Grammatical errors have become commonplace in an era of social media and casual communication. There is no authority grading our DMs or scanning TikTok for subject-verb agreement mistakes. The truth is that most of us don’t need to understand what an appositive phrase is to be understood by our peers. But when it comes to passing the ACT® English section, and subsequently doing well academically and professionally, understanding standardized grammar and punctuation rules is essential.
Fortunately, most students make the same common mistakes on the ACT English section, which makes it much easier to focus on a few important points. This article covers six common mistakes and grammatical errors that students make on the ACT English section and strategies on how to avoid them.
Overview of the ACT English Test
The ACT English section puts you in an editor’s shoes. Each of the five passages is accompanied by 15 questions that assess your knowledge of language (13-19%), understanding of the conventions of standard English (51-56%), and ability to analyze the focus and purpose of a piece of writing (29-32%).
Common Mistakes on ACT English
The ACT English section requires you to have a strong understanding of grammar and punctuation, as well as the ability to read critically and analyze complex sentences. The best way to build these skills is to regularly read material at the edge of your competency and study common grammar and punctuation rules. While this is ideal, we don’t always have the luxury of time.
We’ve curated tips to help you improve your ACT English score even if you don’t have the time to become a bookworm and grammar scholar. We’ll cover:
- Misplaced modifiers
- Using the wrong homophone
- Overusing commas
- Comma splices
- Misuse of plural pronouns
- Wordiness
- Fear of NO CHANGE
1. Misplaced Modifiers
Modifiers are words, phrases, or clauses that provide additional information about another word in a sentence. A modifier can describe or clarify a noun, verb, adjective, or adverb, making it more specific or interesting. For example, in the sentence “The green car drove down the road,” “green” is a modifier that describes the car.
Remember, a phrase can also be a modifier. Take this sentence for example, “Running down the street, he suddenly stopped.” In this sentence, “running down the street” is a modifier phrase that provides additional information about the subject “he.” The modifier phrase begins with the present participle “running” and describes the action of the subject.
Reading a sentence with a misplaced modifier is a bit like taking a wrong turn on a trip. Eventually, you realize you’re going the wrong way, and you have to retrace your steps to get back on track. When a modifier is in the wrong position in a sentence, it appears to modify the wrong thing and causes confusion. It can even change the meaning of a sentence, make it awkward or unclear, or result in unintended humor. Consider the following sentence…
Jack drove home.
Simple right? But communication is rarely simple, so we use modifiers to add details. Let’s add some modifiers to our example sentence…
Having just finished his last class, Jack quickly drove home to meet his girlfriend.
Now let’s identify the modifiers:
- “Having just finished his last class” is a participial phrase that modifies the subject “Jack.” This phrase tells us what Jack had just done before he drove home.
- “Quickly” is an adverb that modifies the verb “drove.” This adverb tells us how Jack drove home, emphasizing the speed at which he drove.
Typically, modifiers are placed next to the words they modify to ensure clarity. When they are misplaced, confusion can arise. Here are a couple of examples of misplaced modifiers:
Incorrect: “I found a wallet on the street with $50 inside.”
Correct: “I found a wallet with $50 inside on the street.”
In this sentence, the modifier (“with $50 inside“) suggests that the street has $50 inside rather than the wallet. By bringing the modifier closer to its subject (the wallet), the sentence becomes clearer. Let’s look at another example…
Incorrect: “I saw the Statue of Liberty flying to New York.”
Correct: “While flying to New York, I saw the Statue of Liberty.”
The modifier in this sentence (“flying to New York“) suggests that the Statue of Liberty was flying to New York rather than the speaker. We can remedy this confusion by breaking off the adverbial phrase (“flying to New York“) and sticking it in the front, closer to its subject (“I”).
Now that you know a little more about misplaced modifiers, let’s practice. Identify the misplaced modifier and correct the sentence below.
The dog chased the mailman with a wagging tail.
If you read this sentence and imagined an excited mailman wagging his tail, you can now understand how misplaced modifiers cause confusion. There are a couple of ways you can fix this sentence: (1) The dog with a wagging tail chased the mailman, (2) With a wagging tail, the dog chased the mailman.
If you stumble onto a misplaced modifier on the ACT English exam, try to identify the modifying word or phrase and its subject. Then move that modifier closer to its subject to provide clarity.
2. Using the wrong homophone
To understand what a homophone is, we can just look at its etymology—”homophone” comes from the Greek words “homos” meaning “same” and “phone” meaning “sound” or “voice.” Therefore, homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings. For example, the words “blue” and “blew” sound the same but have completely different meanings. This is a pretty obvious example, but many homophones are trickier. Here are some common examples:
- their, there, they’re
- your, you’re
- its, it’s
- to, too, two
- affect, effect
- than, then
- hear, here
- whose, who’s
- weather, whether
- accept, except
Many of you will be familiar with the differences between homophones like “their,” “there,” and “they’re.” However, students frequently confuse homophones like “its” and “it’s” or “affect” and “effect,” so let’s quickly review them.
We all know to use an apostrophe to indicate possession. If a pair of shoes belongs to Jack, they are Jack’s shoes. If a tire belonging to a car pops, we can say, “it’s tire popped,” right? Wrong. “It’s” is actually the contraction of “it is” while “its” is the possessive form of “it.” Get it? Here’s an example to help clarify things.
Possessive
That’s the cat’s toy. > That’s its toy.
Contraction
It is cold outside. > It’s cold outside.
A simple way to avoid using the incorrect form of it is to ask yourself whether you can replace the contraction with two words (it is). If you see an “its” that can be replaced by “it is,” it’s wrong.
Let’s go over one more common homophone that often gives students trouble—”affect” versus “effect.” Now, these words may sound slightly different depending on your accent, but they are considered homophones nevertheless. The difference between them is that “affect” is typically a verb that means to influence or produce a change in something, while “effect” is typically a noun that refers to the result or consequence of an action.
“The new policy will affect the company’s profits.” (verb)
“The effect of the new policy on the company’s profits remains to be seen.” (noun)
In this example, “affect” is used as a verb to indicate that the new policy will have an impact on the company’s profits. “Effect” is used as a noun to refer to the result or outcome of the policy. It’s worth noting that “effect” can also be used as a verb, meaning to bring about or cause something to happen, but this usage is less common than the noun form.
One way to remember the difference between these two words is to remember that “affect” starts with the letter “a,” which can stand for “action,” while “effect” starts with the letter “e,” which can stand for “end result.”
There is no quick trick that will magically resolve all your homophone problems. You simply need to learn their differences and remember them. Familiarize yourself with the common homophone examples above and pay attention when you read them or need to use them in writing.
3. Overusing commas
The difference between “Let’s eat, Grandma!” and “Let’s eat Grandma!” should serve as a stark reminder of the importance of commas. Yet, despite their importance, many students have gotten poor advice on where to sit a comma.
For example, as a child, you may have been instructed to place commas wherever you would pause in a sentence. This is wrong. In fact, following this advice will lead to a lot of unnecessary commas. Take this actual example sentence from the ACT English section for example:
In 1948, graduate students, Norman Woodland and Bernard Silver, took on a problem that had troubled retailers for years: how to keep track of inventories.
A) NO CHANGE
B) students, Norman Woodland and Bernard Silver
C) students Norman Woodland and Bernard Silver
D) students Norman Woodland and Bernard Silver,
The correct answer is C, meaning that both commas in the phrase should be omitted. When it comes to commas, if you aren’t sure whether or not you need one, you’re probably better off just leaving it out. But then, when do you use a comma?
To set off nonessential information from the rest of a sentence, as in:
The book, which was written in the 1800s, is still relevant today.
The above example can be written as “The book is still relevant today.” The phrase “which was written in the 1800s” adds an interesting, albeit non-essential, detail. If the phrase is essential, we will leave out the commas, as in the example below. In this sentence, “John Steinbeck” is an essential appositive phrase that renames “the author” and is not set off by commas.
The author John Steinbeck won the Nobel Prize for Literature.
We also need to use commas when a sentence begins with a dependent clause or modifying phrase. To refresh your memory, a dependent clause is a phrase that has a subject and verb but cannot stand alone as a sentence. Therefore, it depends on an independent clause.
We stayed inside because it was raining.
In this example, “because it was raining” is a dependent clause. It cannot stand on its own as a sentence. In contrast, “We stayed inside” is an independent clause because it is a complete sentence. Now, if we wanted to begin the same sentence with the dependent clause, we would need to add a comma.
Because it was raining, we stayed inside.
Always use a comma at the end of a dependent clause when it begins a sentence. Here are some examples to help clarify this rule:
- “Because she was feeling tired, she decided to go to bed early.”
- “Although he had never been to Paris before, he was excited to explore the city.”
- “When I finish this project, I’ll have time to relax.”
- “If you don’t leave now, you’ll miss the train.”
- “Since it’s raining outside, we’ll have to stay indoors today.”
4. Comma splices
Yes, this is another section on commas. No, we aren’t cheating. Comma splices are a common enough issue on the ACT English exam that they deserve their own section. Comma splices occur when two independent clauses are incorrectly punctuated with a comma. Independent clauses should typically be punctuated with a period, semicolon, or comma and coordinating conjunction.
Incorrect: I went for a walk, I saw a bird.
Incorrect: I went for a walk and I saw a bird.
Correct: I went for a walk, and I saw a bird.
Correct: I went for a walk. I saw a bird.
Correct: I went for a walk; I saw a bird.
If you see two independent clauses connected by a comma, you’ve stumbled upon an issue. Try adding a comma and a coordinating conjunction or insert a period or semicolon. To hammer this home, let’s take a look at one of UWorld College Prep’s ACT English practice questions:
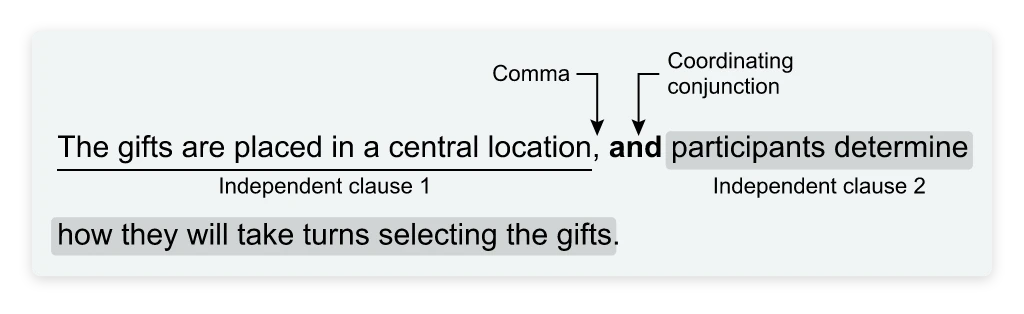
The gifts are placed in a central location; while participants determine how they will take turns selecting the gifts.
A) NO CHANGE
B) location, and
C) location,
D) location
First, we need to analyze the text on either side of the underlined portion. Adding “while” to an independent clause makes it dependent. We find that an independent clause is connected to a dependent clause with a semicolon, which is incorrect.
We know that C is wrong because we can’t connect two independent clauses with a comma only. And D must be wrong because having no punctuation at all would create a run-on sentence. Therefore, the answer must be B—adding a comma and the coordinating conjunction “and.”
5. Wordiness
You may come across a sentence on the ACT English exam that contains unnecessary “fluff.” That means you may need to eliminate a phrase or word despite it being grammatically sound. When it comes to wordiness, one common culprit is redundancy. Redundancy occurs when two words or phrases repeat the same idea without adding anything new, as in:
Incorrect: Annually, Texas averages about 136 twisters every year.
Correct: Texas averages about 136 twisters every year.
Since “annually” and “every year” mean the same thing, by omitting either, the meaning of the sentence is not changed. If you see a sentence like this on the ACT English section, simply select the answer that eliminates the redundancy.
However, not all wordiness comes from redundancy. You may come across a sentence that contains two words that are not outright redundant, but are very similar.
Incorrect: The captain of the plane, who was the person on the plane responsible for operating the aircraft, worked for American Airlines.
Correct: The captain of the plane worked for American Airlines.
Since we all understand that the captain of a plane is responsible for operating it, this information is redundant even though the meanings are not identical. While there are no grammatical issues with the sentence, we should still eliminate its unnecessary wordiness.
Finally, wordiness can result from a lack of concision. Using an economy of words is not related to grammar, but it’s critical where clarity is concerned. The following example is taken from UWorld’s practice question bank:
The Māori describe themselves as “people of the land.” The term additionally can be used to reference the Māori people as a whole in relation to New Zealand as a whole.
A) NO CHANGE
B) is another way of referencing
C) can also refer to
D) is from
You want to select the answer that is the least wordy way to express an idea. When the shortest answer is grammatically correct and makes sense in context, it’s correct. Looking at the options in the example above, we can see that A and B are six and five words, respectively. D contains the least number of words but changes the meaning of the sentence. Therefore, the answer must be C because it contains only four words while retaining the meaning and clarity of the sentence.
6. Fear of NO CHANGE
Examinees are often hesitant to select the “NO CHANGE” option. The ACT English section wants you to correct mistakes, so it must be a trick, right? Wrong. Not only should NO CHANGE be treated like any other answer choice, but it is also actually the correct choice quite often. Take this actual ACT English section question for example:
The first bar code was composed of four white lines set at specific distances from each other on a black background.
A) NO CHANGE
B) distances so that each was separated, one from the
C) locations, each one set apart from the
D) lengths of distance from each
At first, you may suspect that there is nothing wrong with some of the answer options causing you to become suspicious and second guess yourself. If you fall victim to this mentality, rather than seeing NO CHANGE, try imagining the underlined portion next to the A option. This practice will remind you that NO CHANGE is just like any other answer choice.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes on ACT English
While we covered ways to avoid the specific common mistakes we’ve listed above, below are some strategies you should use to avoid making mistakes more generally.
Time management
You have 45 minutes to answer 75 questions distributed evenly across 5 passages. That gives you 36 seconds per question, or 9 minutes per passage and its associated questions. Of course, you’ll be able to answer some questions in seconds, others will take more thought, but all questions are worth the same amount and only correct answers count toward your final score.
That means that spending more time on a difficult question is often a losing strategy. In other words, if you get stuck, move on and come back to it at the end. Anticipating this, you should leave yourself time at the end of the exam to fill in the questions you skipped and double-check your answers. When you take practice tests, give yourself less than 45 minutes so that you adapt to stricter time constraints.
Use the process of elimination
Eliminating answer choices that are clearly incorrect leaves you with a smaller pool of choices to consider, which increases your chances of selecting the correct answer. It can also help you save time. Rather than struggling to answer a difficult question, you can quickly eliminate the answer choices that you know are incorrect, move on to the next question, and come back to it at the end. Take this ACT English practice question from UWorld as an example:
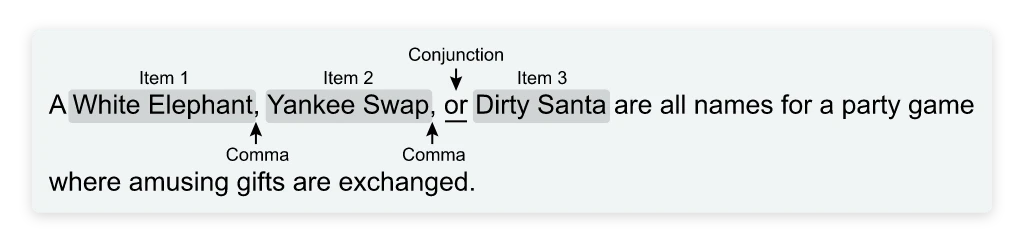
White Elephant, Yankee Swap and, Dirty Santa are all names for a party game where amusing gifts are exchanged.
A) NO CHANGE
B) Elephant, Yankee Swap, and
C) Elephant Yankee Swap, and
D) Elephant Yankee Swap and
We can immediately deduce that A is incorrect because it places a comma after the conjunction rather than before it. Neither C nor D uses a comma to separate the first and second items on the list. Therefore, the correct answer must be B. You can use the process of elimination on any question, but you must have some understanding of the grammar rules behind the question to eliminate incorrect choices, which brings us to our next tip…
Understand fundamentals
There are a number of online tools and resources that can teach you grammar, but when you’re trying to pass the ACT English Test, nothing beats learning with an ACT English-centered resource. UWorld’s in-depth answer explanations help you reason through why each answer choice is correct or incorrect. This process will condition you to deduce correct answers while developing your grammatical proficiency. Here’s an example of UWorld’s answer explanations for the example question we just used:
Rule: Items in lists of more than two are separated by commas.
To decide where the commas go, identify the listed items.
Tip: Although the Oxford comma is technically optional, the ACT always includes it.
Here, three names for the same party game are listed: “White Elephant,” “Yankee Swap,” and “Dirty Santa.” Commas should be placed after the first and second items so that each item is clearly defined. The only answer with correct comma placement is White Elephant, Yankee Swap, and Dirty Santa.
(Choice A) This answer incorrectly places a comma after the conjunction “and” instead of before it, making “and” seem like part of the list instead of the word that joins the last two items.
(Choices C and D) Neither of these answers uses a comma to separate the first and second items in the list, making it sound as if “White Elephant Yankee Swap” is one name instead of two. However, each listed item is usually parallel in structure and the last one is an adjective “Dirty” followed by a noun “Santa.” Therefore, it makes sense that the other items are two words: an adjective (ex. “White” or “Yankee” followed by a noun (“Elephant” or “Swap”).
Things to remember:
Commas show where one item in a list ends and the next begins. On this test, a comma is also used before the conjunction separating the last two items in the list.
Use ACT English Practice Exercises
Simulating the time constraints, format, and difficulty of the actual ACT English section is the best way to prepare for the exam. Think of it this way—if practice feels like the real thing, then the actual exam will feel like practice. If you want to get better at soccer, you play soccer. If you want to improve your ACT English section results, you practice with questions that meet or exceed exam-level difficulty.
Fortunately, the ACT has realistic ACT English practice tests on its website. That’s a great place to get started, but you’ll need a lot more practice to truly improve your chances of getting a high score.
UWorld College Prep offers 2,650+ exam-like questions that cover every section of the ACT. Questions are written by an in-house team of subject-matter experts to meet or exceed exam-level difficulty. Use these questions to generate unlimited, customizable practice tests or take a full-length simulation of the actual exam, then our performance tracking technology will provide a report identifying areas that need improvement. Learn more about the world’s best prep for the ACT Exam.

Conclusion
On the ACT English section, every question counts. By covering the most common mistakes and learning how to avoid them, you can significantly improve your chances of a high score. But don’t stop there, there’s so much more to learn about:
The Pros and Cons of Retaking the ACT
A couple of extra points on the ACT may be the difference between admission and rejection, but do the cons of a retake outweigh the pros? Find out here.
How to Improve your ACT Science Score: 6 Useful Tips
Don’t be intimidated by scientific jargon and data. This guide will help you improve your ACT Science score with actionable tips so you can take the exam with confidence.
Common Mistakes on the ACT Math and How to Avoid Them
Examinees routinely make the same math mistakes on the ACT Math even though there are some simple steps you can take to avoid them. Learn more.
Common Mistakes on the ACT Reading and How to Avoid Them
The ACT Reading’s time constraints can be difficult for students who don’t spend much time reading. Find out how to avoid common mistakes and improve your score here.