3?
Organization matters a great deal in Unit 3 because cultural concepts connect across maps, regions, and patterns that can be confusing without a clear structure. You will see terms like diffusion, ethnic identity, cultural landscapes, and language families appear repeatedly, and without a clear system, it becomes hard to keep everything straight. A structured review method helps you understand how these pieces fit together. Using logical explanations from a resource like UWorld supports this because you learn why cultural patterns form rather than trying to memorize every detail.
A strong organizational system includes:
- Grouping vocabulary by theme, such as diffusion, culture regions, or identity
- Creating map collections showing language, religion, and ethnicity patterns
- Using comparison charts for folk vs popular culture
- Keeping a dedicated notebook page for diffusion examples
- Reviewing concepts with a small set of AP Human Geography Unit 3 MCQ items
- Revisiting complex topics regularly rather than all at once
Once you organize Unit 3 this way, the material becomes easier to understand. You start noticing patterns across cultures and regions and can explain why certain traits spread while others stay localized. Strong organization also helps you prepare for the AP Human Geo Unit 3 practice test questions because you already understand how cultural processes build on each other.
How can I study effectively for AP Human Geography Unit 3 MCQs?
Studying effectively for Unit 3 MCQs means understanding how cultural patterns work rather than trying to memorize long lists of facts. Most multiple-choice questions test your ability to interpret maps, identify diffusion types, analyze cultural processes, and understand how traits spread across space. To succeed, you need to connect the concepts, not just recall definitions. Using a structured resource like UWorld helps you build the reasoning skills these questions require because explanations show why one choice fits the spatial pattern and why the others fail.
A strong MCQ study strategy includes:
- Reviewing diffusion patterns and identifying real examples of each type
- Practicing map interpretation involving language, religion, and ethnicity
- Analyzing cultural landscapes and spatial relationships
- Eliminating answers by spotting inconsistencies in spatial logic
- Practicing AP Human Geo Unit 3 multiple-choice questions regularly
- Reviewing incorrect answers to understand your reasoning errors
As you build these habits, MCQs become more predictable. You learn to recognize cultural convergence and divergence, interpret regional cultural data efficiently, and identify the type of diffusion that best matches a scenario. The more you practice with explanation-driven questions, the easier it becomes to break down complex cultural maps and identify meaningful patterns. This leads to stronger performance on the AP Human Geography Unit 3 MCQ section, progress checks, and the overall exam.
Can I study AP Human Geography Unit 3 offline if I need to?
Yes, you can study AP Human Geography Unit 3 offline, which makes it easier to stay consistent even when you do not have internet access. Offline study works particularly well for this unit because many cultural concepts can be reviewed through maps, short notes, and pattern recognition exercises. UWorld allows you to download question sets, so you can practice AP Human Geo Unit 3 practice test items and review explanations without needing a connection. This flexibility helps you study during commutes, downtime, or anywhere WiFi is limited.
Once you reconnect, the UWorld mobile app syncs your progress, keeping your learning data up to date. You can pair offline practice with printed cultural maps, vocabulary lists, or your own summaries of diffusion, religion patterns, or language families. This combined approach sharpens your ability to recognize spatial patterns and strengthens long-term retention. With offline access, you can maintain momentum, avoid gaps in study time, and stay prepared for AP Human Geography Unit 3 test questions and classroom assessments. It ensures that you continue to build confidence and understanding, no matter where you are.
Learn More About Specific Unit
Thinking Geographically
Population and Migration Patterns and Processes
Political Patterns and Processes
Agriculture and Rural Land-Use Patterns and Processes
Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes
Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes