AP® Biology Unit 1 Review and Practice Test
Prepare for your AP® Biology Unit 1 test with our complete Chemistry of Life review. Unit 1 covers water’s properties, macromolecules, and essential biochemistry concepts—the foundation for the entire course. Use our AP Bio Unit 1 review to study with exam-style MCQs, practice tests, and study guide lessons that reflect exactly what’s on the AP exam. Whether you need quick notes, short review videos, or full practice, this resource will strengthen your understanding and help you aim for a top score.
Boost Your Confidence and Score High with Our AP Biology Unit 1 Review
Dive into AP Biology Unit 1: Chemistry of Life with everything you need to succeed. This AP Bio Unit 1 review covers water’s properties, carbon and macromolecules, and key biochemistry concepts. Practice with AP Biology Unit 1 MCQs and practice tests that mirror the real exam, and reinforce your learning with our step-by-step Unit 1 study guide and engaging video lessons.
AP Biology Unit 1 Review Videos Anytime
Complex concepts like hydrogen bonding, dehydration synthesis, and macromolecule structure are broken down into clear, visual explanations. Learn faster with short, high-yield videos designed for AP Bio students.
Interactive Study Guides
Our AP Biology Unit 1 study guide covers every topic in the College Board’s CED. Built-in knowledge checks test your understanding of macromolecules, properties of water, and biochemistry fundamentals, so you know exactly what to review.
Try These AP Biology Unit 1 Practice Test Questions
Question
During RNA synthesis in a cell, a cytosine nucleotide is added to a growing RNA strand ending in a guanine-adenine dinucleotide. Which of the following correctly illustrates the structure and orientation of each nucleotide as the reaction takes place?
A. 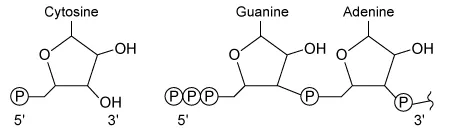 |
|
B. 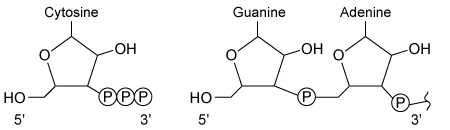 |
|
C. 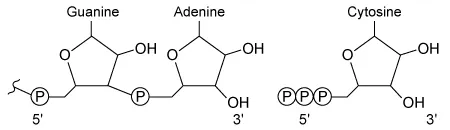 |
|
D. 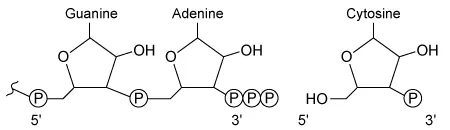 |
Explanation
Nucleotides are biological molecules composed of the following:
- One pentose sugar (ie, ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA)
- One to three phosphates
- One of the five nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine (DNA only), or uracil (RNA only)
The nitrogenous base is attached to carbon 1 of the sugar, all phosphates present are attached to carbon 5 (ie, the 5′ end), and a hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to carbon 3 (ie, the 3′ end).
Nucleotides can combine to form long chains (ie, polymers) known as polynucleotides or nucleic acids (ie, RNA or DNA). In biological systems, this occurs when the 5′ triphosphate (three connected phosphates) on a free nucleotide reacts with the 3′ hydroxyl group of the growing nucleic acid.
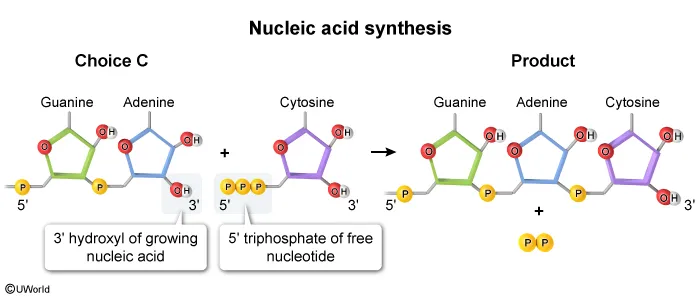
In the given RNA synthesis reaction, cytosine (a free nucleotide) is added to a guanine-adenine dinucleotide on the growing nucleic acid. Because cytosine is the free nucleotide in this scenario, it must contain a 5′ triphosphate, which must align with the 3′ hydroxyl group of guanine-adenine for the addition to occur. The diagram shown in Choice C correctly depicts this structure and orientation.
The diagrams shown in Choice A, Choice B, and Choice D show incorrect structures and/or orientations for the nucleotides.
Things to remember:
Nucleotides consist of a pentose sugar linked to a nitrogenous base (ie, adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine [DNA only], uracil [RNA only]) at carbon 1, one or more phosphates linked to the 5′ end, and a hydroxyl group linked to the 3′ end. Nucleic acids grow when the 5′ triphosphate of a free nucleotide reacts with the 3′ hydroxyl group of the growing nucleic acid chain.
Question
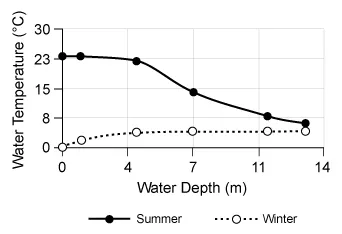
Scientists investigated how water temperature at various depths changed throughout the year in a certain lake. The graph above depicts the relationship between water depth and water temperature recorded during the summer, when environmental temperatures were greater than 4°C, and during the winter, when the environmental temperatures were below the freezing point of water (0°C). Which of the following statements is most consistent with the data shown above?
| A. The water temperature increases with increasing water depth during the summer. | |
| B. Water depth and water temperature are directly correlated throughout the year. | |
| C. There is no relationship between water depth and water temperature. | |
| D. Water temperature increases with increasing water depth during the winter. |
Explanation
Water molecules consist of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The electronegative oxygen pulls harder on the shared electrons than hydrogen, resulting in polar bonds. The increased electron density around the oxygen atom gives it a partial negative charge, and the decreased electron density around each hydrogen atom gives it a partial positive charge.
The attraction between these partial positive and negative charges allows the formation of hydrogen bonds between oxygen and hydrogen atoms of different water molecules.
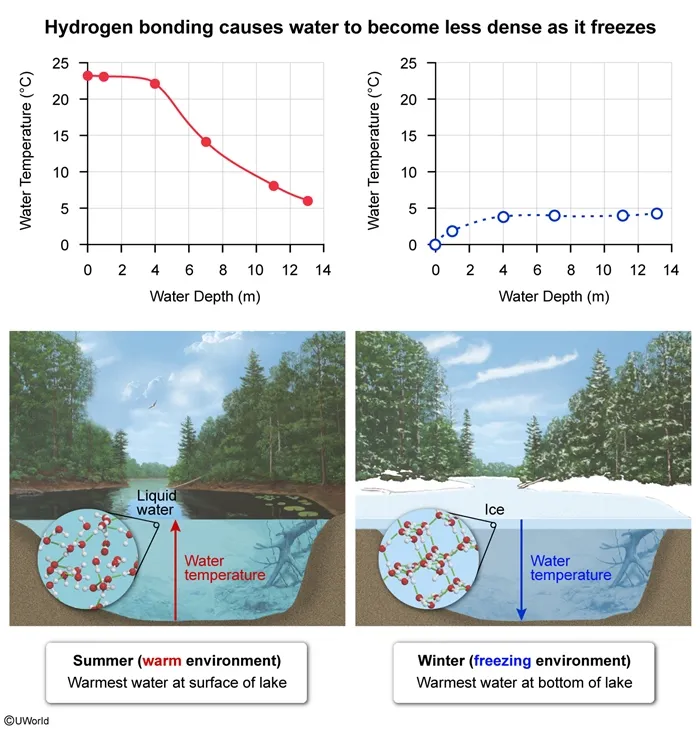
When environmental temperatures are above approximately 4°C (ie, temperature at which water is most dense), the water temperature in a lake decreases with increasing depth, as depicted in the question graph. This occurs because, at these temperatures, warmer water is less dense than cooler water.
When environmental temperatures reach the freezing point of water, more hydrogen bonds form, causing water molecules to adopt a rigid framework in which water molecules are further from each other than they are in liquid water. As a result, ice is less dense than liquid water. Therefore, when environmental temperatures are at or below the freezing point of water, water temperature in a lake increases with depth (Choice D).
(Choice A) The water temperature decreases with increasing water depth during the summer.
(Choices B and C) There is a relationship between water depth and temperature, but the relationship depends on whether environmental temperatures are above or below freezing.
Things to remember:
Hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atoms of adjacent water molecules causes water to become less dense as it freezes.
Question
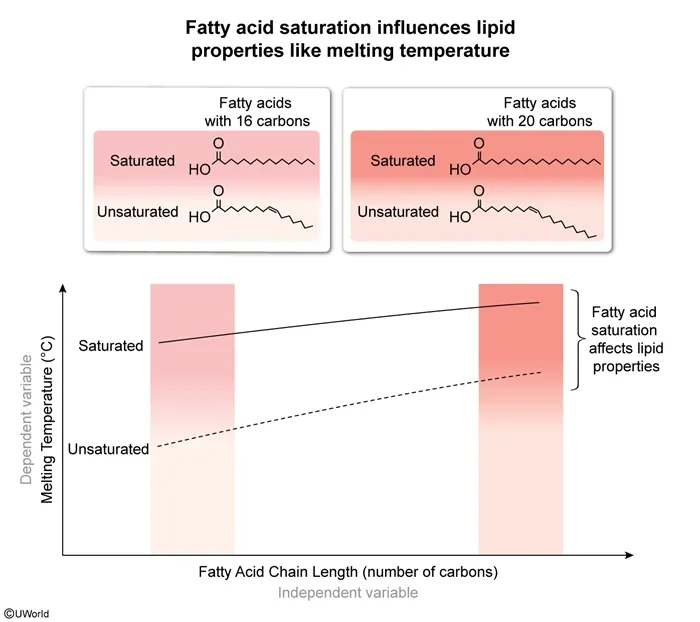
Solid fatty acid samples were slowly heated in special warming pans until the samples melted. The scientists performing the procedure recorded the melting temperatures, noting that they were dependent on chain length and other characteristics of the lipids. Which plot below best represents the likely study results?
A. 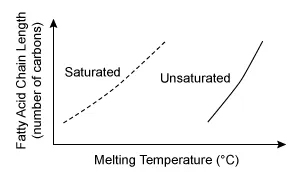 |
|
B. 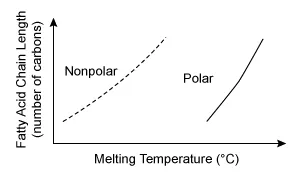 |
|
C. 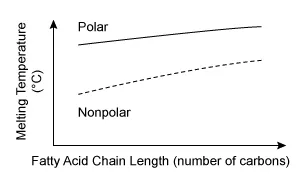 |
|
D. 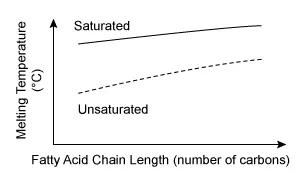 |
Explanation
Lipids are nonpolar biological molecules with many functions (eg, storing energy, providing structure to cell membranes). Lipids may be saturated or unsaturated based on the types of fatty acids that they possess. These fatty acids are composed of carbon-hydrogen (hydrocarbon) chains. In saturated lipids, fatty acids contain carbon atoms linked only by single bonds, making them essentially straight in structure. In contrast, fatty acids of unsaturated lipids have some double bonds between their carbon atoms that cause structural kinks (ie, bends).
The straighter fatty acid chains of saturated lipids can be packed more tightly, whereas bends in unsaturated lipids prevent them from packing together tightly. Tighter packing increases interactions between fatty acid chains, thereby increasing melting temperature.
The question describes fatty acid melting temperatures measured by a team of scientists and states that these melting temperatures were affected by the chain length of the fatty acids. Since melting temperature is the dependent variable, it should be plotted on the y-axis. Therefore, the plot in Choice D, which shows melting temperature being affected by both chain length and fatty acid saturation, best represents the likely results.
The other graphs either are plotted with incorrect orientation (Choices A and B) or incorrectly depict some fatty acids as polar (Choices B and C).
Things to remember:
Lipids are nonpolar biological molecules. The fatty acids in lipids can be saturated (contain only single bonds between carbon atoms) or unsaturated (contain some double bonds between carbon atoms). Dependent variables are plotted on the y-axis of a line graph.
Stand Out
with a Top Score in AP Biology
Finish your Unit 1 AP Biology review and continue mastering all units with UWorld. Boost your performance and set yourself apart as a strong candidate for competitive colleges, majors, and scholarships by earning a top score.
Get our all-in-one course today!
- Focused AP Bio Videos
- Print & Digital Study Guide
- 500+ Exam-style Practice Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Adjustable Study Planner
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards & Digital Notebook
Hear From Our AP Students

UWorld’s service is pretty good and helps provide a lot of explanations on subjects I haven’t been confident on before.

The questions here are the most realistic to the AP tests I've seen so far! I appreciate the ability to customize tests as well.

The best part is that all options are well-explained, telling clearly why they are not the right option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is AP Biology Unit 1 about?
AP Biology Unit 1, commonly known as “Chemistry of Life,” establishes the chemical foundation for all biological processes. This unit explores how atoms bond to form molecules and how those molecules combine to create the 4 essential macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. You’ll discover why water’s unique polarity and hydrogen bonding result in properties like cohesion, adhesion, high specific heat, and its function as a universal solvent. Mastering AP Bio Unit 1 is essential because understanding chemical bonds and functional groups directly impacts your success in later units covering cellular energetics, photosynthesis, and gene expression.
UWorld’s AP Bio Unit 1 study guide provides comprehensive coverage of every topic with visual diagrams and straightforward explanations that make complex chemistry concepts accessible. Our integrated approach helps you read the material, watch high-yield video lessons, and practice with exam-style questions all in one platform.
Which topics are covered in AP Biology Unit 1?
Unit 1 AP Biology covers seven major topics that form the molecular foundation of life, establishing the base for understanding every process that follows in the course.
Properties of Water: Water’s polarity and hydrogen bonding explain cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, temperature regulation, and its ability to act as a universal solvent.
Macromolecules:
A. Carbohydrates – Provide short-term energy and structural support.
B. Lipids – Enable long-term energy storage and membrane formation.
C. Proteins – Drive catalysis, structural integrity, and cellular regulation.
D. Nucleic Acids – Store and transmit genetic information.
Enzyme Function: Enzymes act as biological catalysts, lowering activation energy. This topic explores enzyme specificity, the influence of pH and temperature, and regulation through inhibitors or activators.
These topics require active engagement and consistent reinforcement to master. UWorld’s QBank, aligned with the Course and Exam Description (CED), provides targeted AP Bio Unit 1 practice questions for each area. You can generate customized quizzes on macromolecules or chemistry of life AP Biology concepts to strengthen weak areas and make your Unit 1 AP Bio review more efficient and results-driven.
Where can I find the best AP Bio Unit 1 study guide and notes?
An effective AP Bio Unit 1 study guide presents content and application together rather than separating notes from practice. UWorld’s print and digital study guide for AP Biology Unit 1 covers every learning objective and includes knowledge checks after each section. Instead of just reading, you’ll answer short practice questions to ensure you’ve learned the concept before moving forward. Our Unit 1 AP Bio study guide includes comprehensive visual diagrams, clear explanations, and immediate opportunities to test your understanding. If you prefer digital AP Biology Unit 1 notes PDF materials, the guide is accessible via our mobile app, which also stores flashcards and a customizable study planner for on-the-go learning.
Additionally, UWorld also offers a free trial so you can see how our study guide compares to other AP Biology Unit 1 review PDF materials and classroom notes. Our integrated approach of read, watch, and practice helps you master concepts faster than traditional study methods. Supplement UWorld’s resources with College Board materials or instructional videos for additional perspectives, but make UWorld your primary preparation tool for the most efficient AP Bio Unit 1 review.
Where can I find AP Bio Unit 1 practice tests with detailed answer explanations?
The College Board releases free-response questions with scoring guidelines but doesn’t provide multiple-choice answer keys. UWorld fills this critical gap with our comprehensive AP Biology Unit 1 practice test that offers both MCQ and FRQ questions with detailed answer explanations. Our AP Bio Unit 1 practice test mimics the style and difficulty of the actual exam, and every distractor is explained so you learn not just why the right answer is right but why the wrong choices are wrong.
This approach dramatically improves your performance on Unit 1 AP Biology practice test questions because you understand the reasoning behind each option. You can create custom AP Biology Unit One practice test exams focused specifically on Chemistry of Life content or mix questions from multiple topics. After each practice session, review every question you missed using our detailed explanations with visuals. Regular testing with UWorld’s platform helps improve memory, familiarize you with the exam format, and spot ongoing weaknesses. Our progress dashboard tracks your performance over time, helping you adjust your study plan as you improve.
What are the types of questions usually featured on the AP Biology Unit 1 test?
Typical Unit 1 AP Biology test questions include diverse formats that assess both content knowledge and application skills:
- Multiple-choice questions testing water properties, CHONPS elements, and macromolecule identification. AP Biology Unit 1 MCQ questions often present comparative data or reaction diagrams requiring logical analysis rather than simple recall.
- AP Bio Unit 1 MCQ questions about macromolecules appear frequently, linking molecular composition to biological function. Students must recognize structural formulas of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, and explain how their unique properties affect biological roles.
- Short-answer or FRQ segments asking you to explain carbon’s versatility, describe dehydration synthesis mechanisms, or interpret graphs showing lipid melting points.
- Diagram labeling of functional groups, molecular structures, or enzyme-substrate complexes.
- Data analysis questions require you to conclude from experimental results about enzyme activity, pH effects, or temperature influences.
UWorld’s AP Biology Unit 1 questions cover all these formats with detailed, visual explanations. Because our questions mirror those on the AP exam, when you read our content, watch our video explanations, and practice with our QBank, you’ll gain complete familiarity with the style and difficulty level of actual exam questions. Our AP Bio Unit 1 test materials ensure you’re prepared for anything that might appear.
What are the AP Biology Unit 1 concepts that students should master before the test?
Before your AP Bio Unit One test or semester final, ensure you understand these critical concepts:
- The structure and function of all four macromolecule classes: carbohydrates (short-term energy and structural support), lipids (long-term energy storage and membrane formation), proteins (catalysis, structure, and cellular regulation), and nucleic acids (storage and transmission of genetic information)
- Carbon’s bonding capacity enables molecular diversity and stability through forming chains,
- branches, and rings
- The mechanisms of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis for building and breaking polymers, including the ability to identify these reactions in diagrams
- Water’s role in biological systems includes cohesion, adhesion, temperature regulation, and solvent properties driven by polarity and hydrogen bonding
- How enzyme structure relates to function and how environmental changes like pH and temperature affect reaction rates, including enzyme specificity and regulation through inhibitors or activators
- The relationship between monomers and polymers for each macromolecule type, and how to predict the products of synthesis or breakdown reactions
UWorld’s integrated study guide, high-yield videos, customizable quizzes, and flashcards provide everything you need to master these topics. Students who consistently read UWorld’s content, watch our video lessons, and practice with AP Biology Unit 1 practice questions tend to feel more confident and perform better on both unit tests and the AP exam.
Are there any free resources available for AP Biology Unit 1?
Yes, UWorld offers a free trial that provides access to AP Biology Unit 1 multiple-choice and free-response practice questions, each with detailed explanations and visual learning aids. This trial helps you explore the platform’s interface and understand how its questions connect to key Unit 1 concepts before subscribing. Additionally, other free resources from platforms such as Khan Academy and College Board, when combined with UWorld’s prep system, create a powerful study plan: College Board defines the exam framework, Khan Academy strengthens conceptual understanding, and UWorld’s practice tools refine application and critical thinking.
Using these together allows you to study efficiently, reinforce weak areas, and connect foundational knowledge to real exam scenarios, significantly improving both comprehension and performance.
How can I find an AP Biology Unit 1 cheat sheet?
While a comprehensive study is always best, UWorld’s quick reference materials and condensed summaries can serve as effective AP Biology Unit 1 cheat sheet tools for last-minute review. Our platform includes one-page summaries covering:
- Key macromolecule structures and functions (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids)
- Water properties and their biological significance (cohesion, adhesion, high specific heat, universal solvent)
- Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reaction mechanisms
- Enzyme function basics, including factors affecting activity
- CHONPS elements and their roles in biomolecules
- Important terminology with brief definitions
However, remember that a chemistry of life AP Biology worksheet or cheat sheet should supplement, not replace, thorough studying with UWorld’s practice questions and detailed explanations. Use these tools for quick reviews between study sessions rather than as your primary preparation method. UWorld’s mobile app makes it easy to access these summaries and flashcards whenever you need a quick refresher.
What are the best flashcards for AP Biology Unit 1 review?
The most effective AP Biology Unit 1 flashcards reinforce key concepts, terms, and relationships essential to mastering the Chemistry of Life. UWorld’s AP Bio Unit 1 flashcards are built for active recall and spaced repetition, helping you retain and apply information accurately.
Each deck covers:
- Core Vocabulary: Polarity, hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions, peptide bond, glycosidic linkage, phosphodiester bond, dehydration synthesis, and hydrolysis.
- Macromolecule Pairs: Glucose–polysaccharide, amino acid–protein, nucleotide–nucleic acid.
- Water Properties: Cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, and solvent function are explained chemically.
- Enzyme Function: Structure, activity, and effects of pH, temperature, and inhibitors.
- Functional Groups: Key chemical properties and biological importance.
- Macromolecule Structures: Comparison of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
UWorld’s digital flashcard system works across all devices and uses adaptive spaced repetition to maximize retention. You can tag challenging concepts for extra review, monitor progress, and instantly connect each flashcard to relevant AP Bio Unit 1 practice questions for seamless reinforcement.
How can I maximize my AP Biology Unit 1 review?
A strong AP Biology Unit 1 review integrates reading, watching, and active practice. UWorld combines all these study methods within one structured platform to help you master the Chemistry of Life.
Read: Start with UWorld’s AP Biology Unit 1 study guide, featuring clear explanations and visual diagrams that simplify water properties, CHONPS elements, and macromolecules.
Watch: Learn through UWorld’s high-yield video lessons that use animations and real-world biological examples to clarify complex chemistry concepts.
Practice: Strengthen comprehension with UWorld’s QBank of AP Bio review Unit 1 questions. Each includes detailed, visual explanations that connect concepts to biological functions.
Active Recall & Spaced Repetition: Use UWorld’s customizable quizzes for AP Biology practice questions from Unit 1 and the flashcard system that revisits material at spaced intervals to reinforce memory for your AP Biology test, Unit 1.
Timed Practice: Simulate real exam settings using Unit 1 chemistry of life AP Bio test materials in UWorld’s exam simulator to improve pacing and accuracy.
Targeted Review & Tracking: Analyze results through UWorld’s progress dashboard to identify weak areas, review them with AP Biology Unit 1 biochemistry materials, and track improvement through analytics on Unit 1 chemistry of life AP Biology exam answers.
UWorld’s integrated system ensures comprehensive preparation, guiding you from concept review to confident performance on your Unit 1 test and full AP Biology exam.