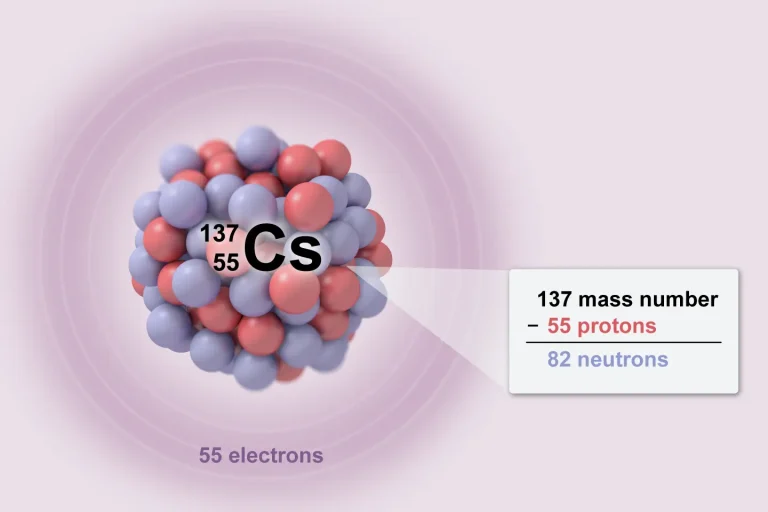
Labs play an important role in the AP® Chemistry course, and understanding experimental procedures is essential to succeed on the final exam. AP Chem Labs account for 25% of class time1. Throughout the year, you will be expected to do at least 16 hands-on experiments, 6 of which must be guided inquiry labs. According to the College Board® course description, "increased lab time is linked to greater AP results."
Why Are AP Chemistry Labs Important?
AP Chemistry labs are crucial for understanding chemical concepts and supporting scientific evidence. The College Board mandates that AP Chemistry teachers allocate at least 25% of instructional time to lab investigations. These inquiry-based labs, outlined in the AP Chemistry lab manual, provide you with practice in designing experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and refining scientific explanations.
With 16 inquiry-based labs2 available, you will gain valuable hands-on experience in "doing science." This practical approach is integral for preparing you for the AP Chemistry exam, which evaluates your science practice skills and content knowledge development. Use our online AP Chemistry Course all year as a companion to your AP class to prep for in-class tests and get you focused for the actual exam.
AP Chemistry Lab Materials
The equipment and materials required for AP Chemistry lab investigations are similar to those used in typical high school-level chemistry courses. However, access to specialized equipment (e.g., pH meters, spectrophotometers, etc.) may be needed. Most lab manuals provide a list of materials and equipment required for each lab investigation.
What Lab Investigations Are in AP Chemistry?
The AP Chemistry lab manual features 16 inquiry-based lab investigations, aligned with the curriculum framework. Teachers have the flexibility to substitute other inquiry-based labs covering content within the curriculum framework. Our print and digital AP Chemistry Study Guide features realistic scenarios to help you apply scientific concepts and reinforce key concepts and lab techniques.
The 16 AP Chemistry labs include:
Investigation 1: Spectroscopy
You will explore the relationship between different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and the types of transitions (molecular and electronic) that are associated with different regions of the spectrum. You will gain experience reading a UV-VIS spectrum, applying graphical information, and designing experimental procedures.
Investigation 2: Spectrophotometry
You will explain the relationship between the amount of light absorbed by a solution and the concentration of that solution. You will get to practice using a spectrophotometer, identifying wavelengths and determining the molarity of a specific solution. You will also use computational skills to identify an element's percent by mass composition in a solution.
Investigation 3: Gravimetric Analysis
You will demonstrate your knowledge of quantity calculation using the mole concept and dimensional analysis skills. You will analyze the relationship between the composition of elements by mass and a pure substance's empirical formula. Skills used in this lab include determining the relationship between microscopic and macroscopic behaviors of a solution and developing experimental protocols. You also explore theoretical yield and the process of filtration.
Investigation 4: Titration
You will gain experience identifying the equivalence point in a titration. You will design a data collection procedure, including selecting appropriate lab equipment and an acid-base indicator, representing your results with diagrams, and making predictions about a real-world application of the experiment.
Investigation 5: Chromatography
You will dive into the relationship between the solubility of compounds in different solvents and intermolecular forces. You will practice the skills of improving experimental results, collecting data, evaluating a paper chromatograph, and making scientific claims. You will also create models to represent the attraction between molecules.
Investigation 6: Bonding in Solids
You will explore the relationship between the type of bonding that occurs between elements and the properties of those elements. You will dive into the relationship between a substance's macroscopic properties, the microscopic structure of that substance, and particle interactions. You will practice designing an experiment, creating particulate models of bonds, analyzing data, and making scientific claims. You will also design a flowchart applying what has been learned in the experiment to identify unknown solid compounds.
Investigation 7: Stoichiometry
You will learn to perform calculations on solutions, including volume, molarity, and the number of solute particles. Additionally, you will use a balanced reaction equation to explain changes in the amount of reactants and products. During this investigation, you will mimic activities in the peer-review process of science, including verification of an experiment that has been performed, checking calculations, and analyzing experimental findings.
Investigation 8: Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Titration
You will learn how to represent changes in matter with a balanced equation (chemical and net ionic) while conducting a redox titration. You will perform calculations to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. You will also get to critically analyze the design of an experiment to find ways to improve upon it.
Investigation 9: Physical and Chemical Changes
You will explore how to identify the pH of a buffer solution by using the concentrations and identities of the conjugate acid-base pair that was used to make the buffer solution. You will gain practice designing a flowchart for the experiment, inferring whether physical or chemical changes have taken place, and improving experimental design. You will also learn the basics of vacuum filtration and how to perform acid-base separation.
Investigation 10: Kinetics: Rate of Reaction
You will explore the relationship between the specific parameters of an experiment and the rate of a certain chemical reaction. In this experiment, you will form a hypothesis, make modifications to an experimental procedure, and gain practice graphing data and drawing conclusions from data. Finally, you will practice sound laboratory skills such as accurately timing the occurrence of reactions.
Investigation 11: Kinetics: Rate Laws
You will relate experimental data to a rate law expression and practice identifying the rate law of a particular chemical reaction. You will apply equations (e.g., Beer's law) to calculate rate laws. Graphing skills are used in this investigation, including how to perform linear regression.
Investigation 12: Calorimetry
You will practice calculating the heat absorbed or released by a particular system that is undergoing heating, cooling, a phase change, or a chemical reaction. In doing so, you will be able to explain a model in terms of chemical theories, evaluate data, and perform calculations to determine the heat of the reaction. You will also gain an understanding of experimental errors and practice analyzing graphical data.
Investigation 13: Equilibrium
You will use Le Châtelier's principle to determine the response of a system at equilibrium due to a perturbation and identify perturbations that can cause a change in a given system. You will be able to predict the direction in which a reaction will proceed to reach its equilibrium. You will gain a further understanding of how to design and execute an experiment, as well as how to interpret data.
Investigation 14: Acid-Base Titration
You will learn how to perform acid-base titrations and explain the results of the titration in relation to the solution's properties and components. In doing so, you will practice drawing models to represent the different protonation states of a titrant during a titration. Furthermore, you will gain practice with calculations of values, including pH and pKa, choosing a testable question, analyzing titration curves, and collecting and comparing data.
Investigation 15: Buffering Activity
You will investigate buffer solutions and how they stabilize pH. You will practice experimental design, accurate observation and collection of data, and graphical representation of obtained data. You will also become familiar with estimating equivalence points and whether an unknown solution can act as a buffer.
Investigation 16: Buffer Design
You will learn how to prepare an effective buffer and test its capacity. You will relate this information to the relative concentrations of a solution's conjugate acid and conjugate base. Given a question from the instructor, you will design an experiment to test that question and brainstorm ways to improve your design.
The more experience you have doing labs aligned with the AP Chemistry curriculum framework, the better prepared you will be for the AP Chemistry exam.
To get a comprehensive plan with everything you need to know about the AP Chemistry exam, check out our guide on AP Chemistry units and how to study for AP Chemistry.
For extra practice, test your knowledge with our AP Chemistry QBank, featuring exam-style questions designed to reinforce key concepts.
With these resources at your disposal, you have everything you need to reach your goals in AP Chemistry!

References
1(2020). Course Overview. Advanced Placement Chemistry Sample Syllabus #1. College Board. Retrieved on March 01, 2024 from https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/media/pdf/ap-chemistry-sample-syllabus-1.pdf
2(2024). The Lab Manual. AP Chemistry Lab Manual. College Board. Retrieved on March 01, 2024 from https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/courses/ap-chemistry/classroom-resources/lab-manual
3(2022). Lab Time. AP Chemistry Course and Exam Description. College Board. Retrieved on March 01, 2024 from https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/media/pdf/ap-chemistry-course-and-exam-description.pdf
Read More About AP Chemistry
Get expert advice on how to write an AP Chemistry lab report. Know how to craft each section of the lab report and what key points to include.
Free AP Chemistry Practice QuestionsWant to test your skills in AP Chemistry? Check out our gold-standard AP Chemistry practice questions and a mock test with explanations to see where you stand!
AP Chemistry Course and Exam DescriptionIt is difficult to go through all the pages of the official CED PDF. Check out this simple “AP Chemistry Course and Exam Description” for detailed information on the exam, units, and topics!
How to Self-Study for AP ChemistrySelf-studying for AP Chemistry? Discover tips on mastering concepts, tackling practice problems, and staying organized to excel on the AP Chemistry exam!
Best AP Chemistry Study Guide ComparisonStruggling to choose the best study guide? Compare Kaplan, Barron's, Princeton Review, and UWorld to find the perfect AP Chemistry study guide for your exam success!
Best AP Chemistry Prep Course ComparisonDiscover the best AP Chemistry prep courses! This in-depth review helps you compare options and pick the course that meets your needs.