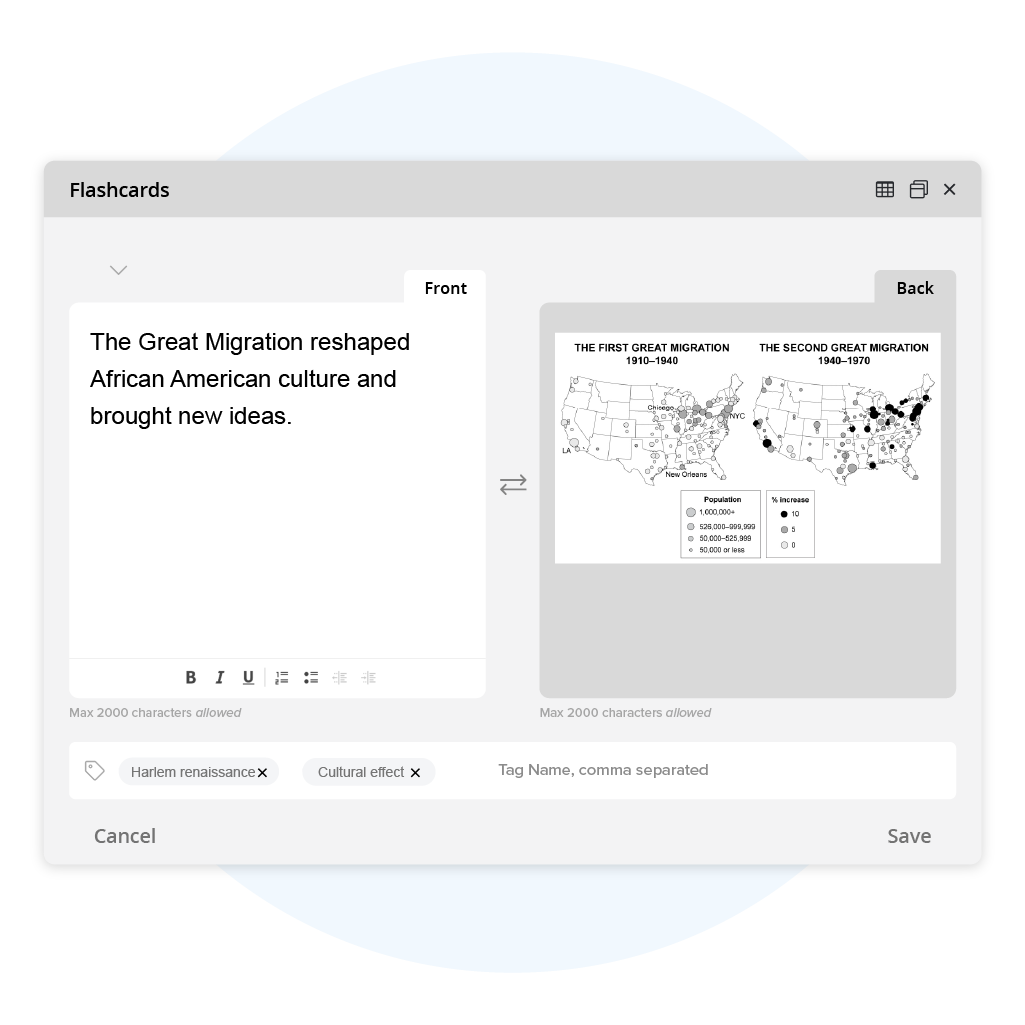
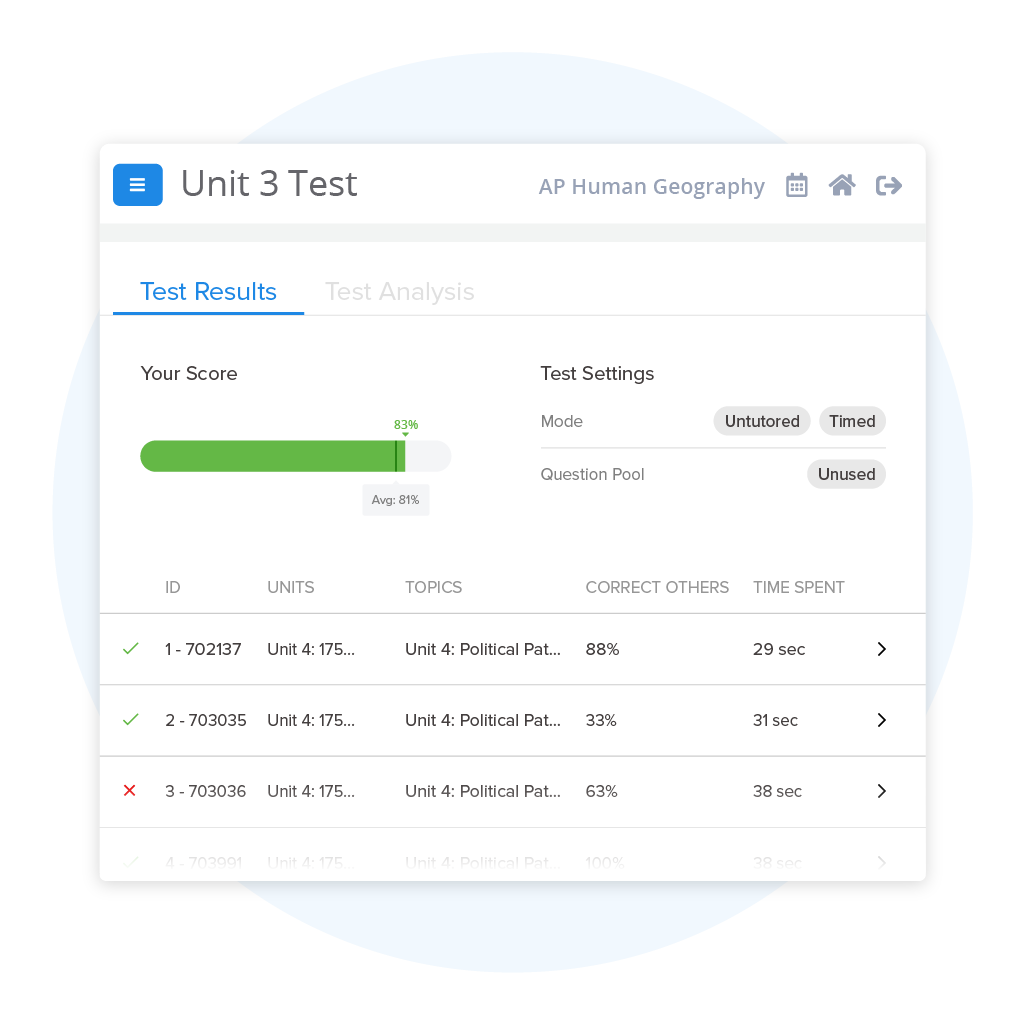
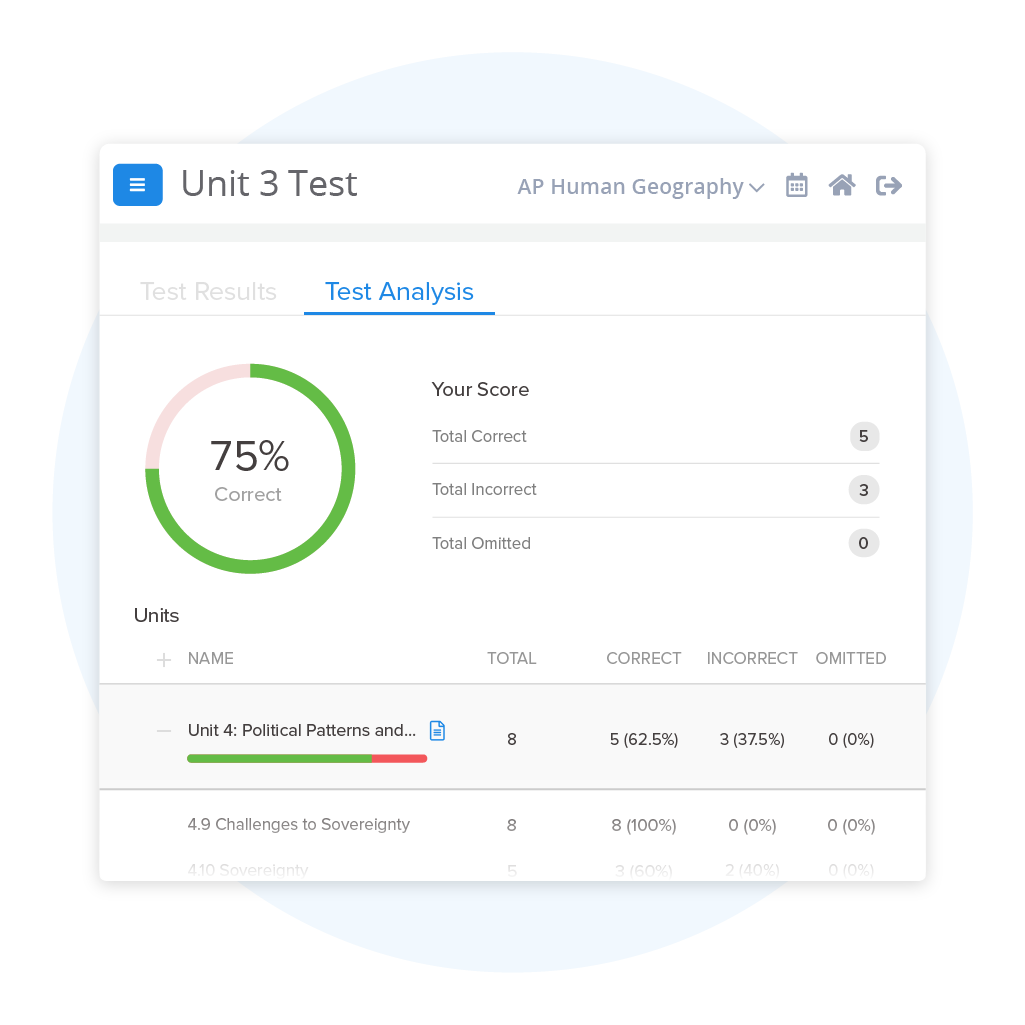
AP® Human Geography Practice Tests & Questions
Master the AP® Human Geography exam with 300+ AP Human Geo multiple-choice and FRQ practice questions written by expert educators. Create unlimited quizzes and full-length practice tests by topic to strengthen your skills.
Every question includes detailed explanations, visuals, and progress tracking to help you study efficiently, learn faster, and score higher on exam day.
Try These Free AP Human Geography Practice Test Questions
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Thinking Geographically
Question
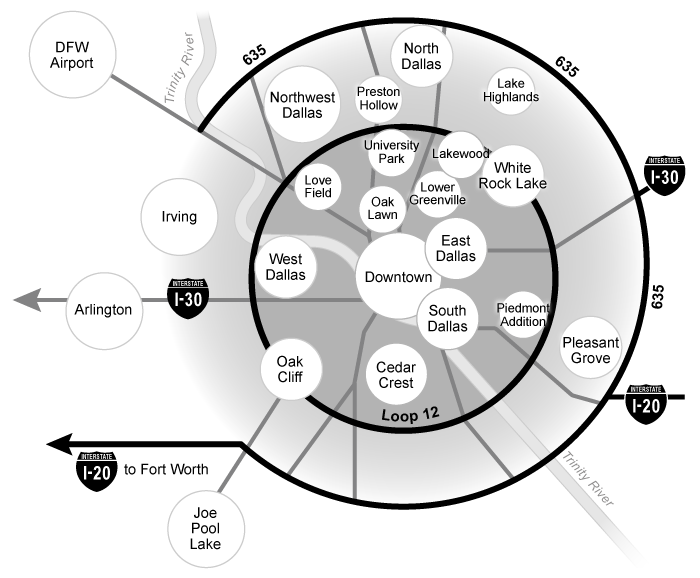
Which of the following best describes the spatial pattern represented on the map?
| A. Relative locations based on personal perceptions | |
| B. Contour lines illustrating elevation | |
| C. Absolute locations determined by GPS | |
| D. Concentrations of urban populations | |
| E. Voting precincts by congressional district |
Explanation
Locations on maps can be either absolute or relative. Absolute location are fixed points on the earth, relative locations are affected by distance, accessibility, and connectivity. Locations on a map may be placed relative to other locations and may not represent a precise point on the landscape.
All mental maps present relative locations because they are based on personal perceptions of spatial relationships. They illustrate how people organize and make sense of the space around them.
On the mental map of Dallas above, the placement of the circles represents relative locations. For example, the map shows that Irving is roughly northwest of downtown and farther from downtown than Oak Lawn. However, the location and distances are relative, and the map does not provide absolute locations and distances.
(Choice B) The map above lacks contour lines, which are used in topographic maps to illustrate elevation and relief.
(Choice C) Mental maps are based on relative locations and do not include absolute locations determined by GPS.
(Choice D) The circles in the map reflect the mapmaker’s interpretation of a location, not its population. For example, the circle representing Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport is bigger than the circle representing South Dallas.
(Choice E) The mental map shows the relative locations of places in the greater Dallas area and doesn’t include voting precincts by congressional district.
Things to remember:
Mental maps are based on personal perceptions of spatial relationships and illustrate relative locations.
Passage:
Question
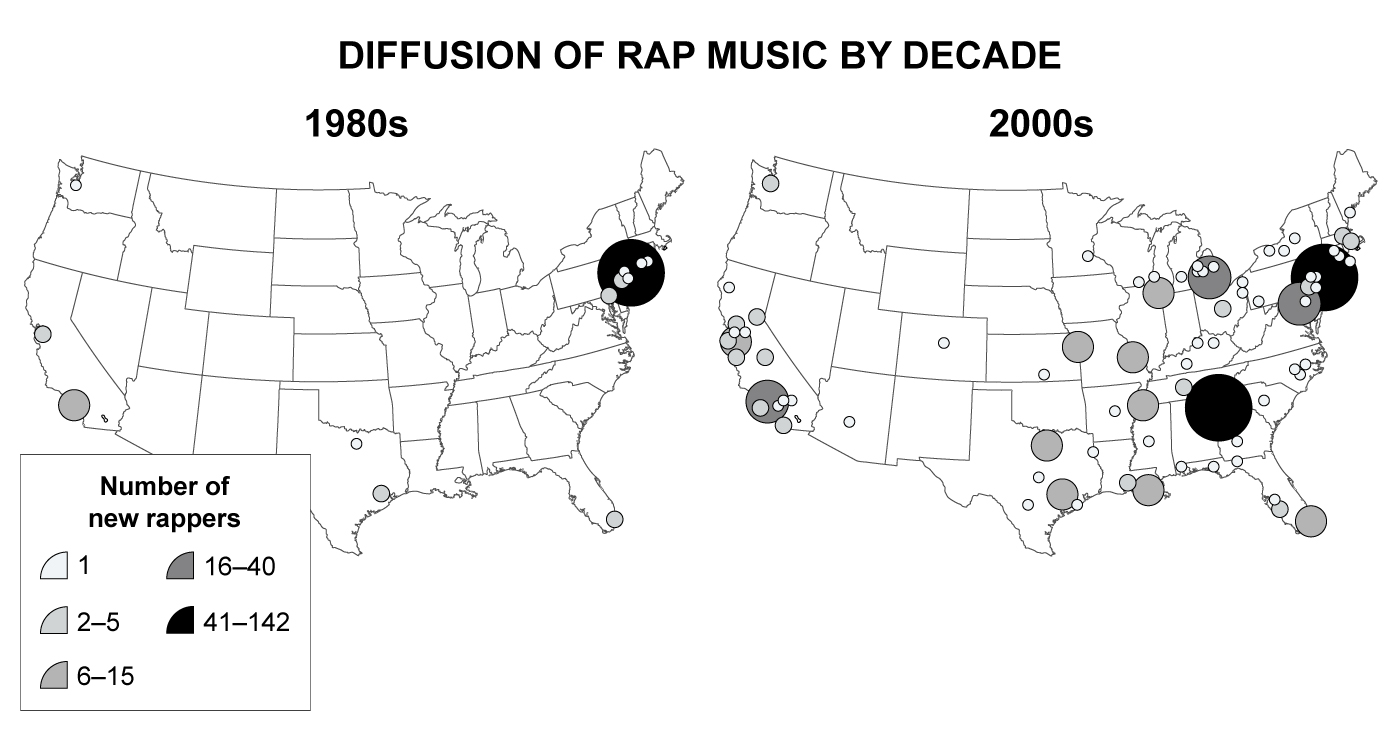
The maps shown above are best described as which of the following?
| A. Isoline | |
| B. Topographic | |
| C. Thematic | |
| D. Regional | |
| E. Reference |
Explanation
Geographers use thematic maps to show distributions of social patterns, trends, or behaviors, such as population distribution or voting turnout. Thematic maps reveal stories, typically showing the degree and movement of an attribute or phenomenon in a geographic location.
The maps above depict the development and spread of rap music across the US between 1980 and 2009. Cultural geographers can use such maps to obtain clues about the innovation and diffusion of the rap genre.
(Choice A) Isoline maps use lines to connect data points of the same values; the maps above do not contain these lines.
(Choice B) Topographic maps show the contours of a physical landscape, which is not shown on the maps above.
(Choice D) The maps present data at the national level, not by region.
(Choice E) The maps are not reference maps because it is not possible to determine absolute distances between locations on these maps.
Things to remember:
Thematic maps reveal stories, typically showing the movement and degree of an attribute or phenomenon in a geographic location.
Question
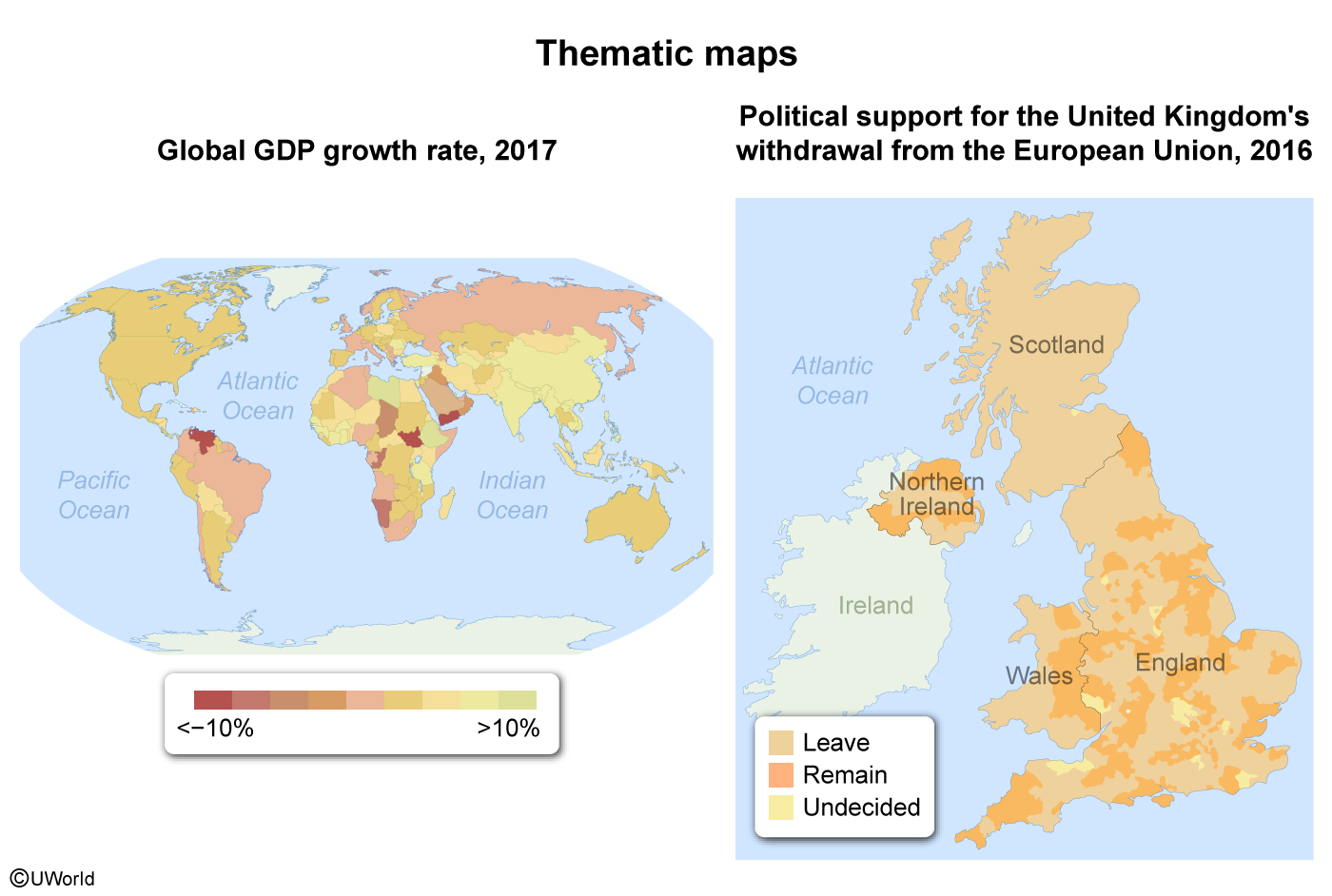
Which of the following is true of a thematic map?
| A. It locates objects relative to a known reference point | |
| B. It is a spatial illustration of specific data | |
| C. It is most useful at the local level | |
| D. It is increasingly used in Global Positioning System navigation | |
| E. It has a large amount of distortion due to the curvature of the Earth |
Explanation
Thematic maps are spatial distributions of specific data, such as economic development or people's political leanings. For example, the map on the left uses data ranges to illustrate increases in gross domestic product worldwide and shows where economic development is occurring the fastest. The map of the United Kingdom on the right illustrates where popular support for leaving the European Union was concentrated in 2016.
(Choice A) Reference maps, not thematic maps, express spatial relationships between objects and known reference points.
(Choice C) Thematic maps are equally useful for local, regional, national, and global scales of analysis.
(Choice D) Global Positioning System navigation relies on absolute locations. It does not use thematic maps, which are spatial illustrations of specific data.
(Choice E) World maps have a large amount of distortion due to the curvature of the Earth. This is not a limitation of thematic maps.
Things to remember:
Thematic maps show the distribution of specific phenomena or observable facts across geographic space.
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Population and Migration Patterns and Processes
Question
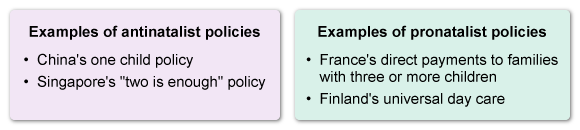
Which of the following is the best example of an antinatalist policy?
| A. Financial assistance for large families | |
| B. Subsidized childcare | |
| C. Restrictions on family size | |
| D. Tax credit for dependent children | |
| E. Extended maternity leave |
Explanation
In the 1960s, the world's natural increase rate peaked at over 2%, and the global population surpassed three billion people. In the following decades, countries such as China and Singapore enacted antinatalist policies, which discouraged large families. The governments in these countries placed restrictions on family size aimed at lowering birth rates and slowing population growth.
China's One-Child policy placed a one-child limit on about half its population between 1979 and 2015. The result was a drastic drop in the birth rate, which, combined with high life expectancy, created an aging population, a high dependency ratio, and a smaller workforce.
(Choices A, B, D, and E) Financial assistance for large families, subsidized childcare, tax credit for dependent children, and extended maternity leave are examples of pronatalist, rather than antinatalist, policies. These policies are intended to remove economic and cultural obstacles to having children.
Things to remember:
Antinatalist policies aim to slow population growth primarily by placing restrictions on family size.
Question
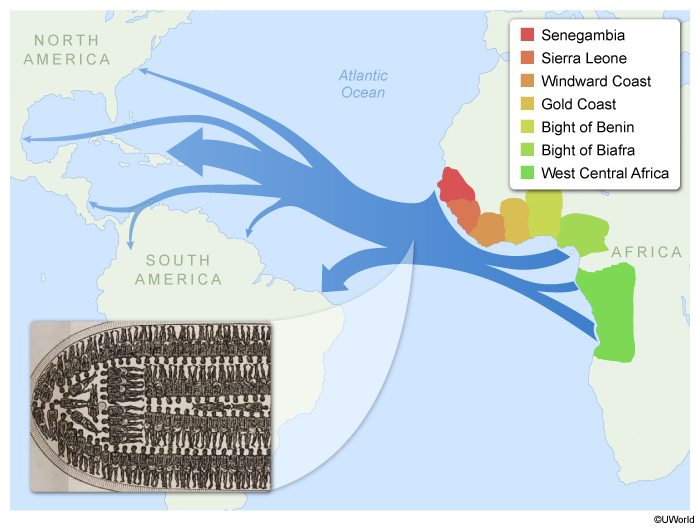
Which of the following is the best example of forced migration?
| A. The Puritan colonization of New England | |
| B. The Bantu migration across sub-Saharan Africa | |
| C. The Italian emigrations to South America | |
| D. The journey through the Middle Passage | |
| E. The African American colonization of Liberia |
Explanation
Forced migrations differ from voluntary migrations in that the migrants usually have no other alternatives except death or imprisonment. A notable example of forced migration is the Transatlantic Slave Trade.
From the 1500s to the 1800s, Europeans transported nearly 15 million enslaved Africans across the Atlantic. During the weeks-long journey by the route known as the Middle Passage, thousands were chained together lying on their backs in specially designed slave ships, and many died before reaching the Americas.
(Choice A) Although the Puritans who colonized New England sought to practice their religion without government interference, they could have stayed in England and practiced in secret. Therefore, the Puritan colonization of New England was not considered a forced migration.
(Choice B) Various push/pull factors influenced the hundreds of years Bantu migrations across sub-Saharan Africa. However, it wasn't a forced migration.
(Choice C) In the 19th century, some South American countries, such as Argentina and Brazil, offered incentives to Italians to emigrate, so this wasn’t a forced migration.
(Choice E) In the early 19th century, the American Colonization Society colonized Liberia. Some African Americans choose to emigrate there as an alternative to racism in the US. These efforts represent a voluntary migration.
Things to remember:
In forced migrations, people face either death or imprisonment and therefore must migrate.
The Transatlantic Slave Trade is an example of forced migration because, for the enslaved, the only other option was death.
Question
In the 1880s, Chinese migrants left the United States for Mexico. Which of the following was the primary push factor for this voluntary migration?
| A. Demographic factors | |
| B. Economic factors | |
| C. Environmental factors | |
| D. Military force | |
| E. Social programs |
Explanation
Beginning in the 1850s, Chinese immigrants came to the US during the California Gold Rush to mine gold and build the Transcontinental Railroad. These immigrants often worked longer hours for less pay than American workers, which caused tensions between the two groups.
Beginning in the 1860s, the US government passed laws restricting Chinese immigrants' ability to earn money. When a financial panic hit the US in 1873, tensions escalated further as American workers blamed the Chinese for the depression. This resulted in the Chinese Exclusion Act, which banned Chinese immigration to the US.
In the 1880s, with the encouragement of the Mexican government and economic restrictions serving as push factors, Chinese immigrants migrated south to Mexico decrease.
(Choice A) Demographic factors, such as age, education, and location, weren't push factors for Chinese immigration to Mexico.
(Choice C) Environmental factors, such as natural disasters, didn't encourage Chinese immigration to Mexico.
(Choice D) The US didn't use the military to force Chinese immigration to Mexico.
(Choice E) Social programs, such as health care and welfare programs, weren't push factors for Chinese migrants to Mexico.
Things to remember:
Economic restrictions limiting Chinese immigration to the US served as push factors, encouraging migration from the US to Mexico.
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Cultural Patterns and Processes
Question
The examination of a culture based solely on that culture's distinctive standards is known as
| A. Cultural convergence | |
| B. Cultural divergence | |
| C. Cultural relativism | |
| D. Cultural diffusion | |
| E. Cultural ecology |
Explanation
Whaling is a controversial practice condemned by many developed nations, especially in the West. However, whaling is a traditional practice that is central to the diets, economies, and cultures of many indigenous peoples.
Cultural relativism looks to understand behaviors within the context of a society's unique cultural norms and is the examination of a culture based solely on its distinctive standards. Cultural relativism has led to exceptions to the international laws that ban whaling, such as granting these peoples limited, noncommercial whaling rights.
(Choices A and B) Cultural convergence and cultural divergence are processes that make cultures more similar or dissimilar, respectively, over time.
(Choice D) Cultural diffusion is the spread of a cultural element from its place of origin to a wider area.
(Choice E) Cultural ecology examines the relationship between humans and their environment and is not based solely on a particular culture's distinctive standards.
Things to remember:
Cultural relativism is the examination of a culture based solely on its distinctive standards.
Question
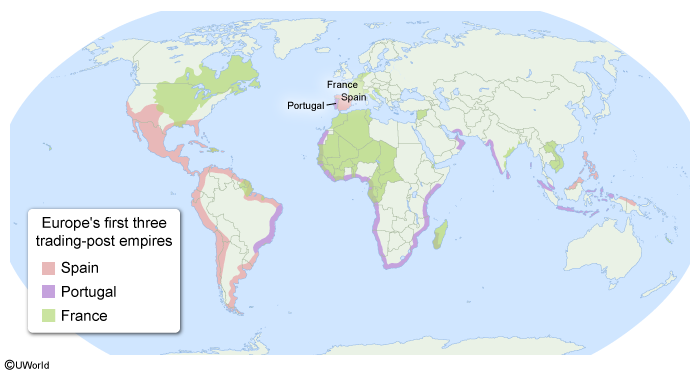
Historically, Carnival has been a Catholic celebration that originated in Europe during the Middle Ages. Today, there are annual celebrations in North America, South America, the Caribbean, Africa, and India. As a result, the spread of Carnival is a good example of which of the following processes?
| A. Colonialism | |
| B. Gentrification | |
| C. Industrialization | |
| D. Suburbanization | |
| E. Independent invention |
Explanation
Carnival, a Roman Catholic festival that originated in Europe, has been celebrated in Catholic countries such as Spain, Portugal, and France since the Middle Ages. During the Age of Exploration, European countries colonized territories in North and South America, the Caribbean, Africa, and Asia. As a result of colonialism, aspects of European culture diffused across the world.
Spain, France, and Portugal spread Catholicism and its traditions, including Carnival. In some countries, such as Brazil, Catholic traditions mixed with African celebrations that had spread through the trans-Atlantic slave trade, a central element of colonialism in the Americas.
(Choices B, C, and D) Gentrification, industrialization, and suburbanization are not responsible for spreading cultural traits such as Carnival across the world.
(Choice E) Independent invention is the opposite of diffusion.
Things to remember:
As a result of colonialism, aspects of European culture diffused across the world. Spain, France, and Portugal spread Catholicism and its traditions, including Carnival, which is still celebrated in many of their former colonies.
Question
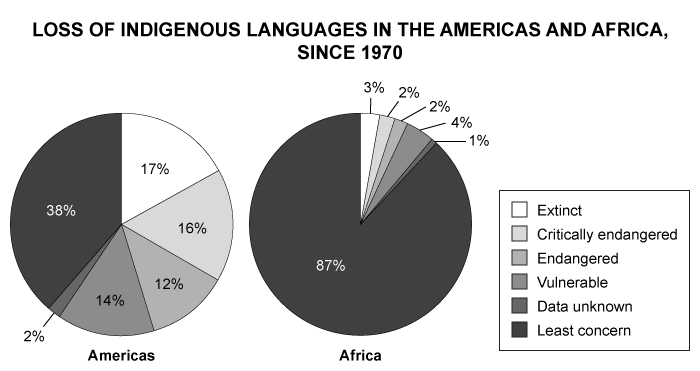
Which of the following is a primary reason for the loss of indigenous languages in the Americas and Africa since 1970?
| A. Communication technologies have accelerated interactions among people | |
| B. Widespread governmental efforts to assimilate indigenous peoples | |
| C. Decolonization accelerated the loss of indigenous languages | |
| D. Globalization has increased distance decay | |
| E. A decrease in the use of English as a worldwide lingua franca |
Explanation
Over the past 50 years, globalization has eroded native cultures. Since the 1970s, television and radio viewership has increased among indigenous peoples in Africa and the Americas, connecting them with the rest of the world. In addition, digital communication technologies, such as cell phones and the internet, have connected isolated indigenous cultures in Africa and the Americas with other cultures worldwide.
Television, radio, and digital communications have accelerated interactions with indigenous peoples and increased the use of English. This has increased cultural convergence, reshaping once-isolated cultures and contributing to the loss of indigenous languages.
(Choice B) In the 19th and early 20th centuries, governmental efforts to assimilate indigenous peoples, such as the creation and upkeep of Indian Boarding Schools, were common in North America.
(Choice C) The decolonization of Africa has helped to temporarily preserve indigenous languages.
(Choice D) Globalization has decreased, not increased, distance decay.
(Choice E) The increase, not decrease, in the use of English as a worldwide lingua franca has caused the loss of indigenous languages in the Americas and Africa since the 1970s.
Things to remember:
Television, radio, and digital communications have accelerated interactions with indigenous peoples, increasing the use of English and contributing to the loss of indigenous languages.
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Political Patterns and Processes
Question
Which of the following was an important social effect of the colonial partition of Africa?
| A. Europeans broadly adopted African art styles and cultural norms | |
| B. European conflicts in Africa rarely targeted African communities | |
| C. Ethnocentrism dramatically decreased in urban areas across Europe | |
| D. Native Africans often lost their cultural and economic connections to traditional lands | |
| E. African leaders increased their power through Europeans' direct rule over Africans |
Explanation
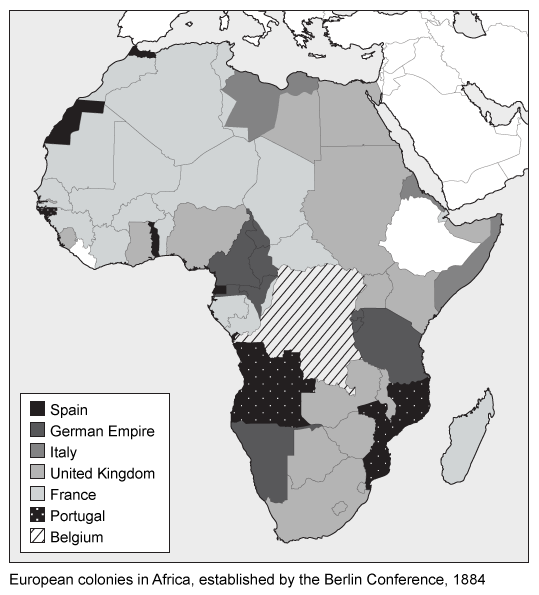
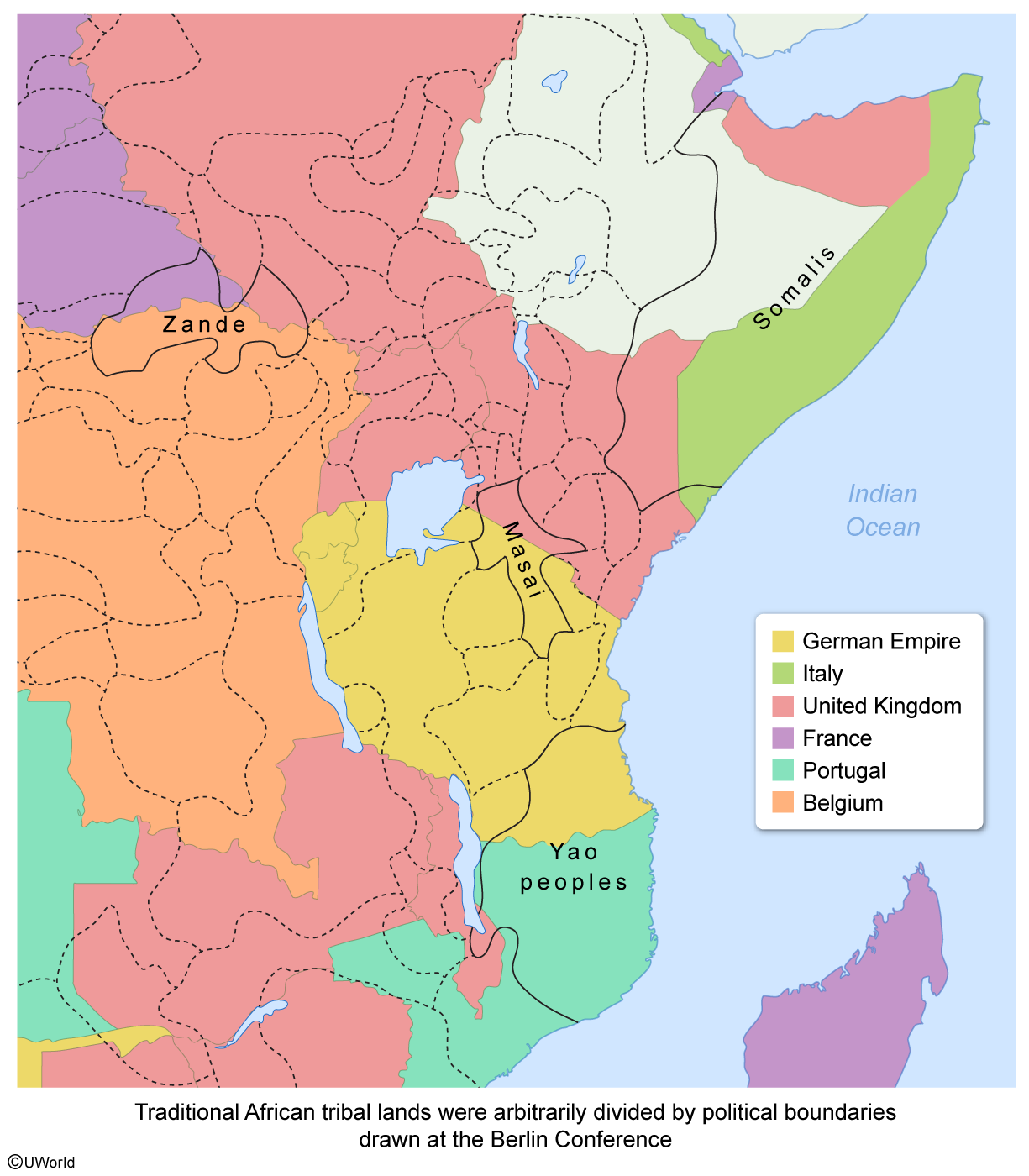
Without consulting African tribal leaders, members of the Berlin Conference arbitrarily established political boundaries across the continent. The new boundaries frequently cut through traditional tribal lands and often divided cultural connections between villages and the economic connections Africans had with their lands.
Culturally, some Zande subjects in the Belgian Congo may have had family members in territories claimed by either France or the United Kingdom. Also, the destruction of Africans' territoriality can be seen in how the Yao peoples were divided between German East Africa and the Portuguese territories.
Economically, nomadic pastoralists like the Masai and Somalis were made vulnerable by boundary changes. Seasonal rainfalls determined their movements, making their herds reliant on different grazing pastures throughout the year. Cut off from important pastures, such groups' nomadic cycles were completely disrupted, which threatened their economic survival.
(Choice A) African cultural norms and styles of African art weren’t broadly adopted in Europe.
(Choice B) Europeans frequently targeted African communities to seize control of African territories.
(Choice C) At the time of the Berlin Conference, most of Europe remained ethnocentric.
(Choice E) Europeans’ use of direct rule decreased, not increased, the power of African leaders.
Things to remember:
The Berlin Conference arbitrarily made political boundaries in Africa that often sliced through traditional tribal lands, dividing cultural connections between villages and economic connections that Africans had with their lands.
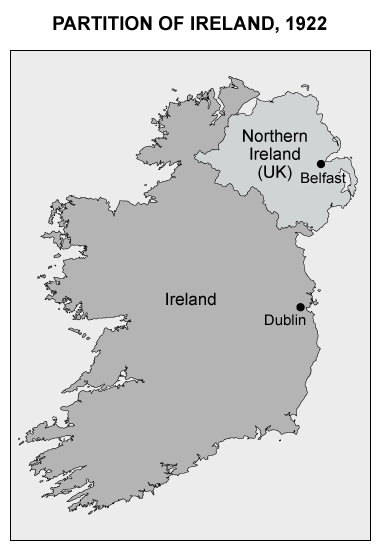
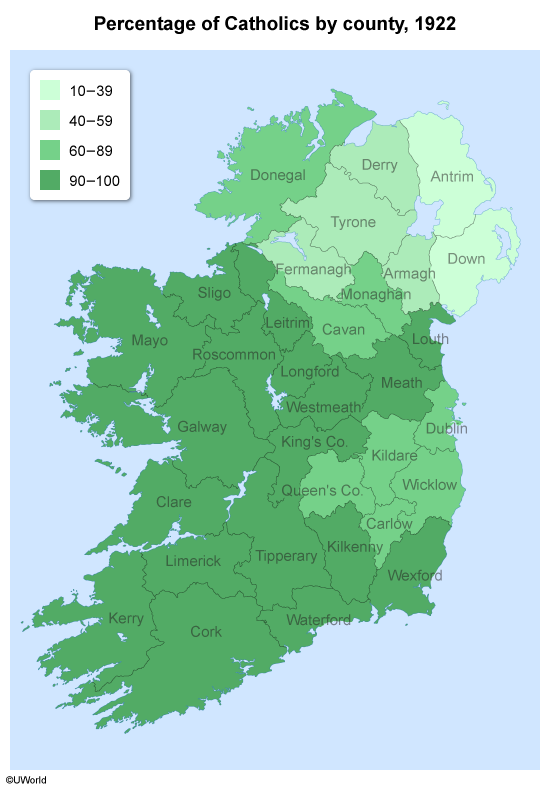
Question
In 1922, after years of conflict, the country of Ireland was partitioned into two territories, Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. A major centrifugal force behind this partition was
| A. economic depression | |
| B. ethnic separatism | |
| C. the Irish Potato Famine | |
| D. neocolonialism | |
| E. religious division |
Explanation
A centrifugal force is a social or cultural force that divides a state. For Ireland, the major centrifugal force behind its partition was religious division. The push in Ireland for independence began as a political movement and became a religious fight in the 16th century, when Britain embraced Protestantism and the Irish remained predominantly Catholic.
The Catholic majority in Ireland, located mostly in the south, demanded a split from the United Kingdom. However, the Protestant minority, located mostly in the north, fought to remain part of the United Kingdom. In 1922, Ireland was divided into two territories:
- Southern Ireland became the Irish Free State and later the Republic of Ireland.
- Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom.
(Choice A) An economic depression is a dramatic economic downturn characterized by a sharp decline in growth, employment, and production. This was not a centrifugal force behind Ireland’s partition.
(Choice B) Ethnic separatism is the process by which an ethnic group that doesn't identify with other groups within a state seeks to form its own independent state. Ireland’s division was based on religious, not ethnic, grounds.
(Choice C) The Irish Potato Famine began in the 1840s and did not contribute to the partition of Ireland in 1922.
(Choice D) Neocolonialism is the establishment of economic and political practices that indirectly influence less powerful nations, especially former colonial territories. It was not practiced in Ireland.
Things to remember:
In 1922, religions division between Catholics and Protestants was the centrifugal force that divided Ireland into two territories.
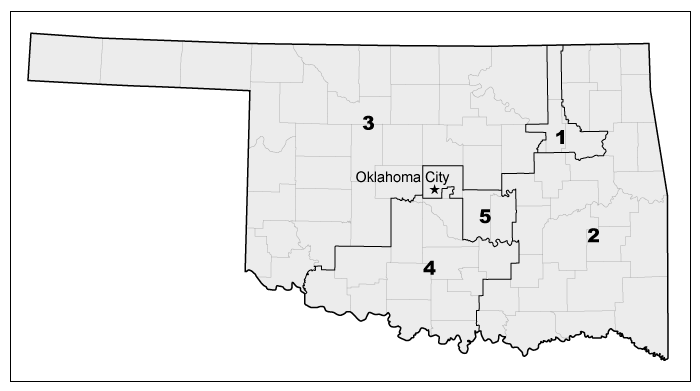
Question
The altering of a voting district boundary by one political party to produce favorable election results is known as
| A. territoriality | |
| B. voter suppression | |
| C. gerrymandering | |
| D. blockbusting | |
| E. apartheid |
Explanation
After census data is collected every ten years in the US, congressional and state voting districts are redrawn to reflect changes in population. The state legislatures are tasked with redrawing districts to make sure they have roughly the same number of voters.
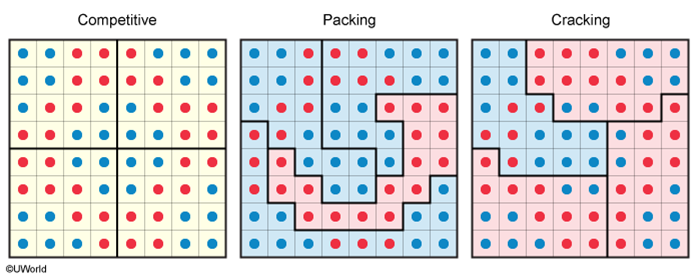
To gain a political advantage, boundaries are often redrawn to favor one party over another; this process is known as gerrymandering. Gerrymandering usually takes two forms:
- Packing groups like-minded voters together to reduce their voting power in another district.
- Cracking spreads like-minded voters apart to dilute their voting power.
Despite the US Supreme Court ruling gerrymandering illegal in 1985, the practice persists, and legal challenges to gerrymandering occur every decade.
(Choice A) Territoriality is a people's attachment to an area of land and its culture. It has no effect on voting district boundaries.
(Choice B) Voter suppression is an effect, rather than a cause, of gerrymandering.
(Choice D) Blockbusting occurs when real estate agents instill in homeowners the fear that their communities are increasingly endangered by an ongoing and increasing influx of people of color. This is unrelated to voting district boundaries.
(Choice E) Apartheid was the brutal policy of segregation of Blacks in South Africa; it didn't affect redrawing voting district boundaries in the US.
Things to remember:
Gerrymandering is the process of redrawing boundaries to give one political party advantage over another. Gerrymandering usually takes two forms: packing and cracking.
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Agricultural and Rural Land-Use Patterns and Processes
Question
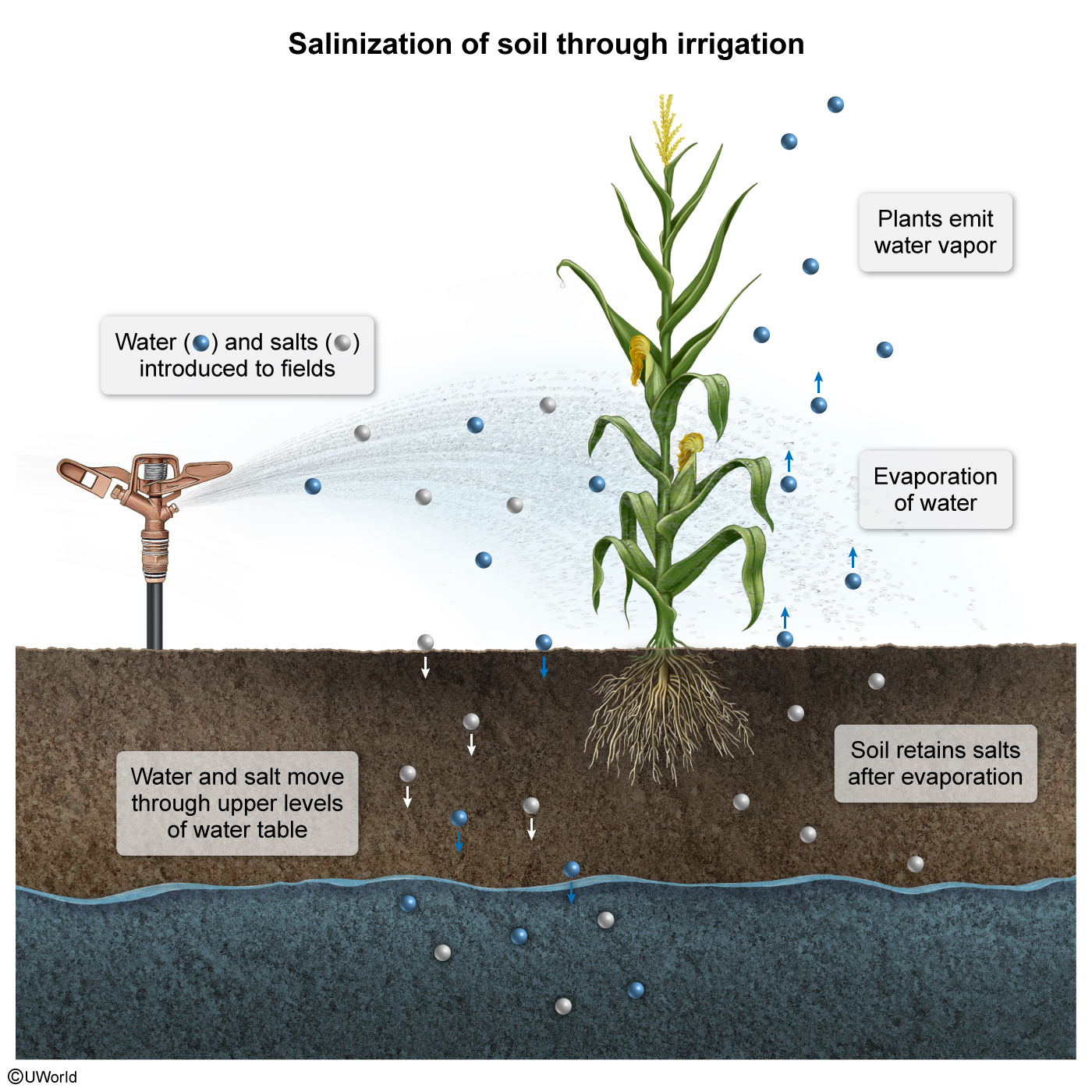
Which of the following best describes an effect of irrigation?
| A. Land cover change | |
| B. Acid precipitation | |
| C. Monoculture | |
| D. Soil salinization | |
| E. No-tillage cultivation |
Explanation
Irrigation systems contribute to the growth of crops by drawing water from environmental sources, such as rivers and reservoirs. In those waters are sediments composed of various minerals, including salt. When fields are irrigated and the water evaporates, the salt is left behind in the soil. Therefore, one effect that irrigation has on the environment is increased soil salinization.
Soil salinization decreases fertility because the high salt content reduces plants' ability to absorb water from the ground. To prevent this, farmers must carefully monitor the irrigation of their fields and periodically test the soil for salinity (salt content).
(Choice A) Irrigation tends to extend or preserve agricultural areas. Therefore, it is unlikely to contribute to land cover change, in which agricultural lands are lost to the growth of urban areas.
(Choice B) Acid precipitation is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide mixing with atmospheric moisture, not water from irrigation.
(Choices C and E) The irrigation of crops has little influence on whether farmers practice monoculture or no-tillage cultivation.
Things to remember:
One adverse effect of irrigation on the environment is increased soil salinization, which reduces the ability of plants to absorb water.
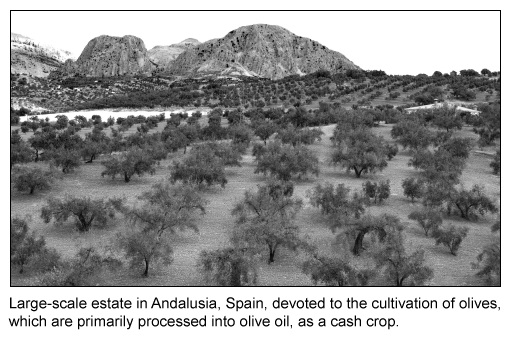
Question
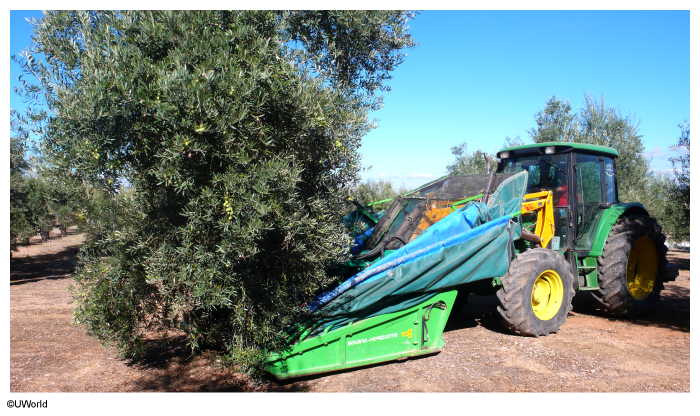
Which factor is most responsible for the large-scale cultivation of Spanish olives shown in the picture above?
| A. A decrease in Spain's dependence on olive oil exports | |
| B. An improvement in harvesting technologies | |
| C. An increase in the salinity of Spanish soils | |
| D. The United States' increased tariffs on Spanish olive oil | |
| E. The reterritorialization of Spanish olives |
Explanation
Mechanization has permitted the expansion of both businesses and economies. In the olive industry, improvements in harvesting technologies increase efficiency and eliminate the cost of harvesting by hand, which is the highest cost in olive production worldwide.
By mechanizing their harvests, Spain's olive growers can expand by buying more land on which to grow olives. This process increases olive producers' economies of scale, a factor that permits the large-scale cultivation of olives worldwide.
(Choice A) Spain exports nearly 50% of the world's olive oil, which has increased the country's dependence on its olive production.
(Choice C) Soil salinization is known to hinder the growth of plants, including olives, so increasing soil salinity would typically prevent the emergence of large-scale olive plantations.
(Choice D) US import tariffs on Spanish olive oil likely restrict the large-scale cultivation of Spanish olives.
(Choice E) Olive production has been a part of this region's culture for thousands of years, so reterritorialization doesn't apply to Spanish olives.
Things to remember:
In the olive industry, mechanical harvesters increase efficiency and eliminate the cost of hand harvesting. This allows Spain's olive growers to expand by buying more land, which increases olive producers' economies of scale.
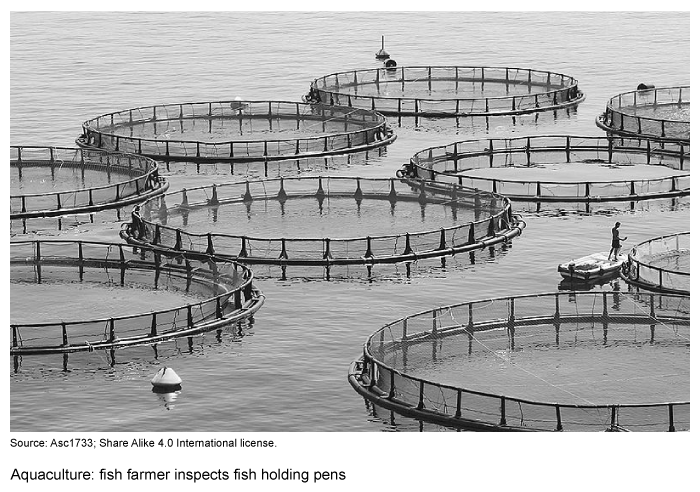
Question
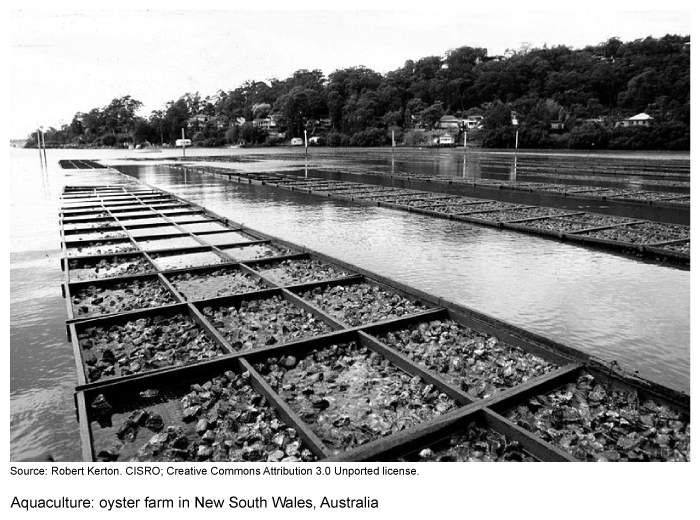
Which of the following statements best describes the effects of aquaculture on developing nations?
| A. Since aquaculture accounts for a small percentage of total food production, the economies of developing countries will likely not change | |
| B. Through the fair trade of cultured fish in international markets, the economies of developing nations will likely improve | |
| C. Owing to the large differences in food distribution systems, the economies of developing nations will likely decline | |
| D. Because of aquaculture's positive effects on the oxygen cycle, the economies of developing nations will likely improve | |
| E. Because of the global trend away from primary economic activities, the economies of developing nations will likely decline |
Explanation
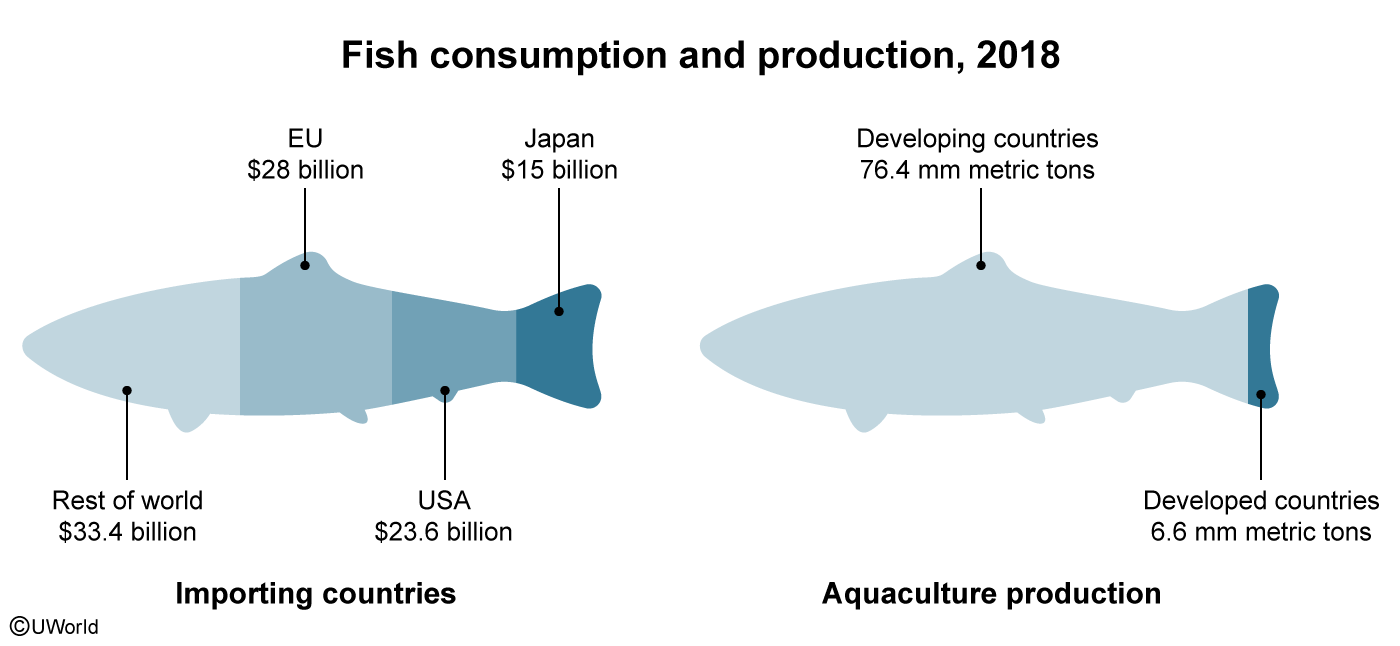
In 2019, the nearly $285 billion aquaculture industry accounted for over 50% of the fish consumed worldwide. Developed nations such as Japan, the US, and European states import the majority of farmed and captured fish harvests—most of which come from aquaculture in the developing world.
To boost their economies, developing nations—which are responsible for 90% of worldwide aquacultural production—pursue fair trade deals to ensure the best prices for their fish farmers. Considering the industry's value and the percentage produced by developing nations, the fair trade of cultured (farm-raised) fish in international markets will likely improve developing nations' economies.
(Choice A) Developing countries account for over 90% of cultured fish consumed worldwide, which helps improve their economies.
(Choice C) Farmers in developing nations sell their fish harvests wholesale and aren't a part of the distribution process.
(Choice D) Aquaculture generally has negative, not positive, effects on the oxygen cycle. These include increased biochemical oxygen demand and undesirable levels of dissolved oxygen in marine ecosystems.
(Choice E) Because primary economic activities are the base source of food for global populations, there isn't a global trend to turn away from activities like aquaculture.
Things to remember:
Accounting for roughly 90% of all aquacultural production, developing nations' economies will likely improve through the fair trade of cultured (farm-raised) fish that they export in international markets.
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes
Question
An argument cited by critics of urban developments like those in the photograph is that they
| A. decrease a city's housing options | |
| B. are not sustainable developments | |
| C. increase urban sprawl | |
| D. diminish historical character in communities | |
| E. decrease a community's tax base |
Explanation
Urban development increases the diversity of housing options and reduces urban sprawl. However, critics of urban design initiatives have identified drawbacks in developments such as infills. One common criticism is that the designs of modern infills diminish historical character in communities.
The buildings on the right side of this Brooklyn, New York, photograph have architectural designs dating from earlier eras, some to the late 1800s. Some critics, including historians and architects, argue that the designs of modern infills diminish a neighborhood's beauty and should not be near historical architecture.
(Choices A and E) Infills that become residential dwellings help increase a city's housing options. As a result, infills also help expand the local tax base.
(Choices B and C) Since infills make use of land that requires redevelopment, they are generally considered sustainable developments, which help decrease urban sprawl.
Things to remember:
One common criticism of urban developments such as modern infills is that their designs diminish historical character in communities.
Question
Which of the following models is depicted in the image?
| A. African city model | |
| B. Harris and Ullman model | |
| C. Hoyt sector model | |
| D. Latin American city model | |
| E. Southeast Asian city model |
Explanation
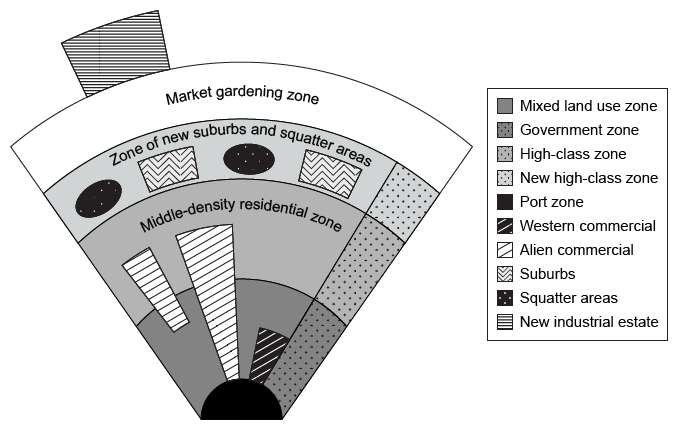
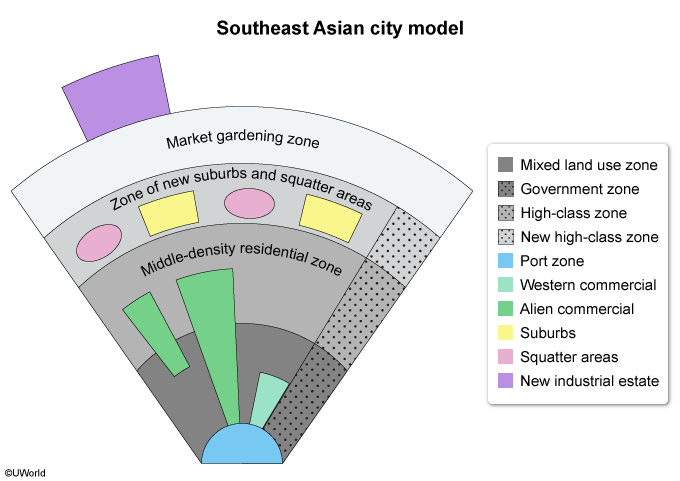
The Southeast Asian city model focuses on the mid-sized port cities in that region and the lack of a central business district (CBD) in these cities. Despite the lack of a CBD, there are two permanent zones: the port zone and the market gardening zone.
Port zones were built in Southeast Asia during the era of colonialism and imperialism, led by European countries such as Portugal and Spain. These zones are typically surrounded by mixed land-use and middle-density residential zones.
The Southeast Asian model also features blended areas, in contrast with other models that have clearly defined, unmixed areas. For example, squatter and suburban areas are found in the same zone in the region's cities. These details indicate that the image depicts the Southeast Asian city model.
(Choices A and B) The African city model and the Harris and Ullman model both feature CBDs, which are absent in the above image.
(Choice C) The Hoyt sector model focuses on the effect that transportation and communication have on a city's layout, features not shown in the above image.
(Choice D) In the Latin American city model, squatter settlements are located on the periphery, away from suburbs.
Things to remember:
The Southeast Asian city model features mid-sized port cities that lack a central business district. However, these cities have a permanent port zone, a market gardening zone, and mixed residential and land-use areas.
Question
Which of the following is a correct statement about world cities?
| A. They require financial support from primate cities | |
| B. They facilitate financial and cultural exchanges with other cities | |
| C. They have little influence in foreign affairs | |
| D. They rarely demonstrate signs of placelessness | |
| E. They are characterized by a lack of public transportation |
Explanation
Due to their role in the process of globalization, world cities, also known as global cities, have tremendous financial and economic impact across the globe. Tokyo, for example, is a dominant player in East Asian financial networks, being home to major banks, corporations, and busy ports that impact regional and global trade. In this way, Tokyo and other world cities facilitate financial exchanges around the world.
World cities like New York also contribute to cultural globalization by serving as sites of intense cultural exchange. This exchange is made possible by transportation systems, as well as the communication and digital networks that dominate media. These connections allow world cities to serve as global cultural nodes.
(Choice A) World cities are financially independent and do not require financial support from primate cities.
(Choice C) Due to being hubs of financial importance, world cities are influential in international political affairs.
(Choice D) World cities tend to experience a great deal of placelessness due to the effects of globalization and being highly interconnected with other parts of the world.
(Choice E) Generally, world cities have large mass transit networks and international airports.
Things to remember:
World cities facilitate financial and cultural exchange with other cities around the world.
AP Human Geography Practice Test: Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes
Question
Which of the following is a likely outcome of microfinancing?
| A. Increasing a country's Gross Domestic Product through loans to corporations | |
| B. Raising the price of food and other basic necessities in the periphery | |
| C. Diverting money from government defense projects to social welfare programs | |
| D. Increasing the involvement of women in the family decision-making process | |
| E. Slowing economic growth in less developed countries |
Explanation
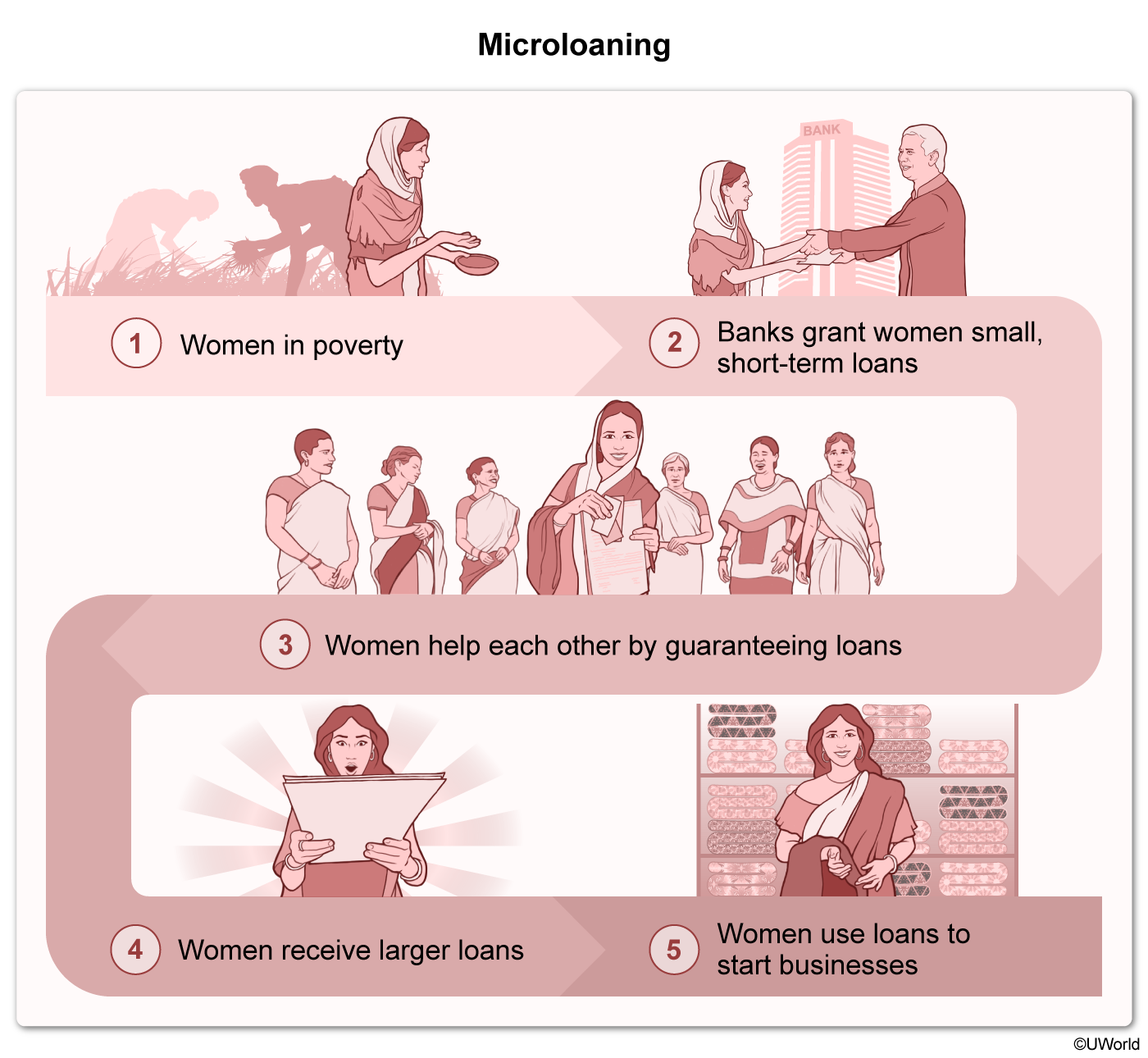
Microfinancing is the act of giving by providing microloans (small loans) to individuals and small businesses, particularly in developing countries. Most of these loans, ranging from $200 to $2,000, are granted to women to improve their economic status in a community. In 2015, 100 million women received roughly $80 billion in microloans.
As a result of their improved economic status, women who receive microloans are increasingly involved in family decisions. For example, they are more likely to make financial choices independent of others in the home.
(Choice A) Microfinancing is directed toward individuals or small businesses, not corporations.
(Choice B) Microfinancing loans are small; therefore, the prices of food and basic necessities in the periphery are unlikely to rise.
(Choice C) Since microfinancing is directed at individuals and small businesses rather than governments, the money cannot be diverted from the military to social programs.
(Choice E) Since microfinancing improves the economic status of individuals and small businesses in less developed countries, it is more likely that economic growth in developing countries would rise, not decline.
Things to remember:
Microfinancing provides small loans to both small businesses and individuals, particularly women in developing countries. As a result, these women experience improved economic status and greater involvement in family decisions.
Passage:
Question
The photograph above reflects which of the following?
| A. Religious differences among Indonesians | |
| B. The importance of foreign diplomacy | |
| C. The significance of high crude death rates | |
| D. The influence of rapid deindustrialization | |
| E. The impact of low human development |
Explanation
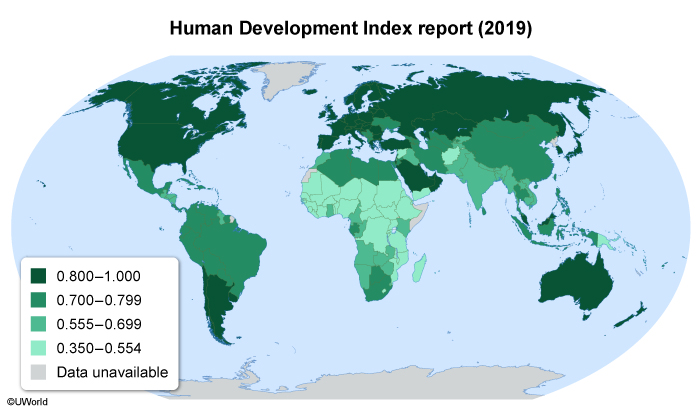
Indonesia's Bantar Gebang landfill contains several villages and as many as 20,000 people. The on-site population consists of families whose children attend underfunded village schools. To supplement their parents' income, most children leave school by age ten to scavenge for recyclables full time, earning the equivalent of $2–$10 per day. This cycle of poverty is largely responsible for the area's low human development.
A country's Human Development Index (HDI) is based on its citizens' life expectancy, educational attainment, and the gross national income per capita. Currently at 0.718, Indonesia's HDI is considered high, but they rank 107th out of 189 countries.
Indonesia's overall HDI ranking has been negatively impacted by the low human development found in Bantar Gebang, where children rarely escape poverty. In response, international observers have pressured Indonesia to help address this concern and raise the area's HDI.
(Choices A and B) The photograph doesn't show religious differences among Indonesians or indicate the importance of foreign diplomacy.
(Choice C) Indonesia has a crude death rate of 6.57 per 1,000 people, which is considered low.
(Choice D) Classified as a newly industrialized country, Indonesia has not undergone deindustrialization.
Things to remember:
A country's Human Development Index (HDI) is based on its citizens' life expectancy, educational attainment, and gross national income per capita. The circumstances of people living and working near Indonesia's Bantar Gebang landfill indicate low human development, which negatively impacts the country's HDI.
Question
Which of the following concepts is most relevant to Rostow's modernization model?
| A. Colonialism | |
| B. Devolution | |
| C. Cultural divergence | |
| D. Economic development | |
| E. Possibilism |
Explanation
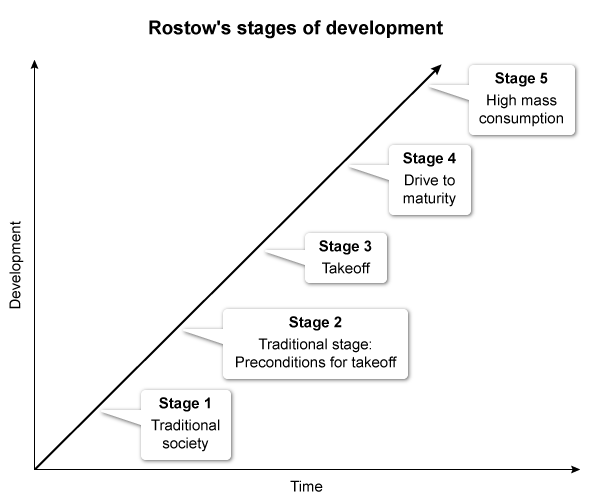
The decolonization of developing countries increased after WWII, and researchers began studying the economic development of the newly independent countries. The economist W.W. Rostow developed a theory that outlines the necessary stages of economic development a country must go through to modernize to be considered a developed nation:
- In Stage 1, a traditional society becomes a developing country.
- In Stage 2, educated individuals or wealthy groups introduce new technology and infrastructure.
- In Stage 3, a limited amount of production occurs in a few industries.
- In Stage 4, technologies spread to other industries and workers become specialized laborers.
- In Stage 5, the country transitions from heavy industry to producing consumer goods.
(Choice A) Rostow's model was created during the postcolonial era and therefore isn't relevant to colonialism.
(Choices B and E) Devolution and possibilism aren't associated with any stage in Rostow's model.
(Choice C) Cultural divergence, the process by which cultural barriers cause increasing difference within cultures over time, doesn't apply to Rostow's model.
Things to remember:
The economist W.W. Rostow developed a theory suggesting that countries pass through five stages of economic development as they modernize and become developed nations.
Make the AP HUG Exam Feel Like Practice
Get exam-ready with our practice tests and quizzes feature AP Human Geography MCQs and FRQs*. Hone your test-taking skills by learning to spot tricky distractors, manage your pacing, and tackle each question with confidence. Practice in realistic conditions so the official exam feels just like another run-through.
Create Custom Quizzes
Simulate Exam Conditions
Boost Your Study Methods
Ready to Get Started?
Practice AP Human Geography the smart way, with both MCQ and FRQ questions designed to match the real exam.
Score Higher with Smart Learning Tools
Detailed Explanations for Every AP Human Geography Question
Go beyond memorization with step-by-step reasoning for every AP Human Geography practice question and FRQ. Each explanation breaks down the logic behind the right answer, helping you understand why it’s correct, not just what to pick. Engaging visuals and examples make key geographic patterns, models, and case studies easier to remember, improving long-term retention by up to 60%. Whether you’re exploring demographic transitions or spatial diffusion, you’ll get clear insights and strategies for avoiding common trap answers so you can recall this knowledge for college-level and professional exams.
Flashcards & Notes That Actually Help You Remember
Build personalized digital flashcards for the topics you find toughest, like distinguishing between formal, functional, and perceptual regions or understanding how globalization impacts cultural landscapes. Use My Notebook to collect key takeaways from AP Human Geography practice questions in your preferred study format: bullet points for migration models, diagrams of urban hierarchies, or detailed notes on development indicators. With one-click transfer from explanations to flashcards or notes, everything stays neatly organized so you can focus on learning, not sorting materials.
Track Your Progress & Focus on What Matters
Monitor your improvement across all AP Human Geography practice tests and multiple-choice practice sets. The performance dashboard highlights your strengths and weak points by topic. Whether it’s political boundaries, economic geography, or population distribution, you can target what needs the most review. Stop guessing what to study next and start seeing measurable score increases with data-driven insights that help you study smarter, not longer.
Choose How You Study and Save
AP Human Geo
Practice Test
Starting at $39
300+ AP Human Geography Practice Questions (MCQs)
Custom AP Human Geography Practice Tests & Quizzes
Progress Tracking Dashboard
Pick Your Study Topics
Smart Study Planner
Realistic FRQ Practice with AI Scoring
300+ AP Human Geography Practice Questions (MCQs)
Custom AP Human Geography Practice Tests & Quizzes
Progress Tracking Dashboard
Pick Your Study Topics
Smart Study Planner
Realistic FRQ Practice with AI Scoring
Score-Predicting Full-Length AP Human Geography Exam
Print and Digital Study Guide
250+ Check-for-Understanding Questions
Expert-led Video Lessons
AP Human Geography Practice Test Reviews
UWorlds multiple choice questions are similar to the ones on the official AP exam and allowed me to time myself for each question. This was very helpful for me as I was able to answer questions faster and could finish the questions on the actual exam. The explanations for each question went in-depth and gave important details pertaining to events in the timeline. Through this, I was able to gain important skills for the exam and get a 5.
See MoreMy performance on unit tests throughout the year was not extraordinary, yet I feel I got a 5 or 4 on the AP exam due to the course's help. Overall, yes, I noticed a difference, as my confidence skyrocketed.
The explanations were clear and I could practice the question based on units. I got a 5 in the end!! So, I think it’s very helpful and I’ll be using it to study for my future exams 🙂 You guys provide so many different functions to help students like me, and I really appreciate it, it’s really worth the money.
See MoreUWorld AP Human Geo Practice Tests & Questions:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can UWorld’s AP Human Geo practice questions help improve my exam score?
UWorld’s AP Human Geo practice questions are built to transform your studying into active learning. Instead of simply memorizing terms, you’ll analyze maps, data sets, and spatial relationships, just like on the actual exam.
- Build Real Exam Confidence:
Practice with hundreds of AP Geo FRQs and Multiple choice questions that match real exam difficulty and structure, helping you understand both multiple-choice and free-response expectations. - Master the “Why,” Not Just the “What”:
Every question includes detailed explanations and visuals that connect human and physical geography concepts in context. - Focus Your Study Efficiently:
Our performance tracking tools identify your strengths and weaknesses so you can target areas that need the most attention.
With UWorld, every AP Human Geo practice test becomes a tool for deeper understanding, helping you retain key concepts and earn a higher score.
Who creates UWorld’s AP Geo practice questions?
All AP Geo practice questions are developed by our in-house team of expert educators. These contributors include AP Human Geography teachers, college-level instructors, and experienced AP exam graders. Each question undergoes multiple rounds of review to ensure it’s clear, accurate, and aligned with College Board® requirements. This expert-led process guarantees that UWorld’s AP Geo practice test questions mirror real exam expectations in both content and format, giving you the most reliable preparation possible.
What kind of AP Human Geography practice test score shows exam readiness?
There isn’t one perfect score that guarantees success, but consistent performance across all units is a great sign. In general, students who score around 70–75% on UWorld’s mixed-topic AP Human Geography practice tests are typically on track for a 4 or 5 on the real exam.
More importantly, you’ll know you’re ready when you can:
- Recognize geographic patterns and relationships in new scenarios
- Identify key concepts quickly without relying on memorization
- Explain not only why the correct answer is right, but why the others are wrong
With UWorld’s detailed feedback, you’ll move from guessing to confidently applying what you’ve learned.
Do UWorld’s AP Human Geography practice tests include every unit and key topic?
Yes, definitely. UWorld’s AP Human Geography practice tests are designed to be fully comprehensive and align closely with the current College Board® Course and Exam Description (CED). We cover every required unit, so you can confidently study all major themes, including:
- Unit 1: Thinking Geographically
- Unit 2: Population and Migration Patterns and Processes
- Unit 3: Cultural Patterns and Processes
- Unit 4: Political Patterns and Processes
- Unit 5: Agriculture and Rural Land-Use Patterns and Processes
- Unit 6: Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes
- Unit 7: Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes
Our customizable quiz builder allows you to create AP Human Geography practice tests by specific topics, like “Urban Land Use,” or mix content across all seven units to simulate a full exam experience.
Where can I find free AP Human Geography practice questions?
You can explore free AP Human Geography practice questions by signing up for UWorld’s 7-day free trial. This trial gives you access to a selection of multiple-choice and free-response questions, each with detailed, step-by-step explanations. The free trial also includes a preview of our complete AP Human Geography course, featuring digital study guides and engaging visuals that help you build a strong understanding of every unit before the exam.
Do UWorld’s AP Human Geography practice exams include both Multiple-Choice and Free-Response Questions?
Yes. UWorld’s AP Human Geography prep includes both types of questions found on the real exam. You’ll practice with:
- AP Human Geo Multiple-Choice Questions: Stimulus-based problems that use maps, graphs, and case studies to test your ability to analyze geographic data.
- AP Human Geo Free-Response Questions: Multi-step prompts that assess how well you can apply geographic models, draw conclusions, and explain spatial relationships.
Every AP Human Geography practice exam is designed to teach you how to think through complex scenarios just like the actual test.
How many full-length AP Human Geo mock exams should I complete before test day?
We recommend completing at least one full-length AP Human Geo mock exam before your actual test. Practicing under timed conditions helps build focus, improve pacing, and reduce anxiety. UWorld’s mock exams are drawn directly from our extensive question bank, so you’ll experience the same structure, difficulty, and realistic interface as the College Board® exam. By practicing this way, you’ll strengthen endurance and walk into test day feeling confident and prepared.
What makes UWorld’s AP Human Geography practice tests stand out from other study tools?
UWorld’s AP Human Geography practice tests combine expert-level question design, in-depth explanations, and adaptive learning tools that help you study efficiently. Each question is written by AP-certified teachers and geography specialists who ensure full alignment with College Board® standards. Unlike traditional flashcards or static worksheets, UWorld tracks your performance, highlights areas that need attention, and allows you to build custom quizzes. This dynamic approach makes your preparation more targeted and effective, helping you perform your best on the AP Human Geography exam.
Can I build my own AP Geo practice tests by topic?
Absolutely. One of the best features of UWorld’s AP Geo QBank is how customizable it is. You can easily build AP Geo practice tests that focus on specific units or concepts to match your study plan.
- Target One Unit: Finished learning “Cultural Patterns and Processes”? Create a short quiz to reinforce that content.
- Combine Multiple Topics: Make a midterm-style test by mixing “Population and Migration” with “Urban Land Use.”
- Simulate the Real Exam: Select all units and use timed mode to experience a complete practice exam.
This flexibility helps you study strategically, whether preparing for a classroom test, midterm, or the actual AP Human Geography exam.
When’s the best time to begin using AP Human Geography practice questions?
The best time to start using AP Human Geography practice questions depends on your goals, but UWorld’s QBank works at any point in your preparation.
- Before School Starts: Preview upcoming units to get familiar with key ideas like population trends and urbanization.
- During the School Year: Reinforce class lessons by creating short practice tests after each unit to check understanding.
- Closer to Exam Time: Use timed mixed-topic exams to simulate real testing conditions and identify final areas for review.
Whether you have months or just a few weeks to prepare, UWorld’s AP Human Geo practice questions help you make the most of your study time.