AP® Chemistry Unit 8 Review and Practice Test
Master the core concepts of AP® Chemistry Unit 8: Acids and Bases with our comprehensive review. This unit explores how acids and bases behave in chemical reactions, covering pH and pOH calculations, Ka and Kb, titration curves, and buffer systems. Use this AP Chem Unit 8 review to strengthen your understanding through visual lessons and realistic practice tests that mirror the AP exam. Whether you’re brushing up on weak acid equilibria or mastering neutralization reactions, these study tools will help you approach acid-base AP Chemistry with clarity and confidence.
Boost Your Confidence and Score High with Our AP Chemistry Unit 8 Review
Gain a deeper understanding of AP Chemistry Unit 8: Acids and Bases with everything you need to succeed. This AP Chemistry Unit 8 review breaks down essential topics like acid-base reactions, equilibrium constants (Ka and Kb), and pH and pOH calculations. Practice with AP Chemistry Unit 8 progress check MCQs and FRQs that reflect real exam difficulty, and reinforce your learning through visual lessons and interactive study materials.
Engaging Video Lessons
Challenging topics like acid-base equilibrium, titration curves, and buffer calculations are broken down into clear, visual explanations. Learn faster with short, high-yield videos tailored for AP Chemistry Unit 8 students preparing for the Acids and Bases unit. These lessons simplify complex equations, show real-life applications, and help you build confidence for both multiple-choice and free-response questions on the AP exam.
Interactive Study Guides
Our AP Chemistry Unit 8 study guide covers every major topic in the College Board’s framework, from acid-base reactions and titrations to pH, pOH, and buffer systems. Built-in concept checks test your understanding of equilibrium constants (Ka and Kb), conjugate acid-base pairs, and neutralization reactions so you know exactly what to review. Designed to align with the AP Chemistry Acids and Bases review, these guides simplify complex relationships and strengthen conceptual mastery for long-term retention.
Try These AP Chemistry Unit 8 Practice Test Questions
Passage:
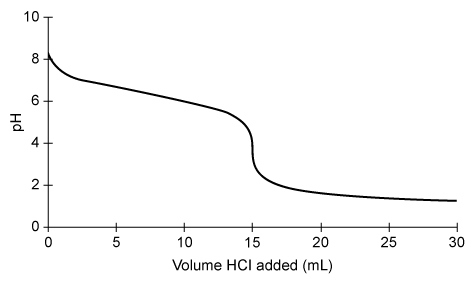
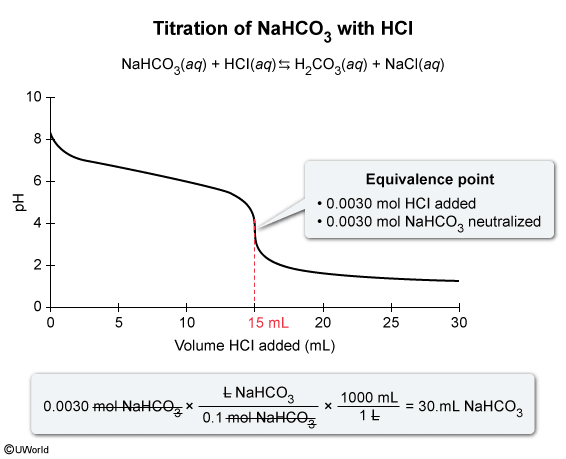
A sample of NaHCO3(aq) is titrated with 0.20 M HCl(aq) and the results are plotted on the graph shown above. The indicator Congo red (In−), which changes color from red to blue as the pH decreases from 5 to 3, is used to visualize the endpoint of the titration. In− has a pKb of 9.9 and reacts with acid according to the equation:
Question
The concentration of NaHCO3(aq) is determined to be 0.10 M. Based on this information and the given graph, what was the volume of the NaHCO3(aq) sample?
| A. | |
| B. | |
| C. | |
| D. |
Explanation
During an acid-base titration, a base (or acid) is fully neutralized at the equivalence point (ie, the number of equivalents of acid and base is equal). The equivalence point is the middle point on the steep slope of the titration curve.
Based on the titration curve and the given information, the equivalence point occurs when 15 mL (0.015 L) of 0.20 M HCl(aq) is added to the sample of 0.10 M NaHCO3(aq). The number of moles of HCl(aq) added is calculated by multiplying the concentration (molarity) of HCl(aq) by the volume added:
Because the neutralization reaction between HCl(aq) and NaHCO3(aq) occurs in a 1:1 mole ratio, there must be an equal number of moles of HCl(aq) and NaHCO3(aq) at the equivalence point; therefore, 0.0030 moles NaHCO3(aq) were titrated. The volume of the NaHCO3(aq) sample is calculated by multiplying the moles of NaHCO3(aq) by the reciprocal of concentration:
Converting the volume from L to mL gives
Therefore, the volume of the NaHCO3(aq) sample titrated is 30. mL.
(Choice A) This value is the number of moles rather than the volume of NaHCO3(aq).
(Choice B) This value is the volume of NaHCO3(aq) in liters rather than mL.
(Choice C) 15 mL is the volume of HCl used at the equivalence point rather than the initial volume of NaHCO3. Even though the number of moles of HCl and NaHCO3 are equal, their volumes are not equal because the concentrations of HCl and NaHCO3 are different.
Things to remember:
In an acid-base titration, the equivalence point occurs when the equivalents of acid and base are equal. The equivalence point is the middle point on the steep slope of the titration curve.
Question
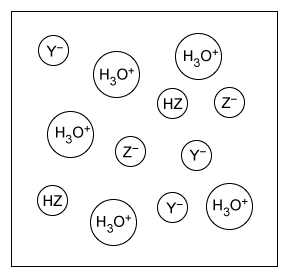
A student makes an aqueous solution of the acids HY and HZ. After fully mixing, the solution contains the species shown in the particle view above. Which of the following statements is consistent with the given information?
| A. HZ is a weak acid because it is completely dissociated in solution. | |
| B. HY is a weak acid because it is partially dissociated in solution. | |
| C. HZ is a strong acid because it is partially dissociated in solution. | |
| D. HY is a strong acid because it is completely dissociated in solution. |
Explanation
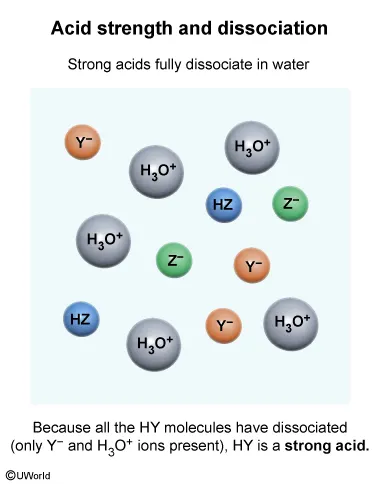
The Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry definitions of acids and bases define an acid as a proton (H+ ion) donor. Strong acids fully dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions and forming hydronium ions (H3O+), whereas weak acids only partially dissociate in water.
The particulate diagram given in this question shows that there are HZ molecules and H3O+, Y−, and Z− ions in the solution. The lack of HY molecules in the diagram indicates that all the HY molecules added to the solution have dissociated into H3O+ and Y− ions. Therefore, HY is a strong acid because it has completely dissociated in solution.
(Choices A and C) The particulate diagram shows both HZ molecules and Z− ions in solution, indicating HZ is only partially dissociated and therefore is a weak acid.
(Choice B) HY has completely dissociated (ie, no remaining HY molecules in the particulate diagram). Therefore, HY is a strong acid, not a weak acid.
Things to remember:
According to the Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry definitions, acids are molecules that donate protons (H+ ions). Strong acids fully dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions and forming H3O+ ions, whereas weak acids only partially dissociate in water.
Question
Two titrations are carried out with 0.10 M NaOH. In the first titration, 50. mL of NaOH is added to a 50. mL sample of 0.10 M HCl to reach the equivalence point and a pH of 7.0. In the second titration, NaOH is added to a 50. mL sample of 0.10 M uric acid (HC5H3N4O3) until the equivalence point is reached. Which of the following identifies the volume of NaOH added to uric acid and the pH of the solution at the equivalence point? (The pKa of uric acid is 5.4.)
| Volume of 0.1 M NaOH | pH of Solution | |
| A. 25 mL | < 7.0 | |
| B. 25 mL | > 7.0 | |
| C. 50. mL | < 7.0 | |
| D. 50. mL | > 7.0 |
Explanation
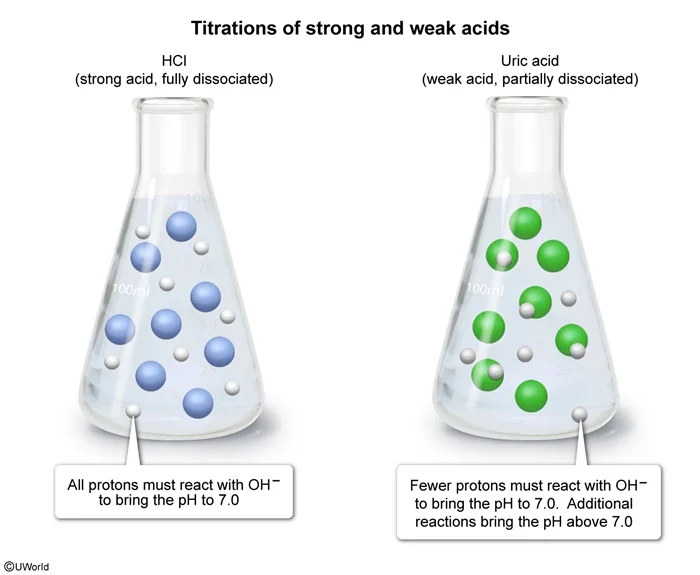
Acids can be titrated with a strong base such as NaOH. The equivalence point occurs when the number of moles of base added equals the number of moles of acid originally present (ie, one equivalent of base). At this point, all protons from the acid have reacted with the base.
When a strong acid is titrated, all of the protons have already dissociated before any base is added. These protons contribute to a decrease in the pH of the solution. When one equivalent of base is added, these protons are neutralized and the solution returns to neutral pH (ie, pH = 7.0). In contrast, only a fraction of the molecules of a weak acid dissociate in water, resulting in a higher pH than that of a strong acid of equal concentration. Therefore, adding base brings the pH back to neutral before one equivalent is added, and once a full equivalent is added, the pH is greater than 7.0.
For a 50. mL solution of 0.1 M uric acid, 50. mL of 0.1 M NaOH is one equivalent because the number of moles of NaOH equals the number of moles of acid. Uric acid has a pKa greater than 0, making it a weak acid. Therefore, when one equivalent of NaOH is added, the pH will be greater than 7.0.
(Choices A and B) 25 mL of 0.1 M NaOH is one half-equivalent, not a full equivalent.
(Choice C) The pH of the solution is greater than 7.0 when one equivalent of NaOH is added, not less than 7.0.
Things to remember:
For strong acid titrations, the equivalence point yields a pH of 7.0. For weak acids, the equivalence point yields a pH greater than 7.0.

Study Anywhere, Anytime
Tackle AP Chemistry Unit 8 practice questions on the go, watch quick acid-base videos between classes, or review buffer concepts while waiting for friends. With the UWorld app, your complete AP Chemistry acids and bases review is always at your fingertips. Whether you’re preparing for AP Chemistry Unit 8 FRQs or reinforcing key acid-base concepts, study anytime, anywhere, and stay consistent all the way to exam day.
Stand Out
with a Top Score in AP Chemistry
Finish your AP Chemistry Unit 8 review and continue mastering all units with UWorld. Boost your performance and make yourself a standout candidate for competitive colleges, majors, and scholarships by earning a top score.
Get our all-in-one course today!
- Focused AP Chem Videos
- Print & Digital Study Guide
- 400+ Exam-style Practice Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Adjustable Study Planner
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards
- Digital Notebook
Hear From Our AP Students

UWorld’s service is pretty good and helps provide a lot of explanations on subjects I haven’t been confident on before.

The questions here are the most realistic to the AP tests I've seen so far! I appreciate the ability to customize tests as well.

The best part is that all options are well-explained, telling clearly why they are not the right option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What topics are included in AP Chemistry Unit 8: Acids and Bases?
Unit 8 focuses on how acids and bases behave and interact in chemical systems, helping you understand the balance of chemical reactions and solution equilibria. Key topics include:
- Properties of acids, bases, and conjugate pairs and how they influence reaction behavior
- pH and pOH calculations using logarithmic relationships
- Ka and Kb equilibrium constants and determining the extent of ionization
- Strong vs. weak acids and bases, buffer systems, and titration curves for neutralization reactions
- How acid-base equilibria relate to changes in concentration and temperature
These AP Chemistry Unit 8 concepts form the foundation for later units like chemical equilibrium and electrochemistry, making mastery of this topic essential for success on the exam.
How is AP Chemistry Unit 8 tested on the exam, and what is its weight?
Acids and bases make up about 11–15% of the total AP Chemistry exam and are tested through both MCQ and FRQ questions. You’ll analyze acid-base reactions, interpret titration curves, and calculate pH, pOH, Ka, and Kb values. Some questions require applying equilibrium and thermodynamic concepts to explain reaction behavior. Expect to justify reasoning with data, show calculations, and interpret graphs. Mastering AP Chemistry Unit 8: Acids and Bases strengthens your performance across several connected units on the exam.
What are the Unit 8 topics most frequently tested on the AP Chemistry exam?
AP Chemistry Unit 8 questions often focus on acid-base equilibrium, titration curves, and buffer systems. You’ll frequently calculate pH and pOH at various points in a titration or determine Ka and Kb to predict reaction outcomes. Many questions test your understanding of strong and weak acids and bases and how equilibrium shifts when concentrations change. Some FRQs may also include interpreting titration data or analyzing buffer effectiveness under different conditions. These topics emphasize quantitative reasoning and conceptual accuracy, making practice with data-driven questions essential.
How should I prepare for an AP Chemistry Unit 8 exam?
Begin by reviewing acid-base theories, pH and pOH formulas, and the relationships between Ka, Kb, and equilibrium. Practice titration and buffer problems to strengthen quantitative reasoning. Use visual diagrams to connect equations to experimental data. As you progress, mix conceptual review with timed problem-solving to improve pacing. Unit 8 AP Chemistry focuses heavily on applying these principles, so consistent practice with problem-solving builds both confidence and accuracy.
How do I self-study for AP Chemistry Unit 8 effectively?
Break Unit 8 into smaller study goals; start with acid-base definitions, then move on to Ka, Kb, and buffer systems. Create flashcards for key formulas and equilibrium relationships to strengthen recall. Dedicate focused time daily to solving pH, pOH, and titration problems. Review incorrect answers right away to understand your weak spots. Use visuals like titration graphs or ICE tables to connect theory with data. Consistent active learning is the most effective way to master acid base AP Chemistry concepts.
What are the common mistakes students make in AP Chem Unit 8?
Many students confuse strong and weak acids or bases, leading to incorrect pH or pOH values. Others forget to adjust concentrations in buffer calculations or use the wrong expression for Ka and Kb. Misreading titration curves and neglecting units are also frequent errors. In AP Chem acid base questions, precision in setup and reasoning is key to earning full credit. Reviewing solved examples from acids and bases AP Chemistry practice helps develop accuracy and confidence.
How can I improve my score on the Free-Response Questions (FRQs) for Unit 8?
Practice writing clear, well-organized responses that show each calculation and reasoning step. Always include units and clearly state formulas when explaining acid–base reactions, buffer behavior, or equilibrium shifts. Review previous AP Chemistry Unit 8 FRQs to understand common question types and scoring patterns. Use past rubrics to evaluate your work and identify areas for improvement. Focus on connecting your explanations to underlying principles rather than just numerical answers. Regular timed practice will help build accuracy and confidence.
Are any free resources available for AP Chemistry Unit 8?
Yes! UWorld offers a free trial with access to AP Chemistry Unit 8: Acids and Bases questions, visual explanations, and interactive feedback. Explore essential topics like Ka, Kb, pH, pOH, and titration curves through realistic practice. This trial helps you experience exam-level problem-solving without commitment. It’s a great way to evaluate UWorld’s teaching approach and build confidence before upgrading to a full subscription. The free trial also allows you to explore how detailed explanations turn difficult acid–base concepts into easy, memorable insights.
Where can I find a good study guide for AP Chemistry Unit 8?
The UWorld AP Chemistry study guide is one of the most reliable resources for mastering Unit 8: Acids and Bases. It provides comprehensive coverage of acid–base theories, pH and pOH calculations, equilibrium constants (Ka and Kb), buffer systems, and titration curves, all fully aligned with the College Board’s CED.
Each section includes concise explanations, clear visuals, and step-by-step worked examples that simplify complex equilibrium and buffer concepts. You’ll also find real-world applications and “Check for Understanding” exercises to reinforce learning. Regular practice with this guide helps improve retention and exam performance.
Can I find practice tests specifically for AP Chem Unit 8?
Yes! UWorld lets you generate custom quizzes and full-length AP Chemistry Unit 8 practice tests focused entirely on acids and bases topics. You can target specific concepts like titrations, buffer systems, Ka/Kb relationships, and pH and pOH calculations for efficient, goal-oriented review. Each question includes detailed explanations, visual breakdowns, and step-by-step reasoning to strengthen conceptual understanding.
When paired with the UWorld AP Chemistry QBank, which includes thousands of exam-style MCQs and FRQs with detailed rationales, it becomes a complete solution for Unit 8 preparation. This combined approach helps you identify weak areas, correct common errors, and build lasting confidence before test day.