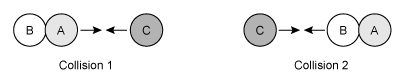AP® Chemistry Practice Tests & Questions
Ace AP® Chemistry with realistic practice exams, multiple choice questions, and detailed explanations in our Question Bank (QBank). Prepare smarter, save time, and earn college credit on your schedule.
Access Includes
- 400+ AP Chem MCQ Questions
- Customizable Quiz Generator
- Realistic Timed Test Simulation
- Colorful Visual Explanations
- Step-by-Step Solutions
- Adjustable Smart Study Planner
- Progress Dashboard
- Smart Flashcards
Try These AP Chemistry Practice Test Questions
Check out sample AP Chemistry MCQs before you commit. Stop wasting hours on material you already know; our practice tests let you focus on the topics you actually need to study. Get exam-style questions with step-by-step answer explanations and visuals that actually make sense. Practice smarter, build confidence, and see how UWorld helps you nail that 5.
Atomic Structure and Properties Practice Test
Question
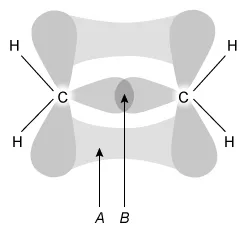
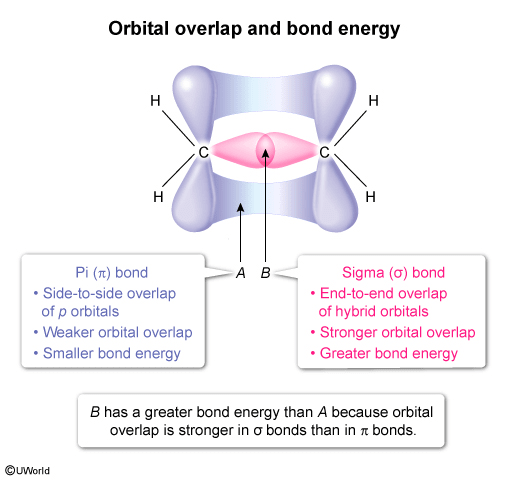
The orbital overlap forming the sigma and pi bonds that make up the C=C bond in C2H4 is shown above. Compared to the bond energy of A, the bond energy of B is
| A. the same, because the orbital overlap is the same strength | |
| B. greater, because the orbital overlap is weaker in sigma bonds than in pi bonds | |
| C. greater, because the orbital overlap is stronger in sigma bonds than in pi bonds | |
| D. smaller, because the orbital overlap is stronger in sigma bonds than in pi bonds |
Explanation
Sigma (σ) bonds are covalent bonds that result from end-to-end overlap of hybrid orbitals, which are formed from a combination of s and p atomic orbitals. Pi (π) bonds result from the side-to-side overlap of p orbitals. Orbital overlap σ bonds stronger than in π bonds, resulting in a stronger bond and greater bond energy (ie, more energy is required to break a σ bond than a π bond).
In this question, the depiction of C2H4 shows the orbital overlaps that form the σ and π bonds in the C=C double bond. The bond labeled A depicts side-to-side overlap of p orbitals and is therefore a π bond. The bond labeled B depicts end-to-end overlap of sp2 hybrid orbitals and is therefore a σ bond. As a result, the bond energy of B is greater than that of A because the orbital overlap is stronger in σ bonds than π bonds.
(Choice A) The bond energy of σ and π bonds cannot be the same because their orbital overlaps are not the same strength.
(Choices B) The bond energy of B is greater than A because orbital overlap is stronger in σ bonds than in π bonds.
(Choices D) Stronger orbital overlap results in greater bond energy rather than smaller bond energy.
Things to remember:
Sigma (σ) bonds result from end-to-end overlap of hybrid orbitals (combination of s and p atomic orbitals), whereas pi (π) bonds result from side-to-side overlap of p orbitals. σ bonds have stronger orbital overlap than π bonds, which results in σ bonds having greater bond energy than π bonds.
Passage:
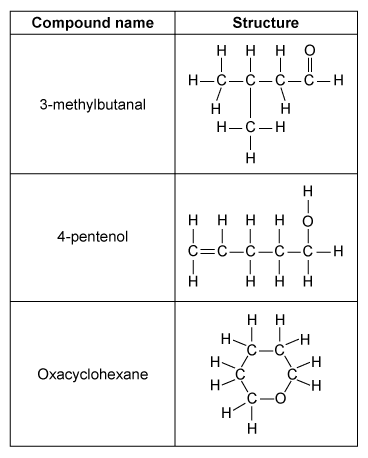
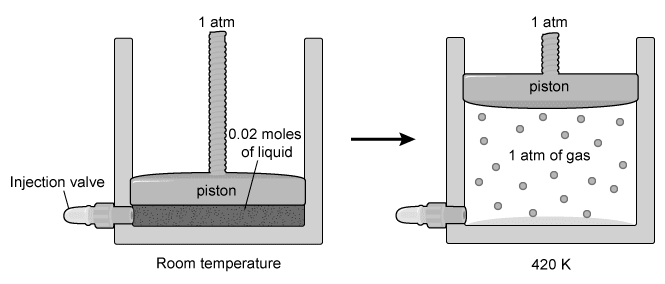
The three molecules shown in the table above are liquids at room temperature, and each have the molecular formula C5H10O. A 0.02 mole sample of each compound is separately injected into three identical containers, each with a movable piston. The compounds are vaporized by heating to 420 K, causing each piston to rise to keep the internal pressure equal to atmospheric pressure (1 atm), as illustrated below.
Question
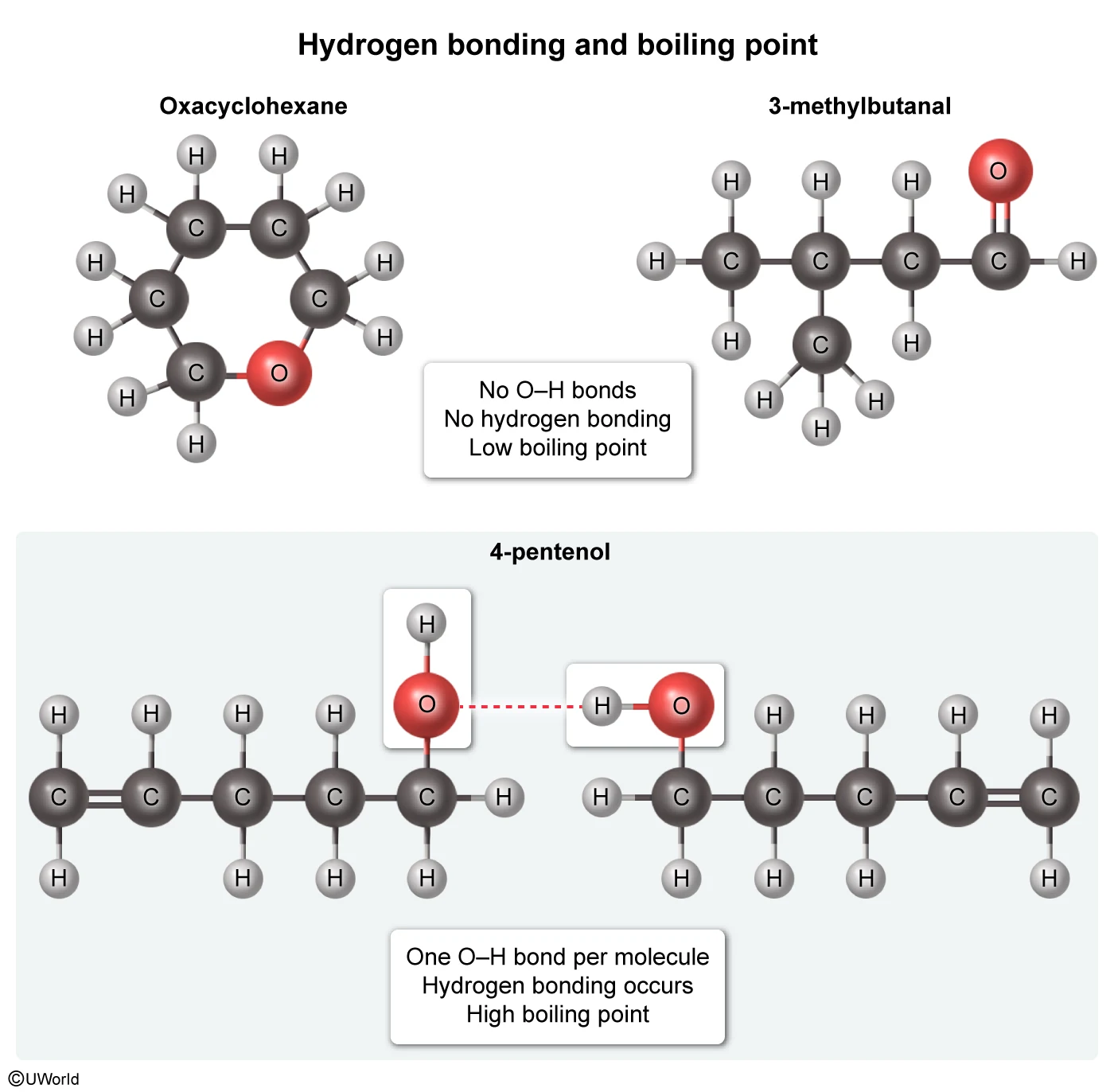
Oxacyclohexane and 3-methylbutanal each boil near 90 °C, but 4-pentenol boils at 141 °C. Which of the following interactions best explains why the boiling point of 4-pentenol is so much higher than the boiling points of the other molecules?
A. 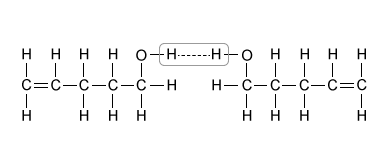 |
|
B. 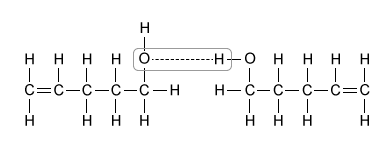 |
|
C. 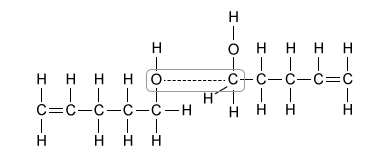 |
|
D. 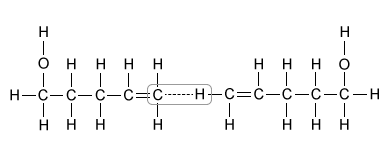 |
Explanation
The boiling point of a compound is determined by the strength of the intermolecular forces holding the molecules together. A compound boils when its thermal energy is sufficient to break these interactions, so the stronger the forces, the higher the boiling temperature.
All three molecules in the table have the same molecular formula (C5H10O), but the arrangement of the atoms differs in each, resulting in different intermolecular interactions. Hydrogen bonds are among the strongest intermolecular forces, and are capable of forming between an N, O, or F atom with a lone electron pair and a hydrogen atom that is covalently bound to a different N, O, or F atom.
Of the molecules in the table, only 4-pentenol can hydrogen bond with itself. This hydrogen bonding, depicted in Choice B, significantly increases the boiling point of 4-pentenol relative to the other compounds, and it accounts for the large difference in boiling points.
(Choice A) Hydrogen bonds occur between an H atom and an N, O, or F atom. They do not occur between two H atoms, as depicted in this option.
(Choice C) Interactions between carbon and oxygen can occur in all three molecules shown in the table, so they are unlikely to account for the difference in boiling point.
(Choice D) Interactions between carbon and hydrogen are examples of London dispersion forces, not hydrogen bonds. London dispersion forces are the weakest intermolecular forces and are present in all three molecules in the table to similar extents, so they most likely do not account for the boiling point difference.
Things to remember:
The boiling point of a compound depends on the strength of the intermolecular forces holding the molecules together. Strong forces such as hydrogen bonds yield higher boiling points than weaker forces such as London dispersion forces.
Passage:
An average sample of a pure, unidentified element is analyzed by mass spectrometry and five isotopes are detected, as listed in the table below.
| Isotope | Mass (amu) | Relative Abundance (mass percent) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90 | 51.34% |
| 2 | 91 | 11.22% |
| 3 | 92 | 17.15% |
| 4 | 94 | 17.38% |
| 5 | 96 | 2.80% |
Question
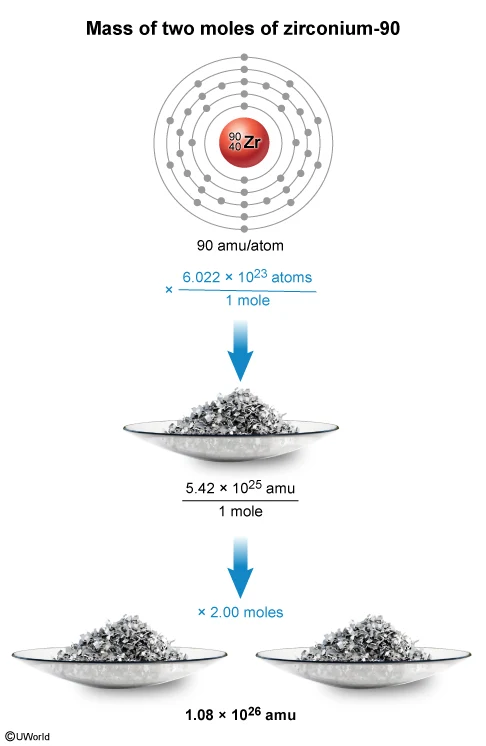
The mass of 2.00 moles of isotope 1 is approximately equal to
| A. 2.99 × 10−22 amu | |
| B. 1.80 × 102 amu | |
| C. 1.20 × 1024 amu | |
| D. 1.08 × 1026 amu |
Explanation
In a sample of a substance, individual particles of matter (ie, atoms, ions, molecules) are too small to be seen and counted separately. Instead, the relationship between the number of particles and their mass must be used. This relationship is provided by Avogadro's number (6.022 × 1023), which is the number of atomic mass units (amu) equal to a mass of exactly 1 gram.
6.022 × 1023 amu = 1.000 gram
Based on this relationship, a counting unit called the mole is defined as:
1 mole = 6.022 × 1023 particles
Accordingly, the number of atoms in 2.00 moles of isotope 1 is calculated as:
The table states that each atom of isotope 1 has a mass of 90 amu. Therefore, the mass (in amu) of 1.20 × 1024 atoms (2.00 moles) of isotope 1 is approximately equal to:
(Choice A) 2.99 × 10−22 amu is obtained if 2.00 moles is divided by Avogadro's number instead of multiplying during the first step of the calculation.
(Choice B) 1.80 × 102 amu is the mass of only 2 atoms of isotope 1. This value results from multiplying the isotope mass by 2 instead of multiplying by Avogadro's number.
(Choice C) 1.20 × 1024 amu is calculated if the number of atoms of isotope 1 is not multiplied by 90 amu (ie, effectively assumes that the atoms have a mass of 1 amu).
Things to remember:
The number of particles in a sample is related to the sample mass through Avogadro's number (6.022 × 1023), which is defined as 1 mole.
Compound Structure and Properties Practice Test
Question
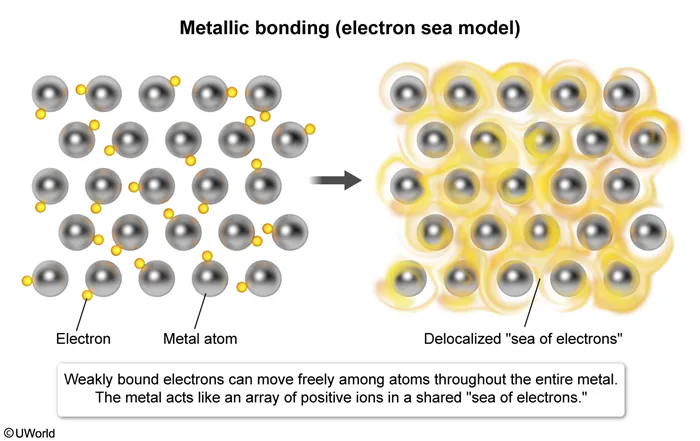
Which of the following diagrams best represents a solid with metallic bonds?
A.
|
|
B.
|
|
C.

|
|
D.
|
Explanation
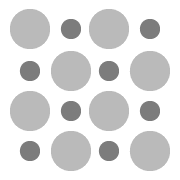
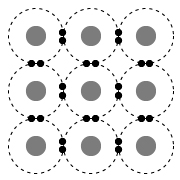
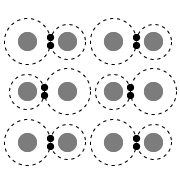
Substances can be classified by their molecular bonding characteristics and physical properties. Metallic bonds form when two or more metal atoms share valence electrons. The valence electrons in a metallic solid are weakly bound, allowing them to move freely among all metal atoms in the solid. As such, metallic compounds can be conceptualized as an array of metal nuclei surrounded by a delocalized "sea of electrons."
Because the valence electrons in metallic bonds can move freely between metal atoms, metallic bonds are nondirectional and remain intact, regardless of orientation. This characteristic causes metallic solids to be ductile and malleable when placed under stress. This feature also causes metals to have a high melting point and to be electrically conductive in both solid and liquid states.
The diagram in Choice C best represents a solid with metallic bonds because it depicts delocalized valence electrons moving freely among atomic nuclei.
(Choice A) This diagram best represents an ionic solid held together by ionic bonds (ie, strong electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions).
(Choice B) This diagram best represents a solid held together by a network of covalent bonds. Covalent-network compounds are large groups of repeating structures interconnected by covalent bonds. These networks function like one large multiatomic molecule.
(Choice D) This diagram best represents a molecular solid consisting of discrete molecules. The atoms in each molecule are covalently bonded, but the molecules themselves are aggregated together in the solid by weak, noncovalent, intermolecular interactions between neighboring molecules.
Things to remember:
Metallic bonds form when two or more metal atoms share weakly bound valence electrons that can move freely among all metal atoms joined in a metallic solid. Metallic compounds can be conceptualized as an array of metal nuclei surrounded by a delocalized "sea of electrons."
Question
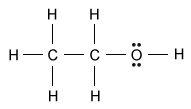
The structure of ethanol, CH3CH2OH, is represented by the Lewis diagram above. Which of the following statements best describes the C–H and C–C bonds in an ethanol molecule?
| A. The C–H bonds are ionic bonds, whereas the C–C bond is a nonpolar covalent bond. | |
| B. The C–H bonds are polar covalent bonds, whereas the C–C bond is a nonpolar covalent bond. | |
| C. The C–H bonds are nonpolar covalent bonds, whereas the C–C bond is a polar covalent bond. | |
| D. The C–H and C–C bonds are all nonpolar covalent bonds. |
Explanation
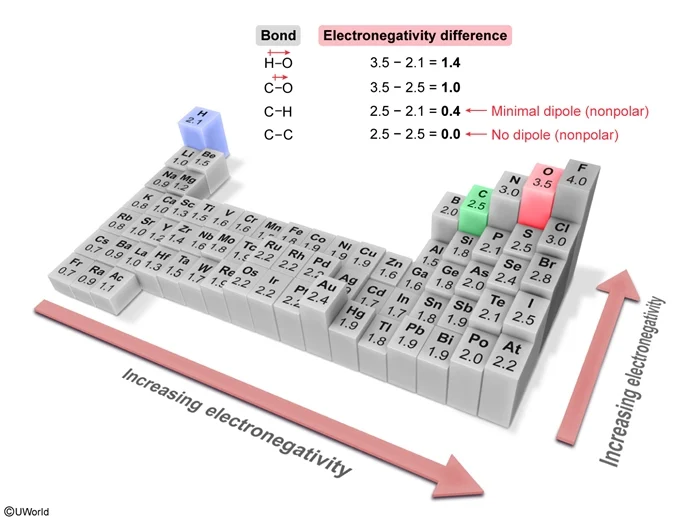
The type of bond formed between two atoms generally depends on the relative difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved. A large difference in electronegativity promotes electron transfer between atoms, which causes ionic bond formation (usually between a metal and a nonmetal). A small difference in electronegativity promotes electron sharing between atoms, which causes covalent bond formation (usually between two nonmetals).
If the electronegativities of two atoms in a covalent bond are significantly different, the electrons in the bond are shared unequally between the atoms, which results in a dipole and produces a polar covalent bond. Conversely, if the electronegativities of two atoms in a covalent bond are similar, the result is a nonpolar covalent bond.
Hydrocarbon bonds (ie, bonds involving only C and H) are examples of nonpolar covalent bonds. Although carbon is a little more electronegative than hydrogen, a C–H bond is essentially nonpolar because the electronegativity difference is small. Similarly, C–C bonds are nonpolar covalent bonds because atoms of the same element have no difference in electronegativity.
(Choice A) The C–H bonds are not ionic bonds because C and H are both nonmetals and do not have a large enough difference in electronegativity to cause ion formation.
(Choices B and C) The differences in electronegativity between the atoms of a C–C bond and a C–H bond are too small for either bond to be considered polar. In ethanol, only the C–O and O–H bonds can be considered polar.
Things to remember:
The difference in electronegativity between two bonded atoms determines the polarity of the bond between the atoms. Larger differences in electronegativity cause larger dipole moments (ie, greater polarity). When the electronegativities of two atoms in a covalent bond are similar, the bond is nonpolar.
Question
| Bond | Bond Length (pm) |
|---|---|
| C–N | — |
| C=N | 138 |
| C≡N | — |
Based on the bond length in the table above, which of the following are the most probable bond lengths of the C–N and C≡N bonds, respectively?
| A. 116 pm, 143 pm | |
| B. 116 pm, 138 pm | |
| C. 143 pm, 116 pm | |
| D. 143 pm, 138 pm |
Explanation
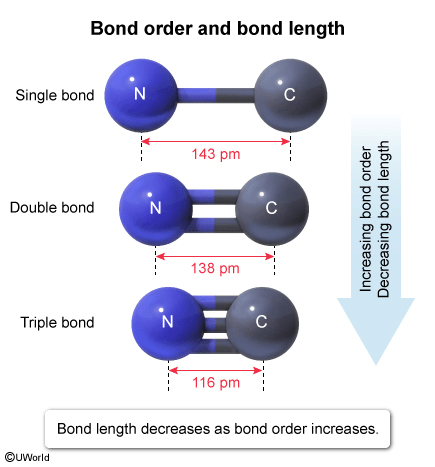
A covalent bond forms when two atoms share electrons. Single, double, or triple bonds can form between two atoms, depending on the how many electron pairs are shared (ie, the bond order). Bond length is the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in the bond, which depends largely on the bond order. As the bond order increases, there is more electron density between the atoms, which draws the atoms closer together and decreases the bond length.
The table in the question states that a C=N double bond (bond order = 2) has a bond length of 138 pm. Because bond length decreases as bond order increases, a C–N single bond (bond order = 1) should be longer than 138 pm, but a C≡N triple bond (bond order = 3) should be shorter than 138 pm. Therefore, 143 pm and 116 pm are plausible bond lengths for a C–N single bond and a C≡N triple bond, respectively.
(Choice A) When comparing the bond length of a single and triple bond between the same two atoms (eg, C–N and C≡N), the single bond will be longer than the triple bond.
(Choices B and D) A double and a triple bond between the same two atoms (eg, C=N and C≡N) cannot have the same bond length because a triple bond has more electron density pulling the atoms closer together than in a double bond.
Things to remember:
Bond length depends largely on the bond order (ie, number of bonds between two atoms). As the bond order increases, there is more electron density between the atoms, which draws the atoms closer together and decreases the bond length.
Intermolecular Forces and Properties Practice Test
Question
A bubble of air with a volume of 21 L is released from a submarine at an ocean depth where the pressure is 6.0 atm. If the bubble expands to a volume of 140 L as it rises near the ocean surface where the temperature is 27 °C and the pressure is 1.0 atm, what is the temperature of the saltwater at the ocean depth where the bubble is released?
| A. −3 °C | |
| B. 7.5 °C | |
| C. 24 °C | |
| D. 30 °C |
Explanation
An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas with well-behaved (idealized) characteristics used to make a simplified model of the behavior of real gases. Following this model, the behavior of a gas can be described by the ideal gas law:
where P is the pressure, V is the volume occupied, n is the number of moles of gas, T is the absolute temperature (Kelvin), and R is a constant. This equation can be rearranged as
For processes in which P, V, and T change but n does not, the initial conditions (indicated by the subscript 1) can be related to the final conditions (indicated by the subscript 2) by the combined gas law:
or simply
In this question, the initial conditions are P1 = 6.0 atm, V1 = 21 L, and T1 = ?, and the final conditions are P2 = 1.0 atm, V2 = 140 L, and T2 = 27 °C (300 K). Solving the combined gas law for T1 and substituting the condition values into the equation yields:
The temperature in Celsius must be converted to Kelvin by adding 273 to give
Without a calculator, this can be solved by factoring and canceling terms
Converting this temperature to Celsius by subtracting 273 yields an initial temperature of −3° C.
(Choice B) A temperature of 7.5 °C results from the P1/P2 ratio being inverted as P2/P1 during the calculation.
(Choice C) An initial temperature of 24 °C results if T2 (27 °C) is not converted to Kelvin prior to the calculation.
(Choice D) A temperature of 30 °C results from both the P1/P2 and V1/V2 ratios being inverted and from T2 not being converted to Kelvin prior to the calculation.
Things to remember:
When the moles of gas in a system remain constant, the ideal gas law can be expressed as the combined gas law to evaluate gas behavior under changing conditions of pressure, volume, and absolute temperature.
Question
2 NI3(s) → N2(g) + 3 I2(g)
A sample of NI3(s) is placed within a rigid, previously evacuated reaction vessel and fully decomposed at a temperature of 20 °C, according to the equation above. After the reaction, the pressure inside the vessel is 1.20 atm. What is the pressure exerted by the I2(g) in the vessel?
| A. 0.30 atm | |
| B. 0.60 atm | |
| C. 0.90 atm | |
| D. 1.20 atm |
Explanation
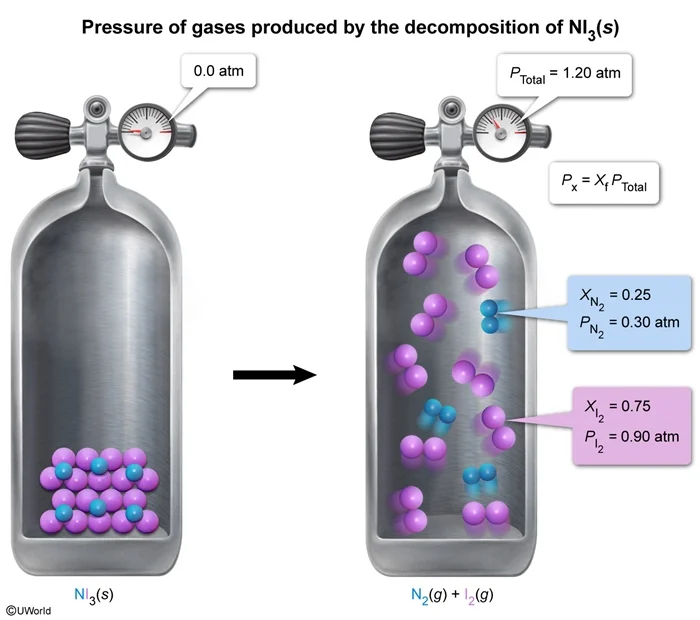
Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the total pressure PTotal in a vessel containing a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressure Px of each component gas within the vessel.
The partial pressure of a gas can be determined using its mole fraction Xf (ie, the moles of component gas nx divided by the total number of moles nTotal).
In the decomposition of NI3(s) described in the question, the sample is placed within a rigid, previously evacuated reaction vessel (ie, no air in the vessel). As a result, the only gases in the vessel at the end of the reaction are the products N2(g) and I2(g). The reaction equation shows that each reaction cycle produces 4 moles of gas. This means that the final product mixture is 25% N2(g) and 75% I2(g), as indicated by the mole fraction of each gas.
Multiplying the total pressure by the mole fraction of I2(g) gives the partial pressure of I2(g):
(Choice A) A pressure of 0.30 atm is exerted by the N2(g).
(Choice B) The difference in the pressures exerted by the N2(g) and I2(g) is 0.60 atm. Based on the mole ratio of the reaction, the pressure exerted by the I2(g) must be 3 times greater than the pressure exerted by the N2(g).
(Choice D) The total pressure in the vessel is 1.20 atm, which is the sum of the partial pressures exerted by the N2(g) and I2(g), as demonstrated by:
Things to remember:
The pressure of an ideal gas does not depend on the identity of the gas. At a given temperature and volume, the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure exerted by each component gas, which is proportional to its mole fraction.
Question
Which of the following techniques would allow for separation of a mixture of two liquids based on intermolecular interactions with mobile and stationary phases?
| A. Distillation | |
| B. Column chromatography | |
| C. Filtration | |
| D. Titration |
Explanation
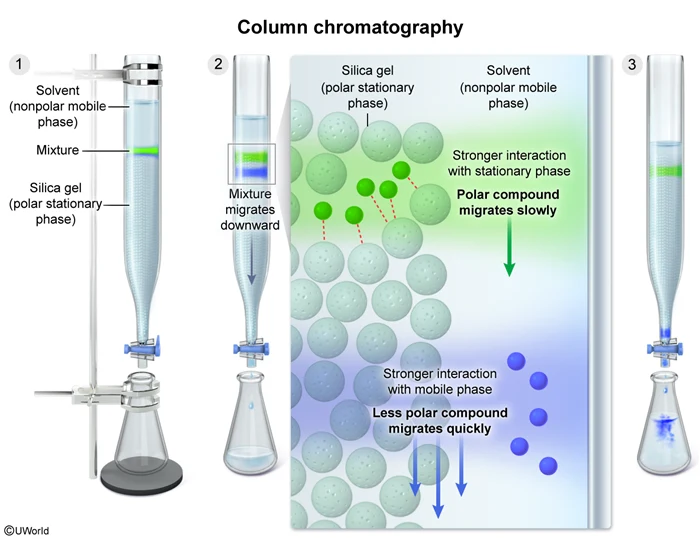
Chromatography (eg, column chromatography, thin-layer chromatography, or paper chromatography) is a technique that uses a stationary phase and a solvent (a mobile phase) to separate the components of a mixture according to their polarity. Separation occurs because the mixture components travel at different rates, depending on the strength of the competing intermolecular interactions between the mixture component and the stationary and mobile phases.
For example, when a mixture is separated by column chromatography using a polar stationary phase and a nonpolar mobile phase, a more polar compound will travel slowly down the column because it has stronger intermolecular interactions with the stationary phase than with the mobile phase. Conversely, a less polar compound will travel quickly down the column because it has stronger intermolecular interactions with the mobile phase than with the stationary phase.
Therefore, column chromatography can be used to separate a mixture of two liquids based on intermolecular interactions with a stationary and mobile phase.
(Choice A) Although distillation can be used to separate a mixture of two liquids, distillation does not have a mobile and a stationary phase. Instead, it is based on boiling points and intermolecular forces between the molecules of the mixture.
(Choice C) Filtration is a physical process used to separate a solid from a liquid, and cannot be used to separate a mixture of liquids.
(Choice D) Titration is a technique used for acid-base neutralization.
Things to remember:
Separation of a mixture using chromatography occurs because the mixture components travel through the column at different rates, depending on the strengths of the competing intermolecular interactions between each component and the stationary phase and mobile phase.
Chemical Reactions Practice Test
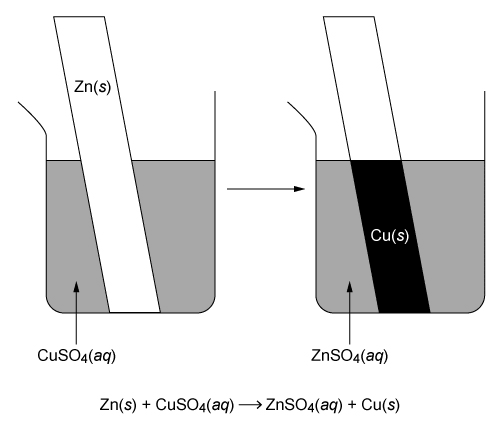
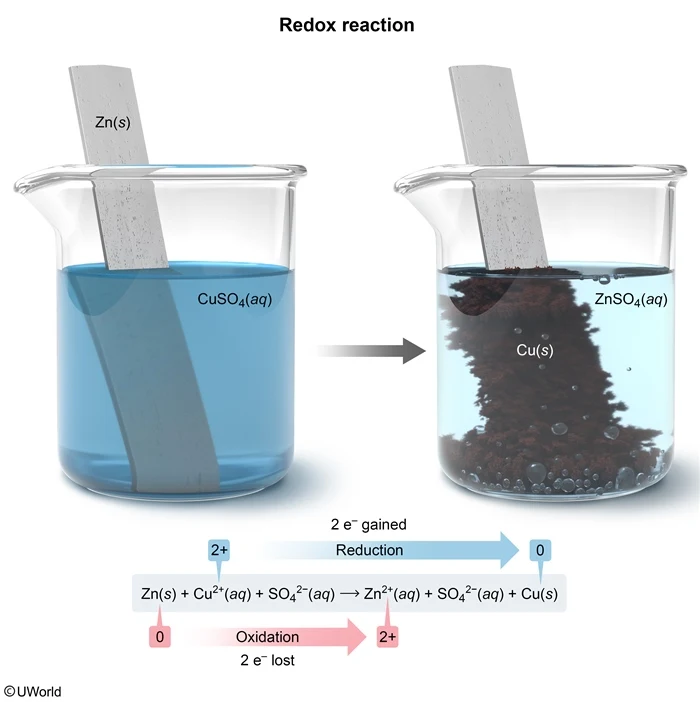
Question
A Zn(s) strip is placed in a CuSO4(aq) solution. A redox reaction occurs, depositing a solid on the Zn(s) strip. Which of the following describes the redox reaction depicted in the diagram above?
| Species being oxidized | Species being reduced | Electrons transferred | ||
| A. Zn | SO42− | 4 | ||
| B. Cu2+ | Zn | 2 | ||
| C. Zn | Cu2+ | 2 | ||
| D. Cu2+ | SO42− | 4 |
Explanation
Redox reactions occur when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. The atom that loses the electron(s) becomes oxidized, and the atom that gains the electrons from the oxidized atom becomes reduced. Oxidation and reduction must occur simultaneously in a redox reaction. The oxidation number of the oxidized atom will increase by the number of electrons lost, and the oxidation number of the reduced atom will decrease by the number of electrons gained.
This question states that a Zn(s) strip is placed in a CuSO4(aq) solution, and Cu(s) is deposited on the Zn strip as a result of the redox reaction.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) + SO42−(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + SO42−(aq) + Cu(s)
Initially, the oxidation number of Zn(s) is 0 because Zn(s) is in its elemental state, but the oxidation number of the ionically bound Cu ion in CuSO4 is +2. During the reaction, Cu2+ becomes reduced to elemental Cu(s) with an oxidation number of 0.
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e− (oxidation)
Cu2+(aq) + 2e− → Cu(s) (reduction)
Therefore, Cu2+ gains 2 electrons, which are lost from Zn as it becomes oxidized to Zn2+. Because the oxidation numbers of Zn and Cu change by 2 units, 2 electrons are transferred in the redox reaction.
(Choices A and D) SO42− is not reduced because its oxidation number is the same on both sides of the reaction arrow, and Cu2+ is not oxidized because it gains electrons rather than losing them. In addition, 2 rather than 4 electrons are transferred in this redox reaction.
(Choice B) Zn and Cu2+ become oxidized and reduced, respectively. This choice has reversed the species being oxidized and reduced.
Things to remember:
Redox reactions occur when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. An atom becomes oxidized when it loses electrons and reduced when it gains electrons. As a result of oxidation or reduction, an atom's oxidation number increases or decreases, respectively, by the number of electrons lost or gained.
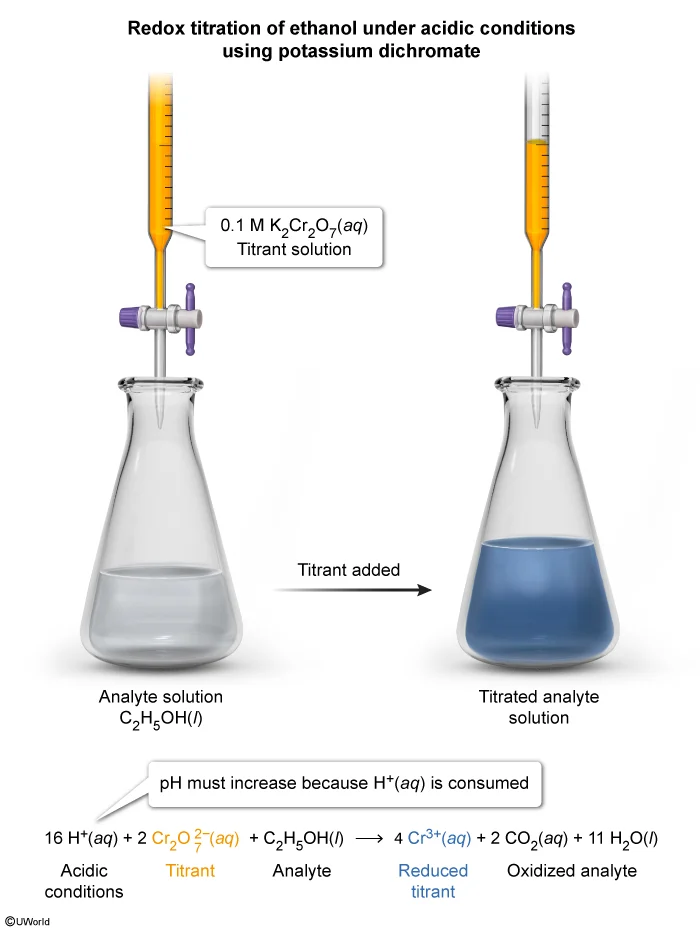
Question
An acidic solution containing an unknown amount of C2H5OH(l) is titrated with a solution of 0.1 M K2Cr2O7(aq). The endpoint is determined when the color of the unknown solution turns blue. As the titration proceeds, the pH of the solution increases. Which of the following equations represents the reaction that occurs as the titration proceeds?
| A.
|
|
| B.
|
|
| C.
|
|
| D.
|
Explanation
During a titration, a titrant (ie, a reactant solution with a known concentration) is slowly added to a solution containing an unknown concentration of an analyte (ie, a species to be detected or measured). A reaction that occurs between the titrant and the analyte is used to detect and calculate the amount of the analyte that is present.
In a redox titration, the reaction that occurs between the titrant and the analyte is an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction. The equivalence point occurs when all the analyte in the solution has reacted. This can be detected either by using an electrode to monitor the solution potential (voltage) or by an indicator that changes color when the reaction is completed.
During the redox reaction described in this question, the K2Cr2O7(aq) in the titrant solution oxidizes the C2H5OH(l), causing it to decompose into CO2(g) and H2O(l). Because the titration is performed in an acidic solution (ie, with an excess of H+ ions) and the pH is observed to increase, some of the H+(aq) ions must be consumed as reactants during the reaction. Among the four equation choices, only Choice B shows H+(aq) being consumed.
(Choice A) This reaction incorrectly shows H+(aq) being produced from the redox titration. Production of H+(aq) would cause the pH to decrease.
(Choice C) Although this reaction would lead to an increase in pH because OH−(aq) is being produced, this equation is for a redox titration in a basic, rather than an acidic, solution.
(Choice D) This reaction incorrectly has OH−(aq) being consumed and H2O(l) being produced. This would cause a decrease in pH, not an increase.
Things to remember:
In a redox titration, an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction occurs between the titrant and the analyte. Redox titrations can be done in acidic, basic, or neutral solutions and may cause pH changes.
Question
NH3(aq) + HCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq)
Two aqueous solutions containing 3.0 g of ammonia (NH3) and 6.4 g of hydrochloric acid (HCl), respectively, are mixed in a beaker, and the reaction shown above goes to completion. The water is evaporated, leaving crystals of solid ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). The crystals are placed on weigh paper and weighed, and a mass of 9.7 g is recorded. If each of the following errors occurred during the experiment, which would not help account for the excess mass?
| A. Some of the water was not evaporated and remained in the sample. | |
| B. The mass of the weigh paper was not determined prior to weighing the sample. | |
| C. The molar mass of ammonium chloride was not calculated correctly. | |
| D. The beaker was not cleaned properly prior to use in the experiment. |
Explanation
The law of conservation of mass states that atoms in a chemical reaction cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged. Because each atom has a fixed mass, the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the products.
In the experiment, 9.4 g of reactants (3.0 g of ammonia (NH3) and 6.4 g of hydrochloric acid (HCl)) were mixed. Because the reaction went to completion, the mass of the resulting ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) product should be 9.4 g. However, the measured mass of the crystals was 9.7 g, so 0.3 g must have been contributed by one or more sources other than the NH4Cl produced by the reaction. These sources may have been introduced by the following errors:
- Incomplete evaporation of the water, which causes a small amount of water to remain in the crystals and contribute additional mass (Choice A).
- Failure to account for the mass of the weigh paper, causing the mass of the paper itself to be included in the final measurement (Choice B).
- Failure to properly clean the beaker prior to the experiment, which causes any contaminants in the beaker to contribute additional mass to the products (Choice D).
The question asks which of the errors would not contribute to the excess mass. An incorrect calculation of the molar mass of NH4Cl could contribute to an incorrect calculation of the number of moles of NH4Cl obtained, but measured quantities such as the mass of the crystals are independent of calculated quantities such as the molar mass of NH4Cl.
Things to remember:
Atoms in a chemical reaction are neither created nor destroyed. Therefore, the mass of the reactants in a reaction equals the mass of the products.
Kinetics Practice Test
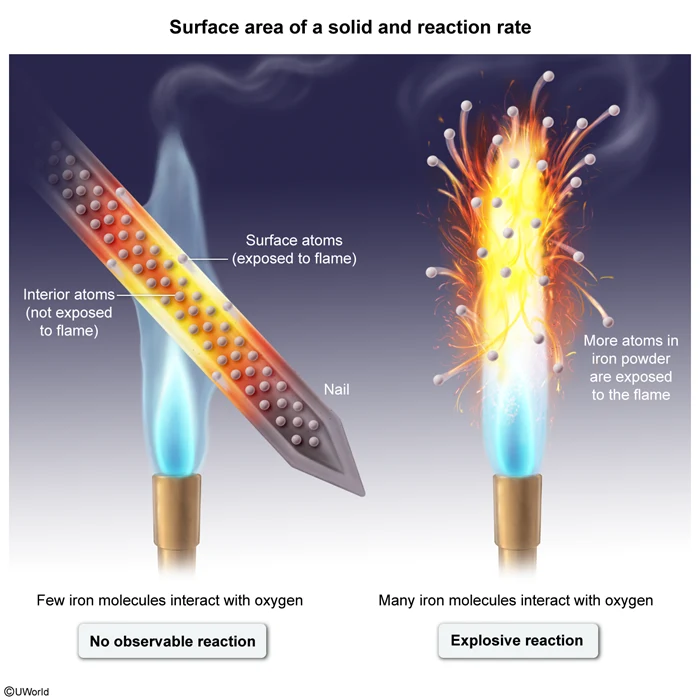
Question
When a clean iron nail with a mass of 20. g is exposed to a flame, no reaction happens. When a 20. g sample of iron filings ground into a fine powder is exposed to a flame, it reacts explosively according to the equation above. Which of the following statements correctly explains why the second reaction occurs but not the first?
| A. The surface area of the iron filings is greater than the surface area of the nail. | |
| B. The boiling point of the filings is lower than the melting point of the nail. | |
| C. The intermolecular forces in the iron filings are weaker than those in the nail. | |
| D. The oxidation number of the iron atoms in the filings is greater than that of the atoms in the nail. |
Explanation
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on the frequency of collisions between particles. Faster reactions have more frequent collisions than slower reactions. Molecular collisions can occur more frequently when more particles are exposed to each other. For solids, an increased surface area leads to more frequent collisions between the solid and its surroundings.
The question asks about two samples of iron of equal mass (ie, equal number of particles in each). In the first sample, most of the iron atoms are on the inside of the nail (ie, little surface area), so these atoms do not interact with the surrounding air. This causes the reaction to happen so slowly that it effectively does not occur at all.
In contrast, the second sample is a fine powder. More of the iron atoms in this sample are exposed to the surrounding air (ie, the powder has a greater surface area than the nail), allowing more frequent collisions and a much faster, explosive reaction.
(Choices B, C, and D) Both samples are made of elemental iron and as such have the same melting point, intermolecular forces, and oxidation number. Additionally, these properties do not impact the rate of a reaction.
Things to remember:
The rate of a reaction increases with increasing frequency of collisions between particles. For solids, collisions with surrounding gas or liquid particles are more frequent when the solid has a greater surface area.
Question
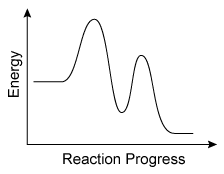
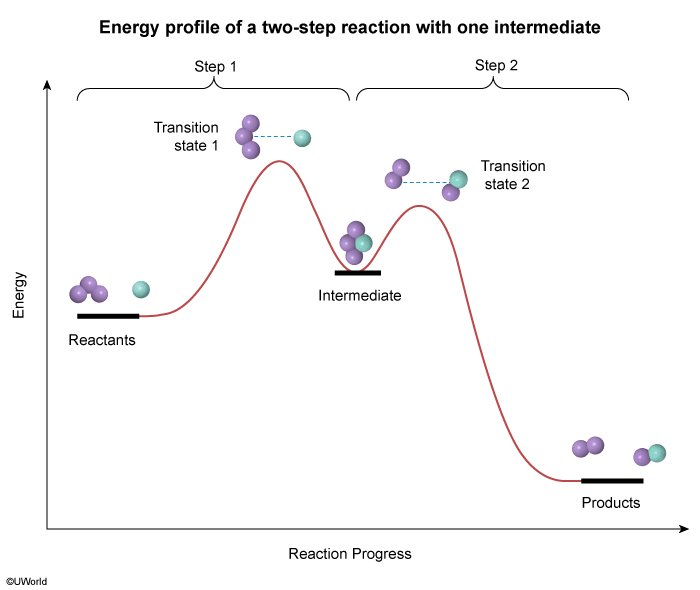
The energy profile of a reaction is shown in the diagram above. Based on the profile, which of the following correctly states the number of transition states involved in the reaction and the number of chemical intermediates that are formed during the reaction?
| Transition States | Intermediates | ||
| A. 1 | 2 | ||
| B. 2 | 1 | ||
| C. 2 | 2 | ||
| D. 3 | 1 |
Explanation
During a reaction, existing bonds are broken, and new bonds are formed. Each step in this process results in a momentary, high-energy transition state that is seen as a peak on a reaction energy diagram (one peak for each step). Intermediates that form during the process appear as "valleys" between the peaks.
For the reaction in this question, the energy profile in the diagram has two peaks, indicating that the reaction happens in two steps and forms two transition states (one for each step). The energy profile also shows one valley between the peaks, indicating that one intermediate is formed.
Therefore, there are two transition states and one chemical intermediate formed during the reaction.
(Choices A and C) The two peaks in the energy profile indicate that there are two steps in the reaction, but these peaks signify transition states, not intermediates.
(Choice D) There are a total of three arcs in the profile (ie, two "peaks" and one "valley"), but only the peaks indicate the number of transition states. The "valley" between the peaks indicates an intermediate.
Things to remember:
On a reaction energy diagram, one transition state peak is seen for each elementary step in the reaction mechanism. Intermediates that form during the reaction process appear as "valleys" between the peaks.
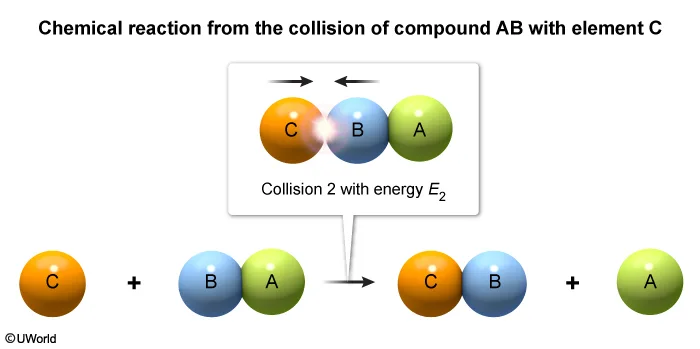
Question
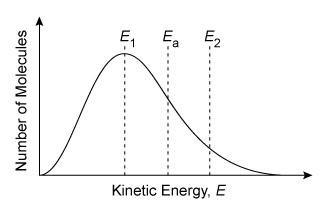
Consider the single-step reaction AB + C → BC + A, in which one particle of compound AB collides with a particle of element C. Two possible collision orientations are shown above, and the kinetic energy distribution of the reacting molecules and the activation energy Ea of the reaction are shown in the graph below.
Which of the following collision orientations and energies (E1 or E2) is most likely to be effective in forming the products BC and A?
| A. Collision 1 with energy E1 | |
| B. Collision 1 with energy E2 | |
| C. Collision 2 with energy E1 | |
| D. Collision 2 with energy E2 |
Explanation
According to collision theory, a reaction can occur between two molecules only when the molecules collide with enough energy and the correct orientation. The minimum energy needed for the reactant molecules to reach the transition state and initiate a reaction is called the activation energy Ea. Molecules that collide with less than the minimum Ea cannot react to form products.
At a given temperature, some molecules of a liquid or a gas in a reaction vessel move more slowly (lower kinetic energy) while other molecules move more quickly (higher kinetic energy). This causes the molecules to display a wide range of kinetic energies, which is represented graphically by the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
The area under a portion of the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve indicates the percentage of the total number molecules that exist within that range of kinetic energies (more area means a greater percentage). Increasing the temperature shifts and widens the distribution toward higher molecular speeds (ie, higher kinetic energies). However, at any temperature, the only molecules that can react are those with an energy that is greater than or equal to Ea.
Two molecules with enough energy to react must also be oriented so that new bonds can be formed between two atoms as other bonds are broken. In this question, only collision 2 orients the molecules so that atoms B and C can interact to form a new B–C bond as the A–B bond is broken.
(Choices A and B) These scenarios will not form products because they have an incorrect collision orientation.
(Choice C) This scenario has the correct collision orientation but will not form products because it has insufficient energy (E1 < Ea).
Things to remember:
A reaction can occur between two molecules only when the molecules collide in the correct orientation and with an energy that is greater than or equal to the activation energy for the reaction.
Thermodynamics Practice Test
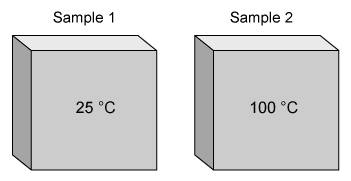
Question
The figure above represents two samples of iron, each at different temperatures. In which sample are the vibrations of the atoms the fastest?
| A. Sample 1 | |
| B. Sample 2 | |
| C. The atoms in both samples have the same kinetic energy. | |
| D. It cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the samples. |
Explanation
At all temperatures above absolute zero, the atoms and molecules in matter are in constant motion. In solids, the motion is primarily vibrational (ie, atoms vibrating in one place). The kinetic energy (energy of motion) of the atoms and molecules in a sample is proportional to the temperature of the sample. Therefore, as the temperature of the sample increases, the kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in the sample increases.
For the two samples of iron described in this question, sample 1 is at a lower temperature than sample 2. Because atoms vibrate faster at higher temperatures, the atoms in sample 2 are vibrating faster than the atoms in sample 1.
(Choice A) Because kinetic energy is proportional to temperature, the atoms in sample 1 (lower temperature sample) are vibrating slower than the atoms in sample 2.
(Choice C) Because temperature is proportional to kinetic energy and the samples are at different temperatures, the atoms in sample 1 and sample 2 cannot have the same kinetic energy.
(Choice D) The mass of an object does not affect the rate of vibration of its individual particles. The masses of the individual particles affect the vibrational rate but because both samples are the same substance (iron, in this case), the atoms in each have the same average mass.
Things to remember:
The kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a sample is proportional to the temperature of the sample. As the temperature of a sample increases, the kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in the sample increases.
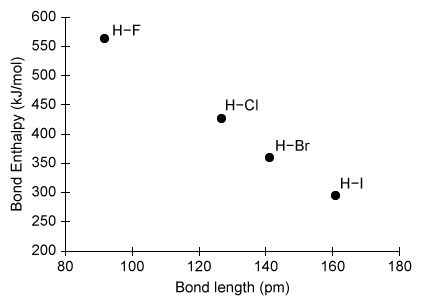
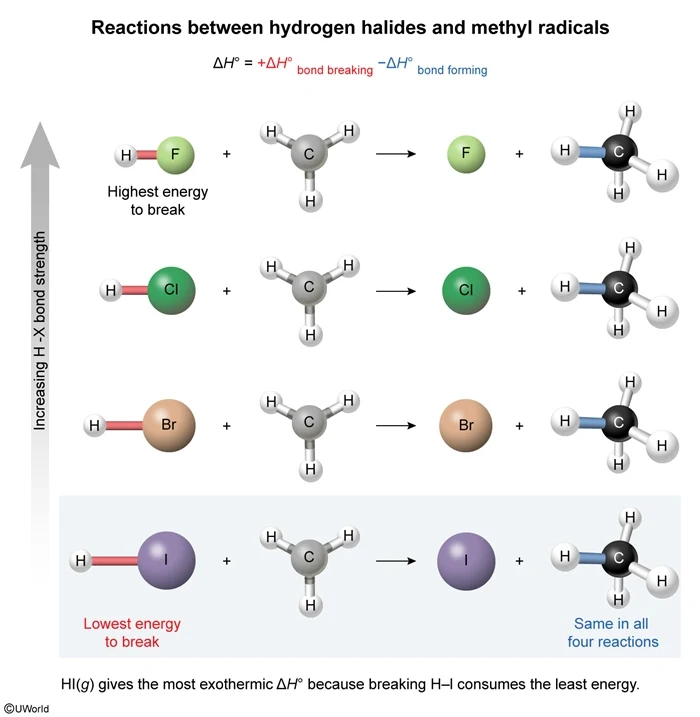
Question
The strength of a chemical bond can be measured using bond enthalpies. Based on the bond enthalpies shown in the graph above, which of the following radical reactions will be most exothermic?
| A. HCl(g) + CH3(g) → Cl(g) + CH4(g) | |
| B. HBr(g) + CH3(g) → Br(g) + CH4(g) | |
| C. HF(g) + CH3(g) → F(g) + CH4(g) | |
| D. HI(g) + CH3(g) → l(g) + CH4(g) |
Explanation
Bond enthalpy (ΔH°bond), also known as bond dissociation energy, is the amount of energy needed to break a particular bond in 1 mole of a molecule in the gas phase. The amount of energy associated with a bond indicates its strength (eg, stronger bonds require more energy to break than weaker bonds). During a chemical reaction, existing bonds must absorb energy to break (an endothermic process with +ΔH°bond), and when new bonds are formed, energy is released (an exothermic process with −ΔH°bond).
The ΔH° of a chemical reaction can be calculated using sums of measured bond enthalpies, according to the following equation:
In this question, hydrogen halides (H–X, where X = F, Cl, Br, and I) are reacted with methyl radicals (CH3) to form halogen atoms (X) and methane (CH4). The amount of energy released from bond formation is the same in all four reactions because each reaction forms one C–H bond. As such, the net ΔH° of each reaction depends on how much energy is consumed in breaking the H–X bond. According to the graph above, the H-I bond has the lowest ΔH°bond and therefore consumes the least energy when broken. As a result, the reaction between H–I and CH3 will be most exothermic.
(Choices A and B) Both H–Cl and H–Br have bond enthalpies greater than that of H–I; therefore, their reactions with CH3 will release less energy.
(Choice C) H–F has the largest bond enthalpy (ie, absorbs the most energy when broken); consequently, the reaction between H–F and CH3 will be least exothermic.
Things to remember:
The energy required to break a chemical bond is called the bond enthalpy (ΔH°bond). Breaking bonds absorbs energy (+ΔH°bond), whereas forming bonds releases energy (−ΔH°bond). The net enthalpy of a reaction (ΔH°) is the sum of ΔH°bond from each bond-breaking and bond-forming step.
Question
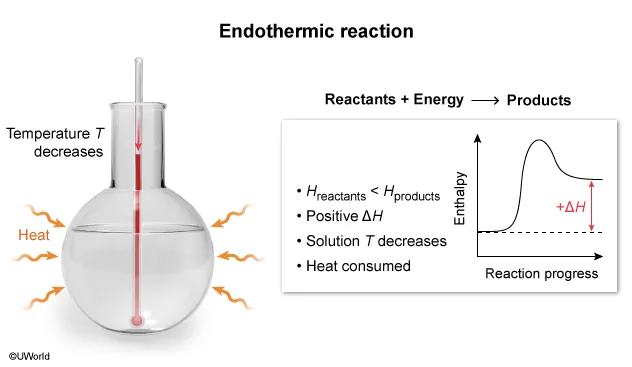
NH4NO3(s) → NH4+(aq) + NO3−(aq)
A student dissolves NH4NO3(s) into H2O(l) and observes an endothermic reaction that proceeds according to the net-ionic equation above. Which of the diagrams below best represents the heat transfer and change in solution temperature T observed by the student during the reaction?
A. 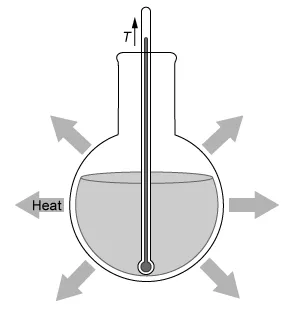 |
|
B. 
|
|
C. 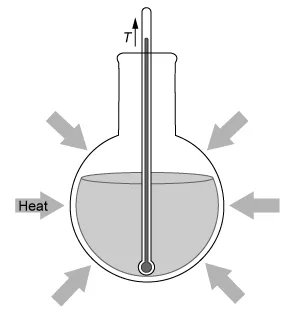 |
|
D. 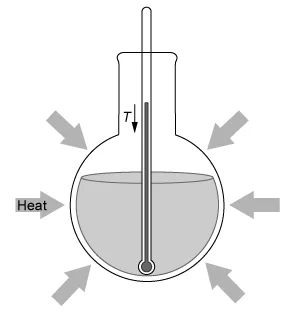 |
Explanation
An exothermic reaction is a process that releases energy (eg, heat, light) to the surroundings.
Reactants → Products + Energy
Because energy is liberated as a product of an exothermic reaction, the reaction mixture's temperature increases as heat is generated and then transferred from the warmer reaction system to the cooler surrounding environment.
Conversely, an endothermic reaction is a process that absorbs energy from the surroundings.
Reactants + Energy → Products
Because energy is consumed like a reactant in an endothermic reaction to enable the reaction to proceed, the reaction mixture's temperature decreases, and heat is absorbed from the warmer surrounding environment by the cooler reaction system.
The change in enthalpy ΔH evaluates the change in the total energy of the system following a reaction or process.
ΔH = Hproducts − Hreactants
If the products are lower in energy than the reactants, ΔH is negative (ie, energy is released from the system). When the products are higher in energy than the reactants, ΔH is positive (ie, energy is absorbed by the system).
In this question, dissolving NH4NO3(s) into H2O(l) is observed to be an endothermic reaction. Therefore, the temperature of the reaction mixture decreases, and heat is absorbed from the warmer surrounding environment, as depicted by the diagram in Choice D.
(Choice A) This diagram depicts an exothermic reaction, but the given reaction is endothermic.
(Choice B) This diagram shows heat being generated and released from the system (an exothermic reaction) with an incorrect change in temperature. If heat is generated by the solution, the solution temperature must increase.
(Choice C) This diagram correctly shows heat being absorbed by the system (an endothermic reaction) but has an incorrect change in temperature. If heat is consumed by the reaction, the solution temperature must decrease.
Things to remember:
An exothermic reaction mixture's temperature increases as heat is generated and then released from the system to the surroundings. An endothermic reaction mixture's temperature decreases as heat is absorbed from the surroundings and consumed by the reaction system.
Equilibrium Practice Test
Question
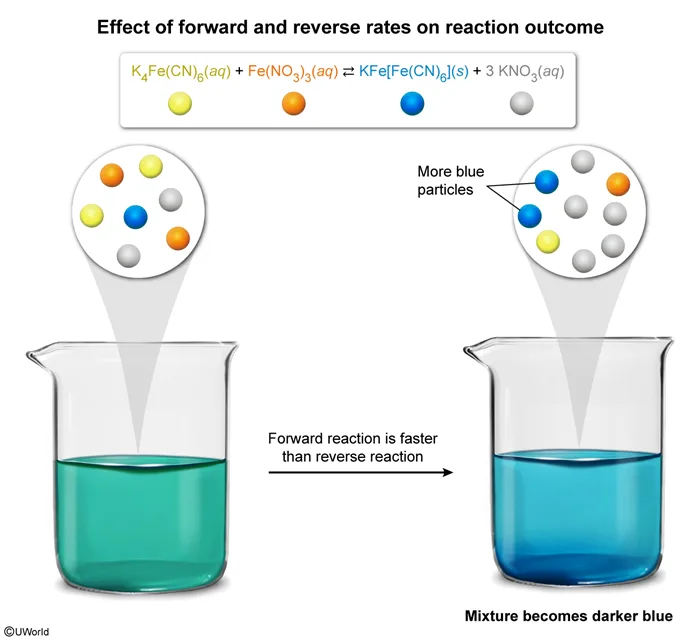
K4Fe(CN)6(aq) + Fe(NO3)3(aq) ⇄ KFe[Fe(CN)6](s) + 3 KNO3(aq)
K4Fe(CN)6(aq) and Fe(NO3)3(aq) are yellow solutions. KFe[Fe(CN)6](s) is a blue solid that can be suspended in water, and KNO3(aq) is a colorless solution. If these four compounds are mixed together so that the rate of the forward reaction is twice as fast as the reverse reaction, then
| A. the amount of KNO3 will increase, resulting in a mixture with less color. | |
| B. the amount of KFe[Fe(CN)6] will increase, resulting in a darker blue suspension. | |
| C. the amounts of K4Fe(CN)6 and Fe(NO3)3 will increase, giving the mixture a yellower appearance. | |
| D. product and reactant levels will remain constant because the mixture contains twice as many product molecules as reactant molecules. |
Explanation
In reversible reactions, reactants can be converted to products and products can be converted back to reactants. When products and reactants are present in the same vessel, both the forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously. If the forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction, there will be a net formation of products. If the reverse reaction is faster, there will be a net formation of reactants. If forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, the system is in equilibrium, and no net formation of products or reactants occurs.
The question states that the given forward reaction is twice as fast as the reverse reaction, and therefore the products (KFe[Fe(CN)6] and KNO3) will form faster than the reactants. KNO3(aq) is colorless and will not contribute to the appearance of the final mixture, but KFe[Fe(CN)6](s) is blue. As more KFe[Fe(CN)6](s) forms, the suspension will become a darker blue.
(Choice A) Although more KNO3 forms, it is colorless and does not contribute to the appearance of the final mixture.
(Choice C) K4Fe(CN)6 and Fe(NO3)3 are reactants and are consumed by the forward reaction. Because the forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction, the amounts of these reactants decrease.
(Choice D) The question says that the forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction (ie, net product formation occurs). It does not give any information about actual product or reactant amounts.
Things to remember:
In a reversible process, products form when the forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction, reactants form when the reverse reaction is faster, and no change occurs when the forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate.
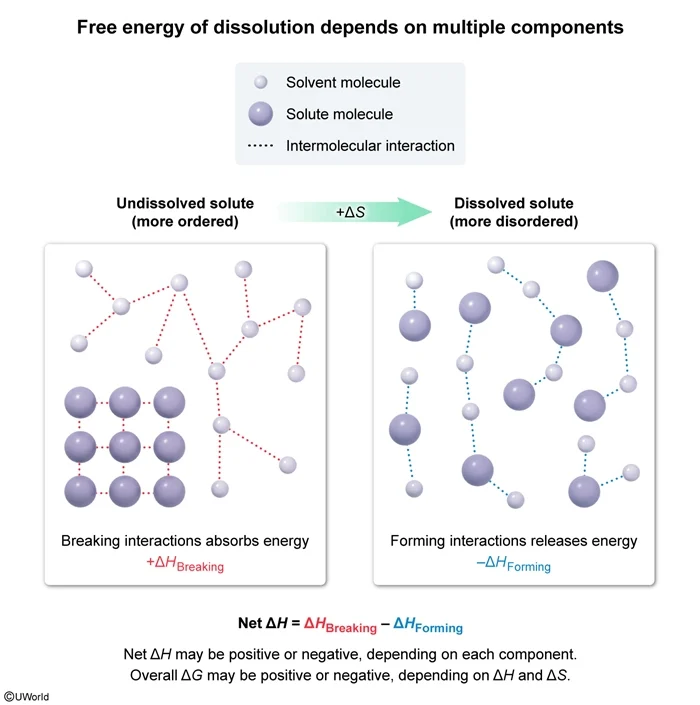
Question
The diagram above shows the interactions between the solute and solvent molecules of a sample in both the dissolved and undissolved states. Based on the diagram, which of the following statements is true concerning the sign of the overall change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG), the net change in enthalpy (ΔH), and the change in entropy (ΔS) for the solute dissolution?
| A. ΔG is positive, because the net ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive. | |
| B. ΔG is negative, because the net ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive. | |
| C. ΔG is negative, because the net ΔH is positive and ΔS is positive. | |
| D. ΔS is positive, but the signs of ΔG and ΔH cannot be determined without additional information. |
Explanation
The Gibbs free energy change (∆G) of a process indicates the energy requirements of that process. A process with a negative ∆G can proceed without energy input, whereas a process with a positive ∆G requires energy input to occur. The value of ∆G depends on the enthalpy change (∆H), the entropy change (∆S), and the temperature T of the system as described by the equation
∆G = ∆H − T∆S
Dissolution of a solute often results in greater disorder and increased entropy (ie, a positive ∆S). The net enthalpy of dissolution is the sum of the enthalpy changes caused by breaking the initial solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions (positive ∆H contributions) and forming new solute-solvent interactions (negative ∆H contribution).
∆H = ∆HBreaking − ∆HForming
If the negative enthalpy contributions exceed the positive enthalpy contributions, the net ∆H is negative. Otherwise, the net ∆H is zero or positive.
The diagrams show increased disorder in the dissolved state, indicating a positive ∆S. The sign of ∆G depends on whether ∆H is positive or negative, and whether ∆H can overcome any contributions from T∆S. The diagrams do not give any information about the types or relative strengths of the intermolecular interactions shown, and therefore neither the sign of ∆H nor of ∆G can be determined from the given information.
Things to remember:
The free energy ∆G of dissolution depends on the change in entropy ∆S and on the net enthalpy change ∆H that results from both the breaking and forming of intermolecular forces.
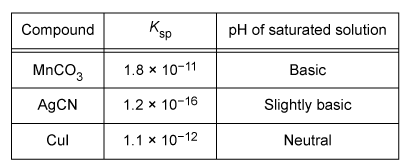
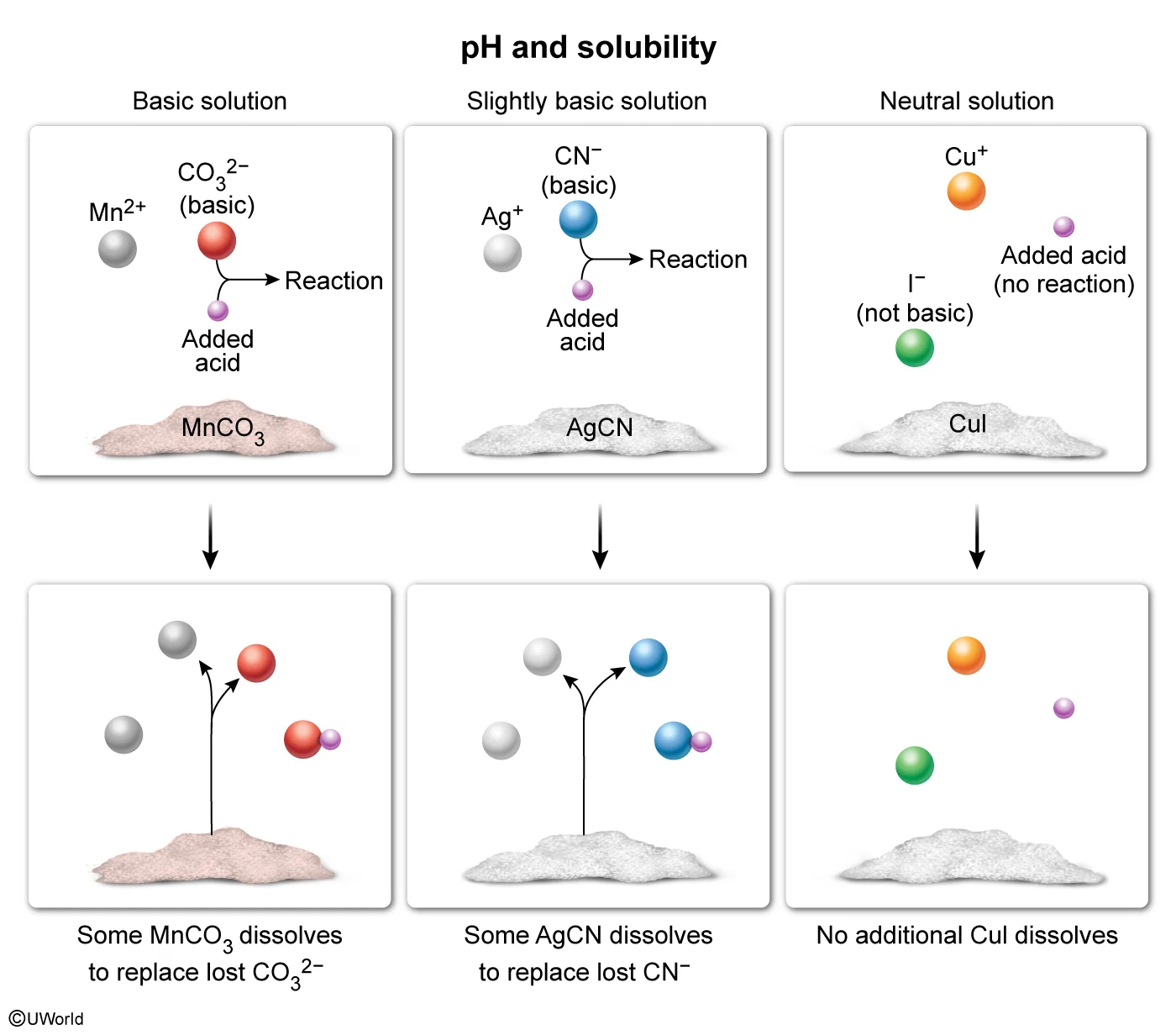
Question
Adding an acid would increase the solubilities of which of the compounds listed in the table?
| A. CuI only | |
| B. MnCO3 only | |
| C. MnCO3 and AgCN only | |
| D. MnCO3, AgCN, and CuI |
Explanation
The solubility of some ionic compounds depends on the acidity or basicity of the solution. If either ion in the compound is a base, it can react with added acid (and vice versa). This acid-base reaction decreases the concentration of the reacting ion. Based on Le Châtelier's principle, this causes additional solid to dissolve and replace the ions that reacted.
According to the table, saturated solutions of MnCO3 and AgCN are at least slightly basic, indicating that one of the ions in each compound is a base (specifically, CO32− and CN− are bases). When acid is added, CO32− and CN− can react with the acid, allowing more of each compound to dissolve. In contrast, CuI produces a solution with neutral pH, indicating that neither ion is acidic or basic. As such, Cu+ and I− will not react with added acid and adding acid will not affect the solubility of CuI. Therefore, only MnCO3 and AgCN would increase in solubility upon addition of an acid.
Things to remember:
The solubility of a salt in which one ion is an acid or base depends on the pH of the solution. Adding an acid to a salt with a basic ion increases its solubility and adding a base decreases its solubility. The opposite is true for salts with an acidic ion.
Acids and Bases Practice Test
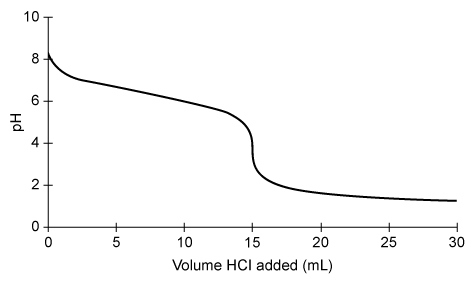
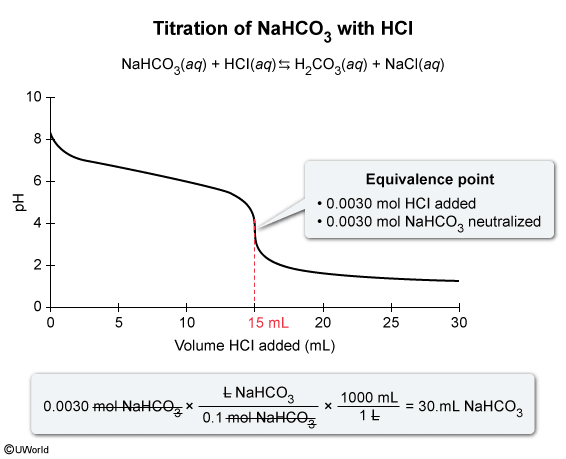
Passage:
A sample of NaHCO3(aq) is titrated with 0.20 M HCl(aq) and the results are plotted on the graph shown above. The indicator Congo red (In−), which changes color from red to blue as the pH decreases from 5 to 3, is used to visualize the endpoint of the titration. In− has a pKb of 9.9 and reacts with acid according to the equation:
Question
The concentration of NaHCO3(aq) is determined to be 0.10 M. Based on this information and the given graph, what was the volume of the NaHCO3(aq) sample?
| A. | |
| B. | |
| C. | |
| D. |
Explanation
During an acid-base titration, a base (or acid) is fully neutralized at the equivalence point (ie, the number of equivalents of acid and base is equal). The equivalence point is the middle point on the steep slope of the titration curve.
Based on the titration curve and the given information, the equivalence point occurs when 15 mL (0.015 L) of 0.20 M HCl(aq) is added to the sample of 0.10 M NaHCO3(aq). The number of moles of HCl(aq) added is calculated by multiplying the concentration (molarity) of HCl(aq) by the volume added:
Because the neutralization reaction between HCl(aq) and NaHCO3(aq) occurs in a 1:1 mole ratio, there must be an equal number of moles of HCl(aq) and NaHCO3(aq) at the equivalence point; therefore, 0.0030 moles NaHCO3(aq) were titrated. The volume of the NaHCO3(aq) sample is calculated by multiplying the moles of NaHCO3(aq) by the reciprocal of concentration:
Converting the volume from L to mL gives
Therefore, the volume of the NaHCO3(aq) sample titrated is 30. mL.
(Choice A) This value is the number of moles rather than the volume of NaHCO3(aq).
(Choice B) This value is the volume of NaHCO3(aq) in liters rather than mL.
(Choice C) 15 mL is the volume of HCl used at the equivalence point rather than the initial volume of NaHCO3. Even though the number of moles of HCl and NaHCO3 are equal, their volumes are not equal because the concentrations of HCl and NaHCO3 are different.
Things to remember:
In an acid-base titration, the equivalence point occurs when the equivalents of acid and base are equal. The equivalence point is the middle point on the steep slope of the titration curve.
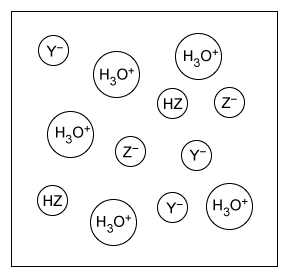
Question
A student makes an aqueous solution of the acids HY and HZ. After fully mixing, the solution contains the species shown in the particle view above. Which of the following statements is consistent with the given information?
| A. HZ is a weak acid because it is completely dissociated in solution. | |
| B. HY is a weak acid because it is partially dissociated in solution. | |
| C. HZ is a strong acid because it is partially dissociated in solution. | |
| D. HY is a strong acid because it is completely dissociated in solution. |
Explanation
The Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry definitions of acids and bases define an acid as a proton (H+ ion) donor. Strong acids fully dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions and forming hydronium ions (H3O+), whereas weak acids only partially dissociate in water.
The particulate diagram given in this question shows that there are HZ molecules and H3O+, Y−, and Z− ions in the solution. The lack of HY molecules in the diagram indicates that all the HY molecules added to the solution have dissociated into H3O+ and Y− ions. Therefore, HY is a strong acid because it has completely dissociated in solution.
(Choices A and C) The particulate diagram shows both HZ molecules and Z− ions in solution, indicating HZ is only partially dissociated and therefore is a weak acid.
(Choice B) HY has completely dissociated (ie, no remaining HY molecules in the particulate diagram). Therefore, HY is a strong acid, not a weak acid.
Things to remember:
According to the Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry definitions, acids are molecules that donate protons (H+ ions). Strong acids fully dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions and forming H3O+ ions, whereas weak acids only partially dissociate in water.
Question
Two titrations are carried out with 0.10 M NaOH. In the first titration, 50. mL of NaOH is added to a 50. mL sample of 0.10 M HCl to reach the equivalence point and a pH of 7.0. In the second titration, NaOH is added to a 50. mL sample of 0.10 M uric acid (HC5H3N4O3) until the equivalence point is reached. Which of the following identifies the volume of NaOH added to uric acid and the pH of the solution at the equivalence point? (The pKa of uric acid is 5.4.)
| Volume of 0.1 M NaOH | pH of Solution | |
| A. 25 mL | < 7.0 | |
| B. 25 mL | > 7.0 | |
| C. 50. mL | < 7.0 | |
| D. 50. mL | > 7.0 |
Explanation
Acids can be titrated with a strong base such as NaOH. The equivalence point occurs when the number of moles of base added equals the number of moles of acid originally present (ie, one equivalent of base). At this point, all protons from the acid have reacted with the base.
When a strong acid is titrated, all of the protons have already dissociated before any base is added. These protons contribute to a decrease in the pH of the solution. When one equivalent of base is added, these protons are neutralized and the solution returns to neutral pH (ie, pH = 7.0). In contrast, only a fraction of the molecules of a weak acid dissociate in water, resulting in a higher pH than that of a strong acid of equal concentration. Therefore, adding base brings the pH back to neutral before one equivalent is added, and once a full equivalent is added, the pH is greater than 7.0.
For a 50. mL solution of 0.1 M uric acid, 50. mL of 0.1 M NaOH is one equivalent because the number of moles of NaOH equals the number of moles of acid. Uric acid has a pKa greater than 0, making it a weak acid. Therefore, when one equivalent of NaOH is added, the pH will be greater than 7.0.
(Choices A and B) 25 mL of 0.1 M NaOH is one half-equivalent, not a full equivalent.
(Choice C) The pH of the solution is greater than 7.0 when one equivalent of NaOH is added, not less than 7.0.
Things to remember:
For strong acid titrations, the equivalence point yields a pH of 7.0. For weak acids, the equivalence point yields a pH greater than 7.0.
Applications of Thermodynamics Practice Test
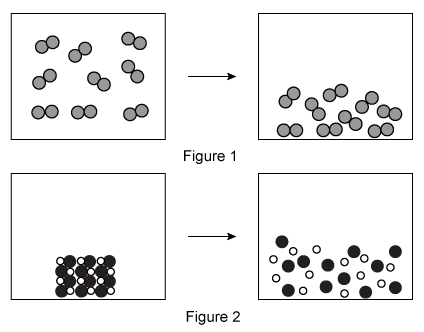
Question
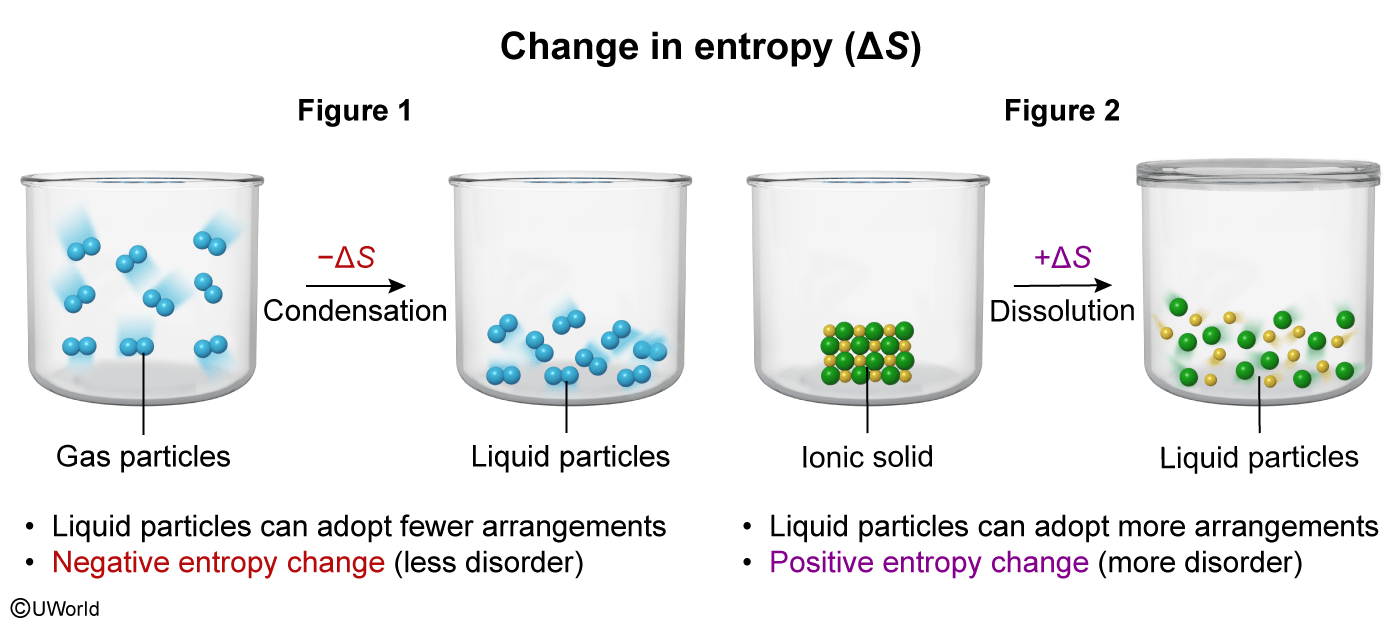
The particulate diagram in Figure 1 above shows a gas condensing into a liquid, and the particulate diagram in Figure 2 shows an ionic solid being dissolved in aqueous solution. Which figure depicts a negative entropy change, and why?
| A. Figure 1, because the liquid particles can adopt more arrangements than the gas particles. | |
| B. Figure 1, because the liquid particles can adopt fewer arrangements than the gas particles. | |
| C. Figure 2, because the ions in solution can adopt more arrangements than the particles in the solid. | |
| D. Figure 2, because the ions in solution can adopt fewer arrangements than the particles in the solid. |
Explanation
Entropy indicates the molecular disorder of a system. A process resulting in a positive entropy change (ΔS > 0) indicates the system became more disordered and can adopt more arrangements whereas a process resulting in a negative entropy change (ΔS < 0) indicates the system became more ordered and can adopt fewer arrangements.
Matter commonly exists in three phases: solid, liquid, or gas. The characteristics of particles in each phase determine its relative entropy:
-
Gas particles have the greatest entropy because they are spaced far apart, can move freely, and can adopt a greater number of arrangements than particles in solids and liquids.
-
Liquid particles are held closely together by intermolecular attractions and can form fewer possible arrangements than gas particles.
-
Solid particles have the lowest entropy because they are closely packed and held together in a fixed arrangement.
The question states that Figure 1 shows a condensation (ie, transitioning from a gas to a liquid). This results in a decrease in entropy because liquid particles can adopt fewer arrangements than gas particles. Therefore, Figure 1 depicts a negative entropy change.
(Choice A) Liquid particles are packed more closely than gas particles and can form fewer arrangements than gas particles.
(Choices C and D) Figure 2 shows dissolution of an ionic solid. Ions in solution can adopt more arrangements than particles in the solid (ie, Figure 2 depicts a positive entropy change).
Things to remember:
Entropy indicates the molecular disorder of a system. Negative entropy changes (a decrease of entropy) result in a system that can adopt fewer arrangements. Positive entropy changes result in more arrangements.
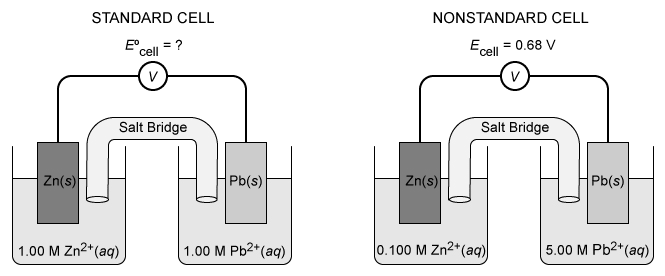
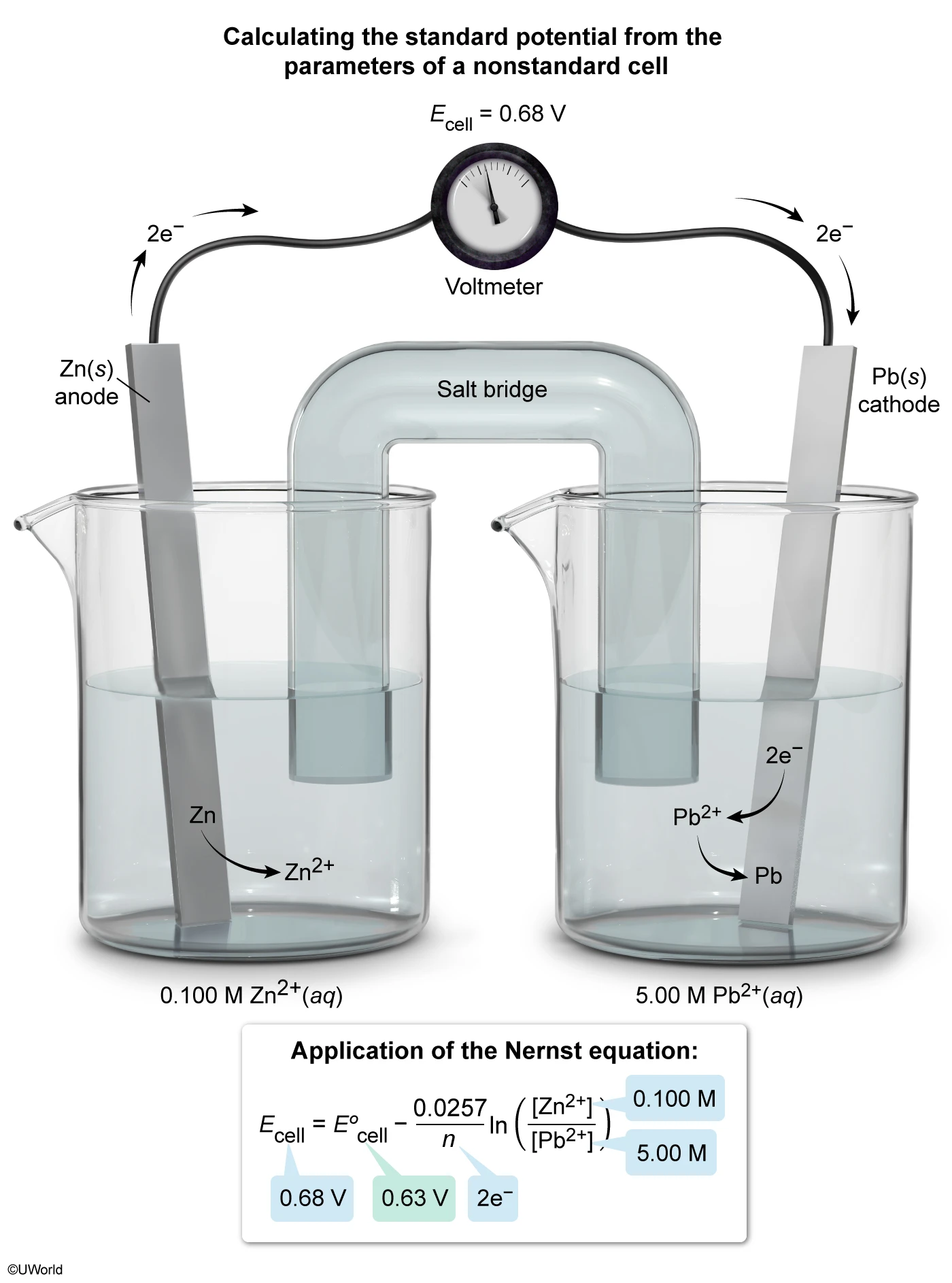
Question
A standard and a nonstandard variation of a galvanic cell are constructed, as shown above. The nonstandard cell produces a potential of 0.68 V at 25 °C. According to the Nernst equation, the potential produced by the standard cell must be:
| A. less than 0.60 V. | |
| B. greater than 0.60 V but less than 0.68 V. | |
| C. 0.68 V. | |
| D. greater than 0.68 V. |
Explanation
In a galvanic cell, a favorable electrochemical reaction that is not at equilibrium drives the production of an electric current. Because the cell reaction is not at equilibrium, Le Châtelier's principle cannot be applied to describe changes in electrochemical cells. These cells are instead described by the Nernst equation:
where Ecell is the observed cell voltage, E°cell is the cell voltage under standard conditions, Q is the reaction quotient, and the other variables are constants and reaction parameters.
Four cases are possible for an electrochemical cell:
| At equilibrium, Q is equal to the equilibrium constant Keq and Ecell = 0 |
| Under standard conditions, where lnQ = 0, Ecell = E°cell. |
| For nonstandard conditions with a small, positive Q, Ecell > E°cell. |
| For nonstandard conditions with a larger, positive Q, Ecell < E°cell. |
For the electrochemical cells in this question, the following redox reactions take place:
Applying the molar concentrations given for the nonstandard cell, its reaction quotient is:
Because Q < 1, Ecell produced by the nonstandard cell must be greater than E°cell produced by the standard cell. The exact value is determined by substituting the values of Ecell and Q into the Nernst equation and solving for E°cell:

Therefore, the potential produced by the standard cell is greater than 0.60 V but less than0.68 V.
(Choice A) Inverting the [Zn2+][Pb2+] ratio as [Pb2+][Zn2+] during the calculation yields a result of 0.58 V.
(Choice C) Because Q < 1, E°cell cannot be equal to Ecell.
(Choice D) E°cell cannot be greater than Ecell unless Q > 1.
Things to remember:
The Nernst equation describes the potential Ecell of a galvanic cell relative to the standard cell potential E°cell for a given reaction quotient Q. Four cases are possible:
- Q = Keq with Ecell = 0
- Q = 1 with Ecell = E°cell
- Q < 1 with Ecell > E°cell
- Q > 1 with Ecell < E°cell
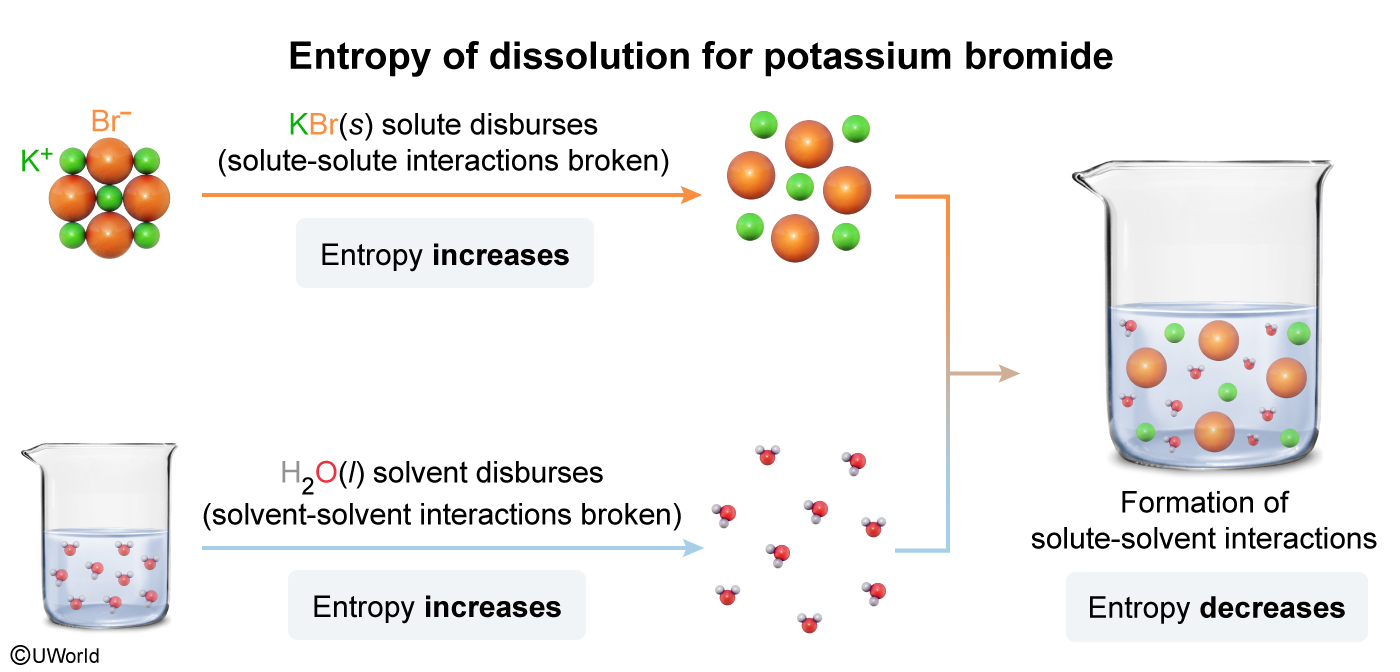
Question
A student dissolves a sample of KBr(s) in a beaker filled with water at 25 °C. During the dissolution process, interactions between the solute ions are broken and interactions between the solute ions and solvent molecules are formed. Which of the following statements correctly describes the contribution to the overall change in entropy caused by breaking and forming these interactions?
| A. Breaking solute-solute interactions increases the entropy whereas forming solute-solvent interactions decreases the entropy. | |
| B. Breaking solute-solute interactions decreases the entropy whereas forming solute-solvent interactions increases the entropy. | |
| C. Breaking solute-solute interactions and forming solute-solvent interactions both increase the entropy. | |
| D. Breaking solute-solute interactions and forming solute-solvent interactions both decrease the entropy. |
Explanation
Entropy is a measure of the molecular disorder, or randomness, of a system. Solids (eg, ionic compounds) contain atoms that are held in a fixed arrangement with little room to move; consequently, solids have relatively low entropy. However, liquids (eg, water) have higher entropy because the atoms in liquids are free to move into many random arrangements.
The process of dissolving an ionic solid (solute) in water (solvent) occurs by simultaneous steps that each involve either an increase or decrease in entropy:
-
Entropy increases when breaking solute-solute interactions (eg, electrostatic attractions between ions), allowing the solute to randomly disperse in the solvent.
-
Entropy increases when breaking solvent-solvent interactions (eg, hydrogen bonding) between the water molecules are broken (ie, allowing greater freedom of movement) so that new solute-solvent interactions can be formed.
-
Entropy decreases when forming new solute-solvent interactions (eg, ion-dipole interactions) between the solute ions and water molecules, causing diminished motion and less disorder.
In this question, dissolving the ionic compound KBr(s) in water involves breaking the solute-solute interactions between the K+ and Br− ions (ie, increases entropy) and forming new solute-solvent interactions between the ions and water molecules (ie, decreases entropy).
(Choices B and C) Forming solute-solvent interactions restricts molecular motion and decreases entropy.
(Choice D) Breaking solute-solute interactions allows molecular motion and increases entropy.
Things to remember:
Entropy describes the disorder (randomness) of a molecular system. Entropy increases when solute-solute interactions and solvent-solvent interactions are broken and decreases when solute-solvent interactions are formed.
Make the AP Chem Exam Feel Like Practice
Our AP Chemistry practice tests and quizzes are just like the exam and make you think critically. They’ll teach you to spot trick answers, handle time pressure and boost your confidence for test day! Practice with realistic exam simulations so test day feels like just another practice run.
One Click AP Chem Quizzes
Practice Under Real Exam Conditions
Study with Exam-Aligned Questions
Achieve Higher AP Chem Exam Scores with Smart Study Tools
Exceptional Explanations
Understand the “why” with our simplified breakdowns of how to approach each question and topic. Our clear AP Chemistry question explanations and vivid visuals help you spot and avoid trick answers so you’ll ace the AP Chem exam. Our exclusive technique, backed by cognitive learning principles, maximizes learning and retention.
Flashcards & Notes That Help You Actually Remember
Create digital flashcards to practice the concepts you struggle with most, like how buffer systems resist pH change or the difference between strong and weak acids, helping you remember information months later, not just for the next unit quiz. Use My Notebook to organize key concepts from AP Chemistry practice questions in the format that works best for you, whether that’s bullet points for equilibrium (ICE table) problems, diagrams showing VSEPR molecular geometries, or detailed notes on the different types of intermolecular forces. One-click transfer from explanations to your flashcards or notebook means everything you need stays in one organized place.
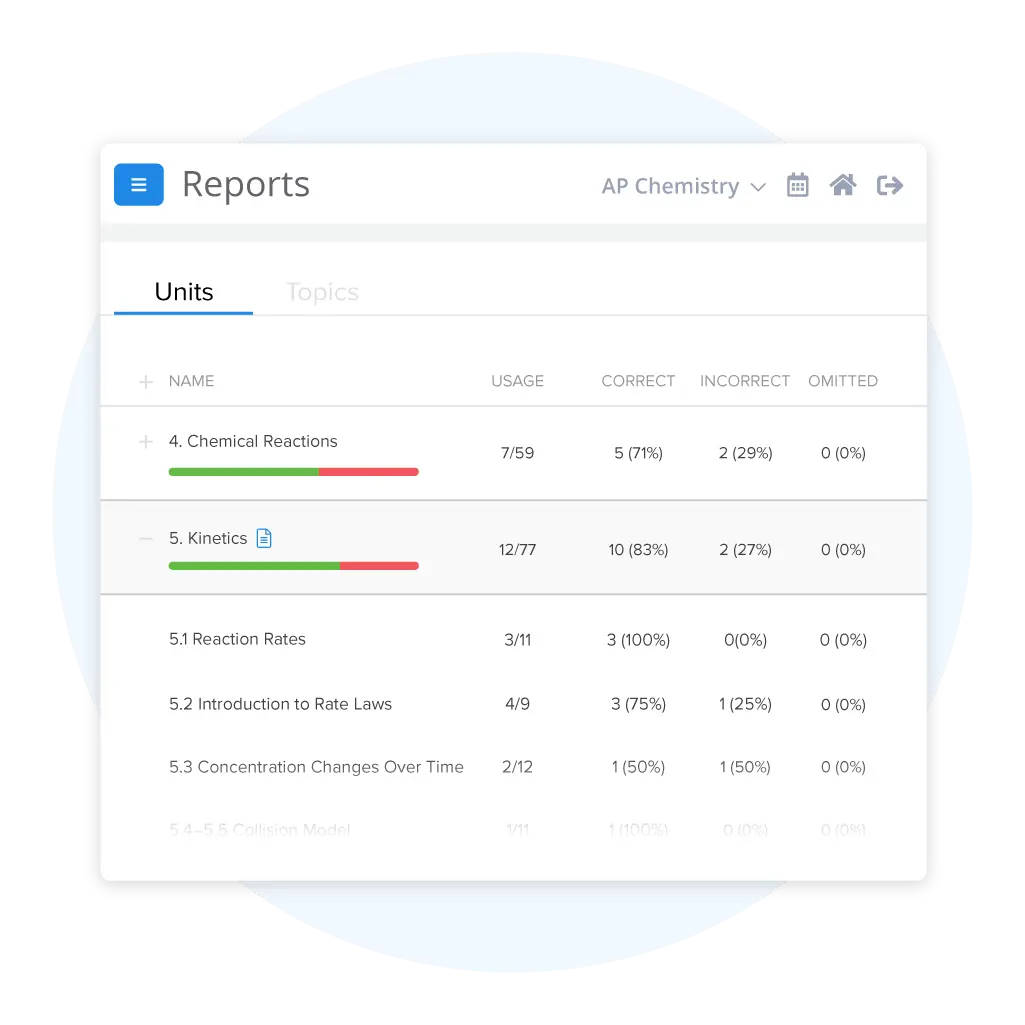
Track Your Progress and Target Weak Spots
See exactly where you stand with detailed performance tracking across all your AP Chemistry practice tests and practice questions. Our analytics dashboard shows which topics you're crushing and which ones need more work. Focus your study time on actual weak areas, stop wasting time on stuff you already know, and watch your scores improve.
Pick Your AP Chemistry Prep Package
Pick Your AP Chemistry Prep Package
AP Chem Practice Tests
Starting at $39
400+ AP Chem Practice Questions (MCQs)
Custom AP Chemistry Practice Tests & Quizzes
Progress Tracking Dashboard
Pick Your Study Topics
Smart Study Planner
400+ AP Chem Practice Questions (MCQs)
Custom AP Chemistry Practice Tests & Quizzes
Progress Tracking Dashboard
Pick Your Study Topics
Smart Study Planner
Realistic FRQ Practice with Scoring Guide*
Score-Predicting Full-Length AP Chemistry Exam*
Print and Digital Study Guide
150+ Check-for-Understanding Questions
Expert-led Video Lessons
* Coming Spring/Summer 2026
AP Chemistry Practice Test Reviews
UWorlds multiple choice questions are similar to the ones on the official AP exam and allowed me to time myself for each question. This was very helpful for me as I was able to answer questions faster and could finish the questions on the actual exam. The explanations for each question went in-depth and gave important details pertaining to events in the timeline. Through this, I was able to gain important skills for the exam and get a 5.
See MoreBefore, I had a hard time studying and staying focused because it was just boring, but now with UWorld, not only can I focus, but I actually feel motivated to learn!
The explanations were clear and I could practice the question based on units. I got a 5 in the end!! So, I think it’s very helpful and I’ll be using it to study for my future exams 🙂 You guys provide so many different functions to help students like me, and I really appreciate it, it’s really worth the money.
See MoreAP Chemistry Practice Tests: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How closely do UWorld's AP Chemistry practice tests match the real AP Chemistry exam?
Our AP Chem practice test questions are crafted to mirror the official AP Chem exam’s format, difficulty, and content scope. Authored in-house by veteran AP chemistry teachers and subject matter experts, our AP Chem MCQ and FRQ* questions reflect the same level of calculation, data interpretation, and conceptual reasoning you’ll face on test day. Every AP Chem question features detailed explanations with visuals, ensuring you understand the nuanced scientific principles behind each correct answer.
Why choose UWorld's AP Chem practice questions over free online resources?
There are a number of free AP Chem resources available to students but they generally focus on overall concepts and basic answer explanations. Our AP Chemistry practice tests and the hundreds of relevant exam-style questions that power them provide students with an entire study ecosystem. Each practice test you generate comes with in-depth, step-by-step rationales that explain all answer choices and for detailed practice we offer customizable quizzes to target specific units (like stoichiometry or thermodynamics). When you choose UWorld, you aren’t just getting a random AP Chemistry test; you’re getting a complete system for high achievement.
Do UWorld’s AP Chem practice questions cover all 9 units of the curriculum?
Yes. Our AP Chemistry practice questions comprehensively cover all 9 units specified by the College Board curriculum:
- Atomic Structure and Properties
- Compound Structure and Properties
- Properties of Substances and Mixtures
- Chemical Reactions
- Kinetics
- Thermochemistry
- Equilibrium
- Acids and Bases
- Thermodynamics and Electrochemistry
Our flexible quiz and test generator can build focused AP Chem exam practice tests for specific units or all topics for a full review.
What’s the best way to use AP Chemistry practice tests when aiming to score a 5?
Start by using our AP Chem practice questions in short, topic-focused quizzes to identify your knowledge gaps. After each AP Chemistry practice test or quiz, we encourage students to meticulously review the detailed explanations for every question, including those you answered correctly. This helps you master the underlying concepts, not just memorize answers. Throughout your prep, use the performance dashboard to track which chemistry units and concepts need more attention, then create targeted AP Chem practice tests to drill on them. This focused strategy is the most efficient path to building the deep conceptual understanding required for a 5 on the exam.
When is the best time to start using AP Chemistry practice questions?
Ideally, you should start integrating AP Chem practice questions as you learn new units in class. This reinforces concepts like reaction rates or equilibrium while they are fresh and makes the material more familiar as you come back to it during the semester. If you begin later in the year, use the tool to focus on high-yield topics and create custom quizzes for your weakest units. We’ve seen students who begin intensive AP Chem exam practice 4-6 weeks before the test date can see significant score improvements by practicing consistently and thoroughly reviewing our explanations.
Can I build custom AP Chem practice tests focused on specific topics?
Yes! Our AP Chem practice test builder allows you to create customized tests and quizzes with a single click. Target specific units, such as electrochemistry, kinetics or acid-base chemistry or filter AP Chemistry multiple choice questions by difficulty and set a specific length for your study session. This flexibility lets you concentrate your AP Chem exam practice time on the areas where you need the most improvement.
What score on an AP Chemistry practice test indicates I am ready for the real exam?
While there isn’t a single magic number, a good benchmark is consistently scoring higher than 70% on UWorld’s AP Chem practice tests (which include both AP Chem multiple choice and FRQs*). This score generally indicates you are on pace for a 4 or 5 on the actual AP Chemistry exam. If your scores aren’t at 70% yet, use the performance dashboard to identify your weakest units and create custom quizzes to target those specific AP Chemistry questions.
Do these AP Chem practice tests include both FRQs and MCQs?
Yes. UWorld’s AP Chem practice tests are built on a robust bank of both AP Chemistry multiple choice questions (MCQs) and free-response questions (FRQs)*. You can practice realistic FRQs that are graded against the same rubrics used by official AP graders, helping you learn exactly how to structure your answers to earn full credit. Our AP Chem multiple choice and free response questions cover all 9 units and when paired with our test generator, they give you an all-in-one AP Chem test preparation platform.
How many AP Chemistry mock exams should I take before the actual exam?
We recommend students take at least one full-length AP Chem mock exam before test day. This timed practice is crucial for building stamina, pacing and easing nerves for the 3-hour-and-15-minute test. You can use UWorld’s AP Chem question bank to build a complete AP Chemistry mock exam that combines both MCQs and FRQs*. In Spring 2026, a pre-built, full-length AP Chem mock exam will also be available as part of our AP Chemistry Online Review Course.
Where can I find free AP Chemistry practice questions online?
You can try high-quality, free AP Chemistry practice questions with UWorld’s 7-day free trial. During your trial you’ll get access to realistic AP Chemistry exam multiple choice questions and FRQs*, all featuring the detailed, step-by-step explanations written by our in-house experts. The free trial also offers a preview of our complete AP Chem Course, which includes video lessons, illustrations, and a digital study guide to help you master the material.